Bonding
... ✦ Metals react with nonmetals ✦ Ions paired have lower energy (greater stability) than separated ions Covalent ✦ Electrons are shared by nuclei ✦ Pure covalent (nonpolar covalent) - electrons are shared evenly ✦ Polar covalent - electrons shared unequally ...
... ✦ Metals react with nonmetals ✦ Ions paired have lower energy (greater stability) than separated ions Covalent ✦ Electrons are shared by nuclei ✦ Pure covalent (nonpolar covalent) - electrons are shared evenly ✦ Polar covalent - electrons shared unequally ...
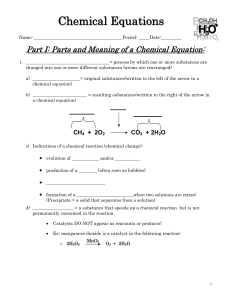
Chemical Equations
... A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A reactant or product in the gaseous state Alternative to (g); used only for a gaseous product Reactants are heated Pressure at which the reaction is carried out, in this case 2 Temperature at which reaction is carried out, in this case ...
... A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A reactant or product in the gaseous state Alternative to (g); used only for a gaseous product Reactants are heated Pressure at which the reaction is carried out, in this case 2 Temperature at which reaction is carried out, in this case ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier (PDF
... The sugar is fermented with yeast at a temperature of about 30 °C. (a) The sustainability of chemical processes depends on a number of factors. One of these factors is the renewability of raw materials. Consider this, and other factors, to compare the sustainability of making ethanol by these two me ...
... The sugar is fermented with yeast at a temperature of about 30 °C. (a) The sustainability of chemical processes depends on a number of factors. One of these factors is the renewability of raw materials. Consider this, and other factors, to compare the sustainability of making ethanol by these two me ...
Chemistry
... 10. bring together knowledge, principles and concepts from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context 11. use chemical skills in contexts which bring together different areas of the subject. These assessment objectives cannot be precisely specified in the Syllabus content b ...
... 10. bring together knowledge, principles and concepts from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context 11. use chemical skills in contexts which bring together different areas of the subject. These assessment objectives cannot be precisely specified in the Syllabus content b ...
Review #7: Solutions, Acids and Bases 1. Definitions: a) Solution: a
... sodium chloride), or a solution that contains these ions in equal concentrations (for example, water). Its pH is 7.0. ...
... sodium chloride), or a solution that contains these ions in equal concentrations (for example, water). Its pH is 7.0. ...
How to Make a Collage
... help you find ways to improve your skills. If you do not practice these skills you lose the ability to perform them quickly, confidently and competently. Flash cards will help you throughout this course. It is good practice to begin using now with these basic math skills. ...
... help you find ways to improve your skills. If you do not practice these skills you lose the ability to perform them quickly, confidently and competently. Flash cards will help you throughout this course. It is good practice to begin using now with these basic math skills. ...
Final Review
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
Chemistry to Remember
... Pressure is the force exerted on a unit surface, and gas pressure is measured via a barometer. A barometer measures the displacement of a column of mercury by air pressure. Standard pressure is 760 mm of mercury or 1 atmosphere (atm), specifically; the air pressure at sea level supports a column of ...
... Pressure is the force exerted on a unit surface, and gas pressure is measured via a barometer. A barometer measures the displacement of a column of mercury by air pressure. Standard pressure is 760 mm of mercury or 1 atmosphere (atm), specifically; the air pressure at sea level supports a column of ...
Spring Exam 2 - Chemistry
... beginning in column A and continuing through column H, column I will be blank, (do NOT use column J at this time); be sure to fill in the correct circles (a common error to be avoided is mistaking "0" for "1"). ...
... beginning in column A and continuing through column H, column I will be blank, (do NOT use column J at this time); be sure to fill in the correct circles (a common error to be avoided is mistaking "0" for "1"). ...
PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... • b) Glycine (H2NCH2COOH) is a covalent compound, but it contains polar N–H and O–H bonds. This would make the molecule interact well with polar water molecules, and make it likely that it would be soluble. c) Pentane (C5H12) has no bonds of significant polarity, so it would not be expected to be so ...
... • b) Glycine (H2NCH2COOH) is a covalent compound, but it contains polar N–H and O–H bonds. This would make the molecule interact well with polar water molecules, and make it likely that it would be soluble. c) Pentane (C5H12) has no bonds of significant polarity, so it would not be expected to be so ...
KEY
... to OH− . Therefore H3 O+ is acting as an acid and OH− is acting as a base. In the reverse reaction, NH+ 4 is the proton donor and thus, it is the other acid. 028 10.0 points In the two reactions represented by HCN + H2 O ⇀ ↽ CN− + H3 O+ , the two Bronsted-Lowry acids are ...
... to OH− . Therefore H3 O+ is acting as an acid and OH− is acting as a base. In the reverse reaction, NH+ 4 is the proton donor and thus, it is the other acid. 028 10.0 points In the two reactions represented by HCN + H2 O ⇀ ↽ CN− + H3 O+ , the two Bronsted-Lowry acids are ...
Unit 9 - Kinetics and Equilibrium
... Write a balanced equation for the system. Place the products as factors in the numerator of a fraction and the reactants as factors in the denominator, Place a square bracket around each formula. The square bracket means molar concentration. Write the coefficient of each substance as the pow ...
... Write a balanced equation for the system. Place the products as factors in the numerator of a fraction and the reactants as factors in the denominator, Place a square bracket around each formula. The square bracket means molar concentration. Write the coefficient of each substance as the pow ...
Document
... However, it is found that in a number of cases, a small amount of the light absorbed can bring about a large amount of reaction, whereas in some other cases, large amount of the light absorbed can bring about only a small amount of reaction. This was explained on the basis that all the molecules pre ...
... However, it is found that in a number of cases, a small amount of the light absorbed can bring about a large amount of reaction, whereas in some other cases, large amount of the light absorbed can bring about only a small amount of reaction. This was explained on the basis that all the molecules pre ...
Document
... However, it is found that in a number of cases, a small amount of the light absorbed can bring about a large amount of reaction, whereas in some other cases, large amount of the light absorbed can bring about only a small amount of reaction. This was explained on the basis that all the molecules pre ...
... However, it is found that in a number of cases, a small amount of the light absorbed can bring about a large amount of reaction, whereas in some other cases, large amount of the light absorbed can bring about only a small amount of reaction. This was explained on the basis that all the molecules pre ...
Acids, Bases, and pH
... health (Vitamin C is a compound called ascorbic acid), and many other aspects of chemistry. In this mini-chapter you will learn the basics of acids and bases and how they are related to pH. I. Acids An Acid is a substance that donates one or more H+ ions (protons) to another substance (called a base ...
... health (Vitamin C is a compound called ascorbic acid), and many other aspects of chemistry. In this mini-chapter you will learn the basics of acids and bases and how they are related to pH. I. Acids An Acid is a substance that donates one or more H+ ions (protons) to another substance (called a base ...
Energy and Chemical Reactions
... states, and enough information to get one of the following, calculate the one not given: (1) the ∆E° for the equation and (2) the ∆H° for the equation. 29. Write or identify general descriptions of bomb and open calorimeters. 30. Explain why heats of reactions are usually determined using bomb calor ...
... states, and enough information to get one of the following, calculate the one not given: (1) the ∆E° for the equation and (2) the ∆H° for the equation. 29. Write or identify general descriptions of bomb and open calorimeters. 30. Explain why heats of reactions are usually determined using bomb calor ...
as a PDF
... As Fig. 1.2 shows, thermodynamics distinguishes lanthanide reactions in which the 4f population changes from those in which the 4f population is conserved. In the latter type of reaction, the second part of our principle states that the energy variation is nearly smooth. Why do we need the qualifica ...
... As Fig. 1.2 shows, thermodynamics distinguishes lanthanide reactions in which the 4f population changes from those in which the 4f population is conserved. In the latter type of reaction, the second part of our principle states that the energy variation is nearly smooth. Why do we need the qualifica ...
1999 Advanced Placement Chemistry Exam Section I: Multiple
... completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. 19. Which of the following best describes the role of (E) The spark provides the heat of vaporization the spark from the spark plug in an automobile for the volatile hydrocarbon. ...
... completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. 19. Which of the following best describes the role of (E) The spark provides the heat of vaporization the spark from the spark plug in an automobile for the volatile hydrocarbon. ...
Test 2 Guide Key
... limiting. Then solve for the moles of CO needed to react with it: #mol CO needed = 2.5 mol H2 (2 mol CO/3 mol H2)=5/3 mol CO=2.67 mol CO needed. But this is less than the 2.1 mol CO we have so in fact, CO is limiting. 13) A catalyst is formed during the transition from reactant to product. False. It ...
... limiting. Then solve for the moles of CO needed to react with it: #mol CO needed = 2.5 mol H2 (2 mol CO/3 mol H2)=5/3 mol CO=2.67 mol CO needed. But this is less than the 2.1 mol CO we have so in fact, CO is limiting. 13) A catalyst is formed during the transition from reactant to product. False. It ...
4.1 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... of atoms on either side of the arrow and comparing these sums to ensure they are equal. Note that the number of atoms for a given element is calculated by multiplying the coefficient of any formula containing that element by the element’s subscript in the formula. If an element appears in more than ...
... of atoms on either side of the arrow and comparing these sums to ensure they are equal. Note that the number of atoms for a given element is calculated by multiplying the coefficient of any formula containing that element by the element’s subscript in the formula. If an element appears in more than ...
Review Answers - cloudfront.net
... getting more disordered and therefore entropy is increased. ΔS° is positive b. What change, if any, will occur in ΔG° for the reaction as the temperature is increased? Explain your reasoning in terms of thermodynamics principles. Since when Temp is increased there are more molecules of PCl3 and Cl2, ...
... getting more disordered and therefore entropy is increased. ΔS° is positive b. What change, if any, will occur in ΔG° for the reaction as the temperature is increased? Explain your reasoning in terms of thermodynamics principles. Since when Temp is increased there are more molecules of PCl3 and Cl2, ...
File
... (ii) The C–C–C bond angle in compound K changes when the polymer is formed. State and explain how the C–C–C bond angle differs between a molecule of K and the polymer. angle changes from ............................................ to ................................................. ...
... (ii) The C–C–C bond angle in compound K changes when the polymer is formed. State and explain how the C–C–C bond angle differs between a molecule of K and the polymer. angle changes from ............................................ to ................................................. ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.