File
... Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down a group. d. Decreases across a period; decreases down a group. ...
... Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down a group. d. Decreases across a period; decreases down a group. ...
Questions and Solutions
... Indicate which terms apply to each species. There is more than one term which applies to each species. N (neutral) ...
... Indicate which terms apply to each species. There is more than one term which applies to each species. N (neutral) ...
College Chemistry 1 Note Guide(free download)
... college chemistry courses. Many programs of study, particularly certain engineering degrees, require one semester of college chemistry as opposed to a two semester course, hence the year long course has been split into two separate courses to accommodate those needs. The second semester course is av ...
... college chemistry courses. Many programs of study, particularly certain engineering degrees, require one semester of college chemistry as opposed to a two semester course, hence the year long course has been split into two separate courses to accommodate those needs. The second semester course is av ...
National 5 - Deans Community High School
... was chlorine. We had to keep clear of the chlorine he said. When the copper went in the gas, it shrivelled up. Then it went on fire. When it stopped there was yellow stuff in the jar This is a CHEMICAL REACTION. ...
... was chlorine. We had to keep clear of the chlorine he said. When the copper went in the gas, it shrivelled up. Then it went on fire. When it stopped there was yellow stuff in the jar This is a CHEMICAL REACTION. ...
English Medium - sakshieducation.com
... 1. What happens when an acid or base is mixed with water? 2. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity where rain water does? 3. Plaster of paris should be stored in a moisture proof container explain why? 4. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How does the pH change as it turns to curd? Explain your a ...
... 1. What happens when an acid or base is mixed with water? 2. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity where rain water does? 3. Plaster of paris should be stored in a moisture proof container explain why? 4. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How does the pH change as it turns to curd? Explain your a ...
Entropy (Part I)
... The sign on ΔS for the system in a certain chemical change is negative. The ΔS value for the surroundings for the same reaction is positive. What would have to be true to make the reaction represent a spontaneous change? A. The ΔS of the system would have to have a greater magnitude than ΔS of th ...
... The sign on ΔS for the system in a certain chemical change is negative. The ΔS value for the surroundings for the same reaction is positive. What would have to be true to make the reaction represent a spontaneous change? A. The ΔS of the system would have to have a greater magnitude than ΔS of th ...
Document
... with a high rate. Some reactions take hundreds, maybe even thousands, of years while others can happen in less than one second. If you want to think of a very slow reaction, think about how long it takes plants and ancient fish to become fossils (carbonization). Ultimately: Molecules moving too slow ...
... with a high rate. Some reactions take hundreds, maybe even thousands, of years while others can happen in less than one second. If you want to think of a very slow reaction, think about how long it takes plants and ancient fish to become fossils (carbonization). Ultimately: Molecules moving too slow ...
Molecular Modeling of Hydrophobic Organic Contaminants
... Modeling Humic Acids and Asphaltenes • There are two major impediments to this conventional approach. • First, the structure elucidation process is carried out manually • This may be prohibitively time consuming for multifunctional geomacromolecules such as humic acids and asphaltenes. ...
... Modeling Humic Acids and Asphaltenes • There are two major impediments to this conventional approach. • First, the structure elucidation process is carried out manually • This may be prohibitively time consuming for multifunctional geomacromolecules such as humic acids and asphaltenes. ...
Thermochemistry
... (Remember that the form of the energy can be changed, but conversion of matter to energy or the reverse requires nuclear processes, not chemistry) We also need to introduce the concept of a State Property A state property is a property of a system that does not depend upon the route taken to reach t ...
... (Remember that the form of the energy can be changed, but conversion of matter to energy or the reverse requires nuclear processes, not chemistry) We also need to introduce the concept of a State Property A state property is a property of a system that does not depend upon the route taken to reach t ...
Second Year - WordPress.com
... nuclear charges (B) Inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge (C) Inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge (D) Directly proportional to effective nuclear charge. ...
... nuclear charges (B) Inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge (C) Inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge (D) Directly proportional to effective nuclear charge. ...
Energy and Energy Changes Heat Transfer and The Measurement
... • Example 15-1: When 3.425 kJ of heat is added to a calorimeter containing 50.00 g of water the temperature rises from 24.00oC to 36.54oC. Calculate the heat capacity of the calorimeter in J/oC. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g oC. • This is a four part calculation. ...
... • Example 15-1: When 3.425 kJ of heat is added to a calorimeter containing 50.00 g of water the temperature rises from 24.00oC to 36.54oC. Calculate the heat capacity of the calorimeter in J/oC. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g oC. • This is a four part calculation. ...
Harrisburg Area Community College 2013/2014
... Chemical Reactions: Classification and Prediction of Products ..........................................................65 Pre-lab Questions ....................................................................................................................................69 Data ................... ...
... Chemical Reactions: Classification and Prediction of Products ..........................................................65 Pre-lab Questions ....................................................................................................................................69 Data ................... ...
ANSWER KEY Chemistry CPA Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam
... kinetic energy. Gas particles collide with one another in perfectly elastic collisions. As temp and KE increase, so do collisions, which raises the pressure within a gas. ...
... kinetic energy. Gas particles collide with one another in perfectly elastic collisions. As temp and KE increase, so do collisions, which raises the pressure within a gas. ...
Review Final 111 Lect
... a. ___________________________ b.___________________________ c. ___________________________ 32. The behavior of a real gas may approach that of an ideal gas at a ____________ temperature (high, or low) and a ____________pressure. (high, or low) ...
... a. ___________________________ b.___________________________ c. ___________________________ 32. The behavior of a real gas may approach that of an ideal gas at a ____________ temperature (high, or low) and a ____________pressure. (high, or low) ...
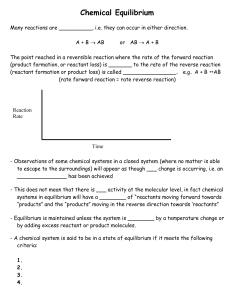
Chemical Equilibrium
... – Only affects reactions in which gases are involved – In order for it to have an affect total moles of gas on the left must be different than total moles of gas on the right ...
... – Only affects reactions in which gases are involved – In order for it to have an affect total moles of gas on the left must be different than total moles of gas on the right ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reactions). ...
... They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reactions). ...
Batteries are all over the place -- in our cars, our
... If you look at any battery, you'll notice that it has two terminals. One terminal is marked (+), or positive, while the other is marked (-), or negative. In an AA, C or D cell (normal flashlight batteries), the ends of the battery are the terminals. In a large car battery, there are two heavy lead p ...
... If you look at any battery, you'll notice that it has two terminals. One terminal is marked (+), or positive, while the other is marked (-), or negative. In an AA, C or D cell (normal flashlight batteries), the ends of the battery are the terminals. In a large car battery, there are two heavy lead p ...
File
... • in solubility equilibrium the ________ solute particles continuously dissolve into solution, while an equal number of dissolved solute particles in solution crystallize or _________ out of solution 2. Phase Equilibrium - in phase equilibrium particles in both phases are gaining or losing kinetic e ...
... • in solubility equilibrium the ________ solute particles continuously dissolve into solution, while an equal number of dissolved solute particles in solution crystallize or _________ out of solution 2. Phase Equilibrium - in phase equilibrium particles in both phases are gaining or losing kinetic e ...
CHAPTER 1 Differentiate b/w Mendeleev`s periodic law and modern
... Why atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group? Ans.The increasing number of shells and increasing. shielding effect increase the atomic radii from top to bottom. How does the nature of orbital influence the value of ionization energies of elements? Ans.The outermost electrons to be removed ...
... Why atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group? Ans.The increasing number of shells and increasing. shielding effect increase the atomic radii from top to bottom. How does the nature of orbital influence the value of ionization energies of elements? Ans.The outermost electrons to be removed ...
Preface from the Textbook - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Main ideas are delineated and highlighted, making for more efficient study and lectures. As a result, the text is over 20 pages shorter than the Second Edition. More worked problems. The much admired—and imitated—four-part (plan, solution, check, practice) Sample Problems occur in both data-based ...
... Main ideas are delineated and highlighted, making for more efficient study and lectures. As a result, the text is over 20 pages shorter than the Second Edition. More worked problems. The much admired—and imitated—four-part (plan, solution, check, practice) Sample Problems occur in both data-based ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
Chemistry English
... With the discovery of atoms came the chemical alphabet of element symbols. Dalton chose the circle as the symbol for oxygen and represented all other elements by variations of the circle. These early primitive symbols evolved into the modern system of using one or two letters of the English alphabet ...
... With the discovery of atoms came the chemical alphabet of element symbols. Dalton chose the circle as the symbol for oxygen and represented all other elements by variations of the circle. These early primitive symbols evolved into the modern system of using one or two letters of the English alphabet ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.