CHEM1001 2012-J-2 June 2012 22/01(a) • Complete the following
... foil. Most of the particles passed straight through or were slightly deflected, but the occasional one was reflected back towards the source. The conclusion drawn was that atoms consist of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. ...
... foil. Most of the particles passed straight through or were slightly deflected, but the occasional one was reflected back towards the source. The conclusion drawn was that atoms consist of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. ...
Unit 3, Lesson 07: Calculating ∆H using Standard Enthalpies of
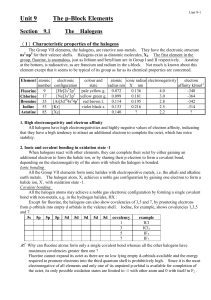
... a) Noble gases are present as neutral atoms in the gas state eg. Ne (g), He (g), Ar (g) b) “HOBrFINCl” elements: these elements are found as diatomic molecules at SATP. Their state is indicated on the Periodic Table eg. H2(g), O2(g), Br2(l), F2(g), I2(s), N2(g), and Cl2(g) c) allotropes are non-meta ...
... a) Noble gases are present as neutral atoms in the gas state eg. Ne (g), He (g), Ar (g) b) “HOBrFINCl” elements: these elements are found as diatomic molecules at SATP. Their state is indicated on the Periodic Table eg. H2(g), O2(g), Br2(l), F2(g), I2(s), N2(g), and Cl2(g) c) allotropes are non-meta ...
Chapter 4,5,6
... 10. A piece of zinc metal is reacted with an excess of aqueous hydrochloric acid. The hydrogen gas which is produced is collected by displacement over water. If the total pressure of the gas collected is 758 torr, the volume of the gas is 250 mL, and the temperature of the gas is 24.00C, calculate t ...
... 10. A piece of zinc metal is reacted with an excess of aqueous hydrochloric acid. The hydrogen gas which is produced is collected by displacement over water. If the total pressure of the gas collected is 758 torr, the volume of the gas is 250 mL, and the temperature of the gas is 24.00C, calculate t ...
Nikolai N. Semenov - Nobel Lecture
... close limits which, on some occasions, are virtually unmeasurable. Similar limit phenomena were observed by Sir Cyril Hinshelwood and collaborators19 in the case of pressures which exceed a certain "second upper limit" (e.g. in the case of the reaction of water formation from oxygen and hydrogen). T ...
... close limits which, on some occasions, are virtually unmeasurable. Similar limit phenomena were observed by Sir Cyril Hinshelwood and collaborators19 in the case of pressures which exceed a certain "second upper limit" (e.g. in the case of the reaction of water formation from oxygen and hydrogen). T ...
Final Exam - Seattle Central College
... Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces (IMF’s): attraction between 2 different molecules in a liquid or solid • Identify the type of intermolecular force for a molecule as London/dispersion forces, dipoledipole forces, hydrogen bonding, or ion-diple forces • Know that hydrogen bonds are the strongest typ ...
... Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces (IMF’s): attraction between 2 different molecules in a liquid or solid • Identify the type of intermolecular force for a molecule as London/dispersion forces, dipoledipole forces, hydrogen bonding, or ion-diple forces • Know that hydrogen bonds are the strongest typ ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... Knowledge of experimental details to determine melting point and boiling point are not required but pupils should be able to interpret a simple heating / cooling curve. It is suggested that examples are chosen from substances mentioned in Section 5.4(b). (e.g. sodium chloride, sodium carbonate and o ...
... Knowledge of experimental details to determine melting point and boiling point are not required but pupils should be able to interpret a simple heating / cooling curve. It is suggested that examples are chosen from substances mentioned in Section 5.4(b). (e.g. sodium chloride, sodium carbonate and o ...
Student Review packet
... current, charge, Faradays, (voltage / EMF) (amps, coulombs and volts – unit problem) ...
... current, charge, Faradays, (voltage / EMF) (amps, coulombs and volts – unit problem) ...
Chemistry notes Important terms *Mass of element in a sample
... of concentration and volume, K does not change. A temperature change, however, does change K: higher T increase K for an endothermic reaction (positive ΔHrxn) and decreases K for an exothermic reaction ( negative ΔHrxn) A catalyst causes a system to reach the equilibrium point more quickly Ammonia p ...
... of concentration and volume, K does not change. A temperature change, however, does change K: higher T increase K for an endothermic reaction (positive ΔHrxn) and decreases K for an exothermic reaction ( negative ΔHrxn) A catalyst causes a system to reach the equilibrium point more quickly Ammonia p ...
Practice Problem Set #6
... 3. Complete and balance the equations for the following reactions. a. Na(s) + Br2(l) → b. Mg(s) + O2(g) → c. Al(s) + F2(g) → d. C(s) + O2(g) → (assume an excess of oxygen has been added) 4. Calcium oxide, CaO, is used to remove SO2 from power plant exhaust. These two compounds react to give so ...
... 3. Complete and balance the equations for the following reactions. a. Na(s) + Br2(l) → b. Mg(s) + O2(g) → c. Al(s) + F2(g) → d. C(s) + O2(g) → (assume an excess of oxygen has been added) 4. Calcium oxide, CaO, is used to remove SO2 from power plant exhaust. These two compounds react to give so ...
Raman Spectroscopy
... However, it is found that in a number of cases, a small amount of the light absorbed can bring about a large amount of reaction, whereas in some other cases, large amount of the light absorbed can bring about only a small amount of reaction. This was explained on the basis that all the molecules pre ...
... However, it is found that in a number of cases, a small amount of the light absorbed can bring about a large amount of reaction, whereas in some other cases, large amount of the light absorbed can bring about only a small amount of reaction. This was explained on the basis that all the molecules pre ...
1 - Academics
... a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a particle cannot be simultaneously ...
... a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a particle cannot be simultaneously ...
Chemistry I Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
... A) When two elements combine with each other to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine with a fixed weight of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers. B) The rate of any chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the masses of the reacting substances, w ...
... A) When two elements combine with each other to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine with a fixed weight of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers. B) The rate of any chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the masses of the reacting substances, w ...
Ahmed Fazary_Click Chemistry
... units together as nature does. In biochemistry, proteins are made from repeating amino acid units and sugars are made from repeating monosaccharide units. The connecting units are based on carbon - hetero atom bonds C-X-C rather than carbon carbon bonds. In addition, enzymes ensure that chemical pro ...
... units together as nature does. In biochemistry, proteins are made from repeating amino acid units and sugars are made from repeating monosaccharide units. The connecting units are based on carbon - hetero atom bonds C-X-C rather than carbon carbon bonds. In addition, enzymes ensure that chemical pro ...
Chapter 7-8-9
... d. tetrahedral 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? a. CO b. Cl c. CO d. N 24. What cause ...
... d. tetrahedral 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? a. CO b. Cl c. CO d. N 24. What cause ...
Powerpoint
... Copper metal of the anode completes with OH-. The potential of the first half-reaction is larger. Copper metal, rather than OH-, gives out electrons. In principle, if platinum electrode is used, platinum may also give out electrons to form platinum ion. But in practice, it seldom happens due to the ...
... Copper metal of the anode completes with OH-. The potential of the first half-reaction is larger. Copper metal, rather than OH-, gives out electrons. In principle, if platinum electrode is used, platinum may also give out electrons to form platinum ion. But in practice, it seldom happens due to the ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment THIS
... AP Chemistry can be considered as the second year of a two year program. The topics covered at the beginning of the year are mostly review from first year chemistry so we will move very quickly through this material. The purpose of this assignment is to review some of the material you learned last y ...
... AP Chemistry can be considered as the second year of a two year program. The topics covered at the beginning of the year are mostly review from first year chemistry so we will move very quickly through this material. The purpose of this assignment is to review some of the material you learned last y ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... Acid-base titrations: The impact of hydrolysis Salt hydrolysis has an important effect on the pH profile of acid-base titrations. The equivalence point may be above or below neutral conditions (i.e. pH = ...
... Acid-base titrations: The impact of hydrolysis Salt hydrolysis has an important effect on the pH profile of acid-base titrations. The equivalence point may be above or below neutral conditions (i.e. pH = ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions
... How do you know when a chemical reaction takes place? Temperature Change ...
... How do you know when a chemical reaction takes place? Temperature Change ...
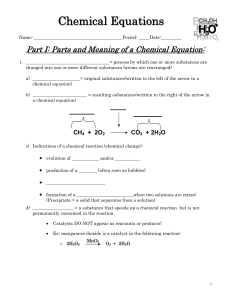
Chemical Equations
... A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A reactant or product in the gaseous state Alternative to (g); used only for a gaseous product Reactants are heated Pressure at which the reaction is carried out, in this case 2 Temperature at which reaction is carried out, in this case ...
... A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A reactant or product in the gaseous state Alternative to (g); used only for a gaseous product Reactants are heated Pressure at which the reaction is carried out, in this case 2 Temperature at which reaction is carried out, in this case ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.