2011-2012 ACAD REVIEW SHEET Chapter 16
... 24. Describe Le Chatelier’s principle. (ANS: The reaction will shift to minimize the disturbance to reestablish equilibrium.) 25. What factors alter the equilibrium position in chemical reactions? (ANS: Concentration, Pressure and temperature) ...
... 24. Describe Le Chatelier’s principle. (ANS: The reaction will shift to minimize the disturbance to reestablish equilibrium.) 25. What factors alter the equilibrium position in chemical reactions? (ANS: Concentration, Pressure and temperature) ...
Chemistry 1: Second Semester Practice Exam Read each question
... 51. Balance the equation written below. The coefficient in front of the O2 is ___ C2H5OH + __ O2 Æ __ H2O + __ CO2 A. 3 B. 5 C. 7 D. 9 52. A double replacement reaction is likely to occur when A. a metal, such as zinc is placed in a concentrated acid B. a hydrocarbon is burned in the presence of oxy ...
... 51. Balance the equation written below. The coefficient in front of the O2 is ___ C2H5OH + __ O2 Æ __ H2O + __ CO2 A. 3 B. 5 C. 7 D. 9 52. A double replacement reaction is likely to occur when A. a metal, such as zinc is placed in a concentrated acid B. a hydrocarbon is burned in the presence of oxy ...
Thermodynamics
... Not speed of reaction (kinetics) A reaction can be thermodynamically favored but still be ...
... Not speed of reaction (kinetics) A reaction can be thermodynamically favored but still be ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
07 Aromatic compounds. Acids of arom.s.,their salts, esters,amides
... The term vitamin K was applied to the vitamin isolated from alfalfa, and a similar principle from fishmeal was named vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 refers to a series of compounds called the menaquinones. These have a longer side chain with more unsaturation. Many other closely related compounds possess vit ...
... The term vitamin K was applied to the vitamin isolated from alfalfa, and a similar principle from fishmeal was named vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 refers to a series of compounds called the menaquinones. These have a longer side chain with more unsaturation. Many other closely related compounds possess vit ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment Summer 2015 Ms. Osquist
... 1.3 Label each of the following as either a physical process or a chemical process: (a) corrosion of aluminum metal, (b) melting of ice, (c) pulverizing of aspirin, (d) digesting a candy bar, (e) explosion of nitroglycerin. 1.4 What exponential notation do the following abbreviations represent in t ...
... 1.3 Label each of the following as either a physical process or a chemical process: (a) corrosion of aluminum metal, (b) melting of ice, (c) pulverizing of aspirin, (d) digesting a candy bar, (e) explosion of nitroglycerin. 1.4 What exponential notation do the following abbreviations represent in t ...
Types of Reactions
... • The neutral Ca has lost two electrons to 2 H+1 to become Ca+2. • We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca+2. When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) 2 CaO (s). • In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O–2 in CaO. • We say O2 has be ...
... • The neutral Ca has lost two electrons to 2 H+1 to become Ca+2. • We say Ca has been oxidized to Ca+2. When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) 2 CaO (s). • In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O–2 in CaO. • We say O2 has be ...
Chapter 8
... 8. The activity series given in Table 8.2 shows the relative activity of certain metals and halogens. As you move up the table starting with gold (Au) and ending with potassium (K) the activity increases. The same is true as you move up from iodine (I2) to fluorine (F2). The table is useful for pred ...
... 8. The activity series given in Table 8.2 shows the relative activity of certain metals and halogens. As you move up the table starting with gold (Au) and ending with potassium (K) the activity increases. The same is true as you move up from iodine (I2) to fluorine (F2). The table is useful for pred ...
Solution - gearju.com
... The sodium hydroxide solution standardized in Example 4.11 is used to titrate 25.00 mL of a sulfuric acid solution. The titration requires 43.79 mL of the 0.1172 M NaOH solution to completely neutralize the acid. What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution? ...
... The sodium hydroxide solution standardized in Example 4.11 is used to titrate 25.00 mL of a sulfuric acid solution. The titration requires 43.79 mL of the 0.1172 M NaOH solution to completely neutralize the acid. What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution? ...
Covalent Bonding
... Group 1 and 17 elements are always at ends Atoms that are less numerous are usually in the middle Hydrogen always forms one single bond Oxygen has two bonding electrons and two lone pairs Nitrogen has three bonding electron and one lone pair Group 13 elements have three bonding electrons and z ...
... Group 1 and 17 elements are always at ends Atoms that are less numerous are usually in the middle Hydrogen always forms one single bond Oxygen has two bonding electrons and two lone pairs Nitrogen has three bonding electron and one lone pair Group 13 elements have three bonding electrons and z ...
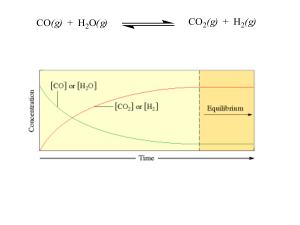
Test review
... What will happen to a reaction mixture at equilibrium if a. H2O(g) is removed? b. The temperature is increased (the reaction is endothermic)? c. An inert gas is added? d. CO(g) is removed? e. The volume of the container is tripled? 11. What will happen to the number of moles of SO3 in equilibrium wi ...
... What will happen to a reaction mixture at equilibrium if a. H2O(g) is removed? b. The temperature is increased (the reaction is endothermic)? c. An inert gas is added? d. CO(g) is removed? e. The volume of the container is tripled? 11. What will happen to the number of moles of SO3 in equilibrium wi ...
친환경 촉매 Iron (III) phosphate: 실온/무용매 반응조건에서 알코올과
... Also, isoamyl acetate is a kind of flavor reagent with fruit taste. It is traditionally prepared with H2SO4 as catalyst.7 The use of H2SO4 often causes the problems such as corrosion for equipments and pollution for environment. Until now, the tried replaces include FeCl3, CuSO4, ferric tri-dodecane ...
... Also, isoamyl acetate is a kind of flavor reagent with fruit taste. It is traditionally prepared with H2SO4 as catalyst.7 The use of H2SO4 often causes the problems such as corrosion for equipments and pollution for environment. Until now, the tried replaces include FeCl3, CuSO4, ferric tri-dodecane ...
Kinetics and Mechanism of Uncatalyzed and Ag (I) Catalyzed
... N-bromo-benzenesulphonamide [11], in both acid and alkaline media have been studied. Although, various types of the reaction models have been suggested by different researchers [12-16], the specific details are yet to be discovered. Also, there are still controversies regarding the mechanistic pathw ...
... N-bromo-benzenesulphonamide [11], in both acid and alkaline media have been studied. Although, various types of the reaction models have been suggested by different researchers [12-16], the specific details are yet to be discovered. Also, there are still controversies regarding the mechanistic pathw ...
35. Number of reactions - Royal Society of Chemistry
... The best answers are those that identify A, and identify the correct reactions. Some of these can be written as: ...
... The best answers are those that identify A, and identify the correct reactions. Some of these can be written as: ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... Illustrate, using aspirin as an example, how biochemists modify the structure of drugs to eliminate undesirable side effects. A16. Salicylic acid was used as a pain killer but found was to found to cause bleeding of the stomach walls. Its structure was modified by reaction salicylic acid (aspirin) w ...
... Illustrate, using aspirin as an example, how biochemists modify the structure of drugs to eliminate undesirable side effects. A16. Salicylic acid was used as a pain killer but found was to found to cause bleeding of the stomach walls. Its structure was modified by reaction salicylic acid (aspirin) w ...
Thermodynamics - Ian Dalgleish
... We end up with less free energy than we started with, therefore free energy has been given out during the reaction ; the reaction has done work. The work done by the reaction is - ∆G. Reactions with a negative ∆G are spontaneous - they proceed without outside aid. The rate of change of free energy h ...
... We end up with less free energy than we started with, therefore free energy has been given out during the reaction ; the reaction has done work. The work done by the reaction is - ∆G. Reactions with a negative ∆G are spontaneous - they proceed without outside aid. The rate of change of free energy h ...
Unit 8 Packet - Page 1 of 18 Honors Chemistry
... Current Unit Material: 6. Write balanced equations for the following reactions: A. Calcium metal is added to water. B. A solution of tin (II) chloride is added to a solution of iron (III) sulfate C. Chlorine gas is bubbled into a solution of lithium iodide. D. C3H8 is burned in oxygen 7. How is 2Cl ...
... Current Unit Material: 6. Write balanced equations for the following reactions: A. Calcium metal is added to water. B. A solution of tin (II) chloride is added to a solution of iron (III) sulfate C. Chlorine gas is bubbled into a solution of lithium iodide. D. C3H8 is burned in oxygen 7. How is 2Cl ...
Document
... Worked Example 8.3 Determine whether each of the following equations represents a combination reaction, a decomposition reaction, or a combustion reaction: (a) H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g), (b) 2HCO2H(l) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l), (c) 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g). Strategy The equation in part (a) de ...
... Worked Example 8.3 Determine whether each of the following equations represents a combination reaction, a decomposition reaction, or a combustion reaction: (a) H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g), (b) 2HCO2H(l) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l), (c) 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g). Strategy The equation in part (a) de ...
Chemistry 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. A 10.0 g sample of a substance has 34.8 J of energy added to it and its temperature increases by 25.0°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the substance? A. 0.139 J/g°C B. 0.338 J/g°C C. 0.718 J/g°C D. 0.870 J/g°C 3. If the ΔH for a reaction is positive, which of the following statements is t ...
... 2. A 10.0 g sample of a substance has 34.8 J of energy added to it and its temperature increases by 25.0°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the substance? A. 0.139 J/g°C B. 0.338 J/g°C C. 0.718 J/g°C D. 0.870 J/g°C 3. If the ΔH for a reaction is positive, which of the following statements is t ...
Redox - edl.io
... 5. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation state of -2. Exceptions to this rule include peroxides (compound containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of -1, as in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and OF2 in which oxygen is assigned a +2 oxidation state. 6. In its covalent ...
... 5. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation state of -2. Exceptions to this rule include peroxides (compound containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of -1, as in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and OF2 in which oxygen is assigned a +2 oxidation state. 6. In its covalent ...
AH 2015 incl MG
... made up to the mark with deionised water. 25·0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated with 0·050 mol l−1 sulphuric acid. ...
... made up to the mark with deionised water. 25·0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated with 0·050 mol l−1 sulphuric acid. ...
Name__________________________________________ Answers to Sample Exam Questions #1 Chemistry 112
... b) Atoms of the same element can be different. c) Compounds form when atoms combine in whole number ratios. d) A chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms. 3. Which of the following pairs of compounds illustrates the law of multiple proportions? a) Fe, FeO3 b) Cl, Cl2 c) H2SO4, NaOH d) H2O, ...
... b) Atoms of the same element can be different. c) Compounds form when atoms combine in whole number ratios. d) A chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms. 3. Which of the following pairs of compounds illustrates the law of multiple proportions? a) Fe, FeO3 b) Cl, Cl2 c) H2SO4, NaOH d) H2O, ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry: The Hydrosphere
... 4.1 SOLUTIONS ON EARTH AND OTHER PLACES aqueous solution: a solution where water is the dissolving medium (the solvent) – For example, when table salt (NaCl) is dissolved in water, it results in an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, NaCl(aq), with Na+ and Cl- ions dissolved in water. – Note: The p ...
... 4.1 SOLUTIONS ON EARTH AND OTHER PLACES aqueous solution: a solution where water is the dissolving medium (the solvent) – For example, when table salt (NaCl) is dissolved in water, it results in an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, NaCl(aq), with Na+ and Cl- ions dissolved in water. – Note: The p ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.























