water, h2o
... It has long been recognized – remarkably, for 200 years - that protons have the potential for a unique mode of transport in water and, by extension, in other highly connected hydrogen bonding systems. The Grotthuss mechanism involves a simple shift of hydrogen bonds to effectively relocate a net pro ...
... It has long been recognized – remarkably, for 200 years - that protons have the potential for a unique mode of transport in water and, by extension, in other highly connected hydrogen bonding systems. The Grotthuss mechanism involves a simple shift of hydrogen bonds to effectively relocate a net pro ...
Which indicator is best in silver nitrate titrations
... This investigation is based the article by Christopher Parkin in the School Science Review and students need to consult this article. The practical techniques are initially very tricky as the rate of reaction is slow but students should be able to obtain results fairly quickly once the apparatus is ...
... This investigation is based the article by Christopher Parkin in the School Science Review and students need to consult this article. The practical techniques are initially very tricky as the rate of reaction is slow but students should be able to obtain results fairly quickly once the apparatus is ...
Lecture 7. Fundamentals of atmospheric chemistry: Part 2 1
... (endothermic reactions), and a decrease in temperature favors the process that releases the heat (exothermic reactions). For the reaction above, the forward reaction releases the heat, and the reverse reaction absorbs heat. Therefore, the production of ammonia is favored by lowering T, because this ...
... (endothermic reactions), and a decrease in temperature favors the process that releases the heat (exothermic reactions). For the reaction above, the forward reaction releases the heat, and the reverse reaction absorbs heat. Therefore, the production of ammonia is favored by lowering T, because this ...
Study Guide
... Know the following terms: activation energy (EA), burning/combustion, bombardment, dissolving, enthalpy, molar heat, nucleon and resting mass. Compare exothermic and endothermic reactions/notation. Calculate the heat released or absorbed by dissolving. Conduct quantities of heat calculations using Q ...
... Know the following terms: activation energy (EA), burning/combustion, bombardment, dissolving, enthalpy, molar heat, nucleon and resting mass. Compare exothermic and endothermic reactions/notation. Calculate the heat released or absorbed by dissolving. Conduct quantities of heat calculations using Q ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-pola ...
... water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-pola ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
Combining and Choosing Analytical Techniques
... substance, this can be used to identify the substance from an on-line database or to give information about the structure of a new or unknown compound. ...
... substance, this can be used to identify the substance from an on-line database or to give information about the structure of a new or unknown compound. ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... Balancing Chemical Equations Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Balance the different types of atoms one at a time. • First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. • Balance polyatomic ions that ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Balance the different types of atoms one at a time. • First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. • Balance polyatomic ions that ...
Chemistry exam review
... 1. Which example indicates that a chemical change has occurred? a. When aqueous solutions are mixed, a precipitate is formed. b. As ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, it causes the temperature to decrease. c. Alcohol evaporates when left in an open container. d. Water is added to blue copper(II) c ...
... 1. Which example indicates that a chemical change has occurred? a. When aqueous solutions are mixed, a precipitate is formed. b. As ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, it causes the temperature to decrease. c. Alcohol evaporates when left in an open container. d. Water is added to blue copper(II) c ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, SYMBOLS, FORULAS 7
... There are four H atoms on the reactant side (coefficient of 2 x subscript 2) and four H atoms on the product side (coefficient 2 x subscript 2). There are two O atoms on the reactant side (coefficient 2 x (understood) subscript 1) and two O atoms on the product side (understood coefficient 1 x subsc ...
... There are four H atoms on the reactant side (coefficient of 2 x subscript 2) and four H atoms on the product side (coefficient 2 x subscript 2). There are two O atoms on the reactant side (coefficient 2 x (understood) subscript 1) and two O atoms on the product side (understood coefficient 1 x subsc ...
Test-tube Reactions - University of Manitoba
... hence, an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. This makes sense since as one reactant is losing electrons (being oxidized), the other is gaining electrons (being reduced) Oxidation numbers can be helpful in determining whether a reaction is redox or non-redox. When a change in oxidation number occu ...
... hence, an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. This makes sense since as one reactant is losing electrons (being oxidized), the other is gaining electrons (being reduced) Oxidation numbers can be helpful in determining whether a reaction is redox or non-redox. When a change in oxidation number occu ...
2. Covalent network
... o A cation is smaller than its parent atom Lattice energy: the change in energy when ions are packed together to form an ionic solid o Lattice energy=k(Q1 Q2/r) o K= constant o Q1, Q2 = charges on the ions ...
... o A cation is smaller than its parent atom Lattice energy: the change in energy when ions are packed together to form an ionic solid o Lattice energy=k(Q1 Q2/r) o K= constant o Q1, Q2 = charges on the ions ...
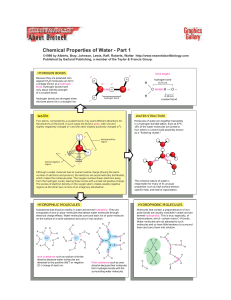
Water Chemistry - Biology12-Lum
... Many substances, such as household sugar, dissolve in water. That is, their molecules separate from each other, each becoming surrounded by water molecules. ...
... Many substances, such as household sugar, dissolve in water. That is, their molecules separate from each other, each becoming surrounded by water molecules. ...
A2 Chemistry key word list
... similar chemical properties and their atoms have the same number of outer-shell electrons. ...
... similar chemical properties and their atoms have the same number of outer-shell electrons. ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.