Unit 5 Study Guide
... c. Neither b. Pb d. Both 15. Which of the following displacement reactions will NOT occur? a) CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) ---> Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) b) 2NaNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Na(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) c) 2AgNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Ag(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) d) 2HCl(aq) + Zn(s) ---> H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) 16. An iron rod is place ...
... c. Neither b. Pb d. Both 15. Which of the following displacement reactions will NOT occur? a) CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) ---> Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) b) 2NaNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Na(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) c) 2AgNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Ag(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) d) 2HCl(aq) + Zn(s) ---> H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) 16. An iron rod is place ...
Name - rwebbchem
... 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
... 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
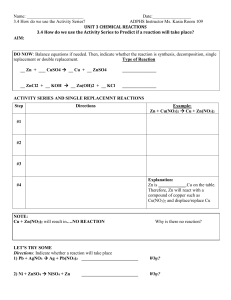
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... ADPHS Instructor Ms. Kasia Room 109 UNIT 3 CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... EXAM #2 Version 1 This exam is twenty five questions long. Each question is worth 4 points. Please read through all of the questions first and ask about anything you do not understand. You will have one hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam. Exams will be picked up at the end of the class period ...
... EXAM #2 Version 1 This exam is twenty five questions long. Each question is worth 4 points. Please read through all of the questions first and ask about anything you do not understand. You will have one hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam. Exams will be picked up at the end of the class period ...
Practice Test 11 - U of L Class Index
... argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compounds can react, producing phosphorus trifluoride (a gas that is colourless and odourless, ...
... argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compounds can react, producing phosphorus trifluoride (a gas that is colourless and odourless, ...
Chemical Reactions
... • An element reacts with a molecule. One of the elements in the molecule recombines with the original element. • The reactants and products are both one element and one molecule. A + BC AC + B “unhappy breakup” ...
... • An element reacts with a molecule. One of the elements in the molecule recombines with the original element. • The reactants and products are both one element and one molecule. A + BC AC + B “unhappy breakup” ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1984 Free Response Questions
... (b) Burning coal containing a significant amount of sulfur leads to "acid rain." (c) Perspiring is a mechanism for cooling the body. (d) The addition of antifreeze to water in a radiator decreases the likelihood that the liquid in the radiator will either freeze or boil. ...
... (b) Burning coal containing a significant amount of sulfur leads to "acid rain." (c) Perspiring is a mechanism for cooling the body. (d) The addition of antifreeze to water in a radiator decreases the likelihood that the liquid in the radiator will either freeze or boil. ...
study guide and review for first semester final
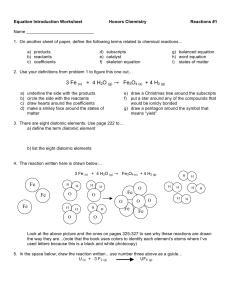
... 11. Write and balance chemical equations (other than redox) and identify the reaction type as composition, decomposition, single replacement, or double replacement. Ex. potassium hydroxide + sulfuric acid ------> potassium sulfate + water 2KOH + H2SO4 K2SO4 + 2H2O Double replacement 12. Identify th ...
... 11. Write and balance chemical equations (other than redox) and identify the reaction type as composition, decomposition, single replacement, or double replacement. Ex. potassium hydroxide + sulfuric acid ------> potassium sulfate + water 2KOH + H2SO4 K2SO4 + 2H2O Double replacement 12. Identify th ...
rules for predicting products of chemical reactions
... PREDICTING REACTION PRODUCTS: COMBUSTION REACTIONS - A hydrocarbon and oxygen (O2) indicate a combustion reaction - If it is combustion, then just write H2O and CO2 as products - Then, balance the equation (can be tricky) Examples: __CH4 + _2 O2 ___ CO2 + __2 H2O _2 C4H10 + __13 O2 __8 CO2 + _10 ...
... PREDICTING REACTION PRODUCTS: COMBUSTION REACTIONS - A hydrocarbon and oxygen (O2) indicate a combustion reaction - If it is combustion, then just write H2O and CO2 as products - Then, balance the equation (can be tricky) Examples: __CH4 + _2 O2 ___ CO2 + __2 H2O _2 C4H10 + __13 O2 __8 CO2 + _10 ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized e ...
... represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized e ...
File - Kheriaty Chemistry
... a. What element will Li bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element will O bond to? d. What is the chemical formula of that new product? 16. Potassium oxide reacts with magnesium bromide. a. What element will potassium bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of tha ...
... a. What element will Li bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element will O bond to? d. What is the chemical formula of that new product? 16. Potassium oxide reacts with magnesium bromide. a. What element will potassium bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of tha ...
NOTES CHEMICAL REACTIONS:
... • Remember! In order for a reaction to take place you must produce a gas or a precipitate from 2 liquids. • Solubility rules tell us whether or not a ...
... • Remember! In order for a reaction to take place you must produce a gas or a precipitate from 2 liquids. • Solubility rules tell us whether or not a ...
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
File
... constant per 100 g of acetone is 17.2°C. 21. Chromium erystallises in a body certred cubic lattice, whose density is 7.20 g/cm3. The length of the edge of unit cell is 288.4 p.m. Calculate Avogadro’s number. (Atomic mass of chromium = 52). 22. What do you mean by activity and selectivity of a cataly ...
... constant per 100 g of acetone is 17.2°C. 21. Chromium erystallises in a body certred cubic lattice, whose density is 7.20 g/cm3. The length of the edge of unit cell is 288.4 p.m. Calculate Avogadro’s number. (Atomic mass of chromium = 52). 22. What do you mean by activity and selectivity of a cataly ...
1 ChE 505 WORKSHOP 1 1. Why are chemical reactions important
... What is the relationship between the initial moles of reactants and products, the moles for each of the above after some reaction time, the stoichiometric coefficients and reaction extent? ...
... What is the relationship between the initial moles of reactants and products, the moles for each of the above after some reaction time, the stoichiometric coefficients and reaction extent? ...
Predicting Products Answers
... Predicting Products Part 1: Identify each of the following reactions by writing the mane of the reaction on the line to the left of the chemical reaction. Complete the reaction on the line to the right. Be sure to balance the equation. Reaction Type Reaction 1) double replacement ...
... Predicting Products Part 1: Identify each of the following reactions by writing the mane of the reaction on the line to the left of the chemical reaction. Complete the reaction on the line to the right. Be sure to balance the equation. Reaction Type Reaction 1) double replacement ...
Types of Chemical Reactions - Celebrity Examples
... y Emission of heat and y Giving off light y Formation of a precipitate y Formation of a gas y Color change ...
... y Emission of heat and y Giving off light y Formation of a precipitate y Formation of a gas y Color change ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... 1. Carbon monoxide can be combined with hydrogen to produce methanol, CH 3OH. If you had 152.5 g CO and 24.50 g H2, how many kilograms of CH3OH would be produced? (Hint: make sure equation is balanced first!) CO ...
... 1. Carbon monoxide can be combined with hydrogen to produce methanol, CH 3OH. If you had 152.5 g CO and 24.50 g H2, how many kilograms of CH3OH would be produced? (Hint: make sure equation is balanced first!) CO ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. ...
... reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. ...
KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical
... A catalyst lowers activation energy. • Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. – decrease activation energy – increase reaction rate ...
... A catalyst lowers activation energy. • Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. – decrease activation energy – increase reaction rate ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.