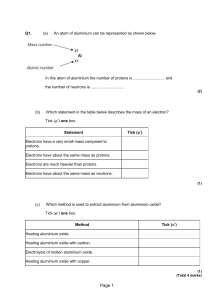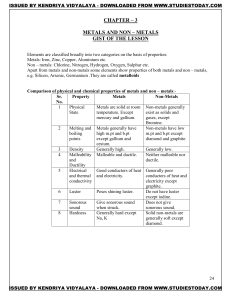
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... 2. Melting point and boiling point:have high M.P and B.P, as large amount of heat energy is required to break strong ionic attraction. 3. Solubility: soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and pertrol. 4. Conduction of electricity:ionic compounds in solid state-----does not conduct electricity. ...
... 2. Melting point and boiling point:have high M.P and B.P, as large amount of heat energy is required to break strong ionic attraction. 3. Solubility: soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and pertrol. 4. Conduction of electricity:ionic compounds in solid state-----does not conduct electricity. ...
Practice Exam #2 with Answers
... water bath at 99°C. The barometric pressure is 753 torr. If the mass of the liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
... water bath at 99°C. The barometric pressure is 753 torr. If the mass of the liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
Classwork – Nature, Properties, and Classification of Matter
... Classwork – Chemical Quantities (Stoichiometry) 1. Using sandwich making as an analogy to chemical reactions, show the balanced equation that requires 2 pieces of bread, 3 slices of meat and on slice of cheese to make 1 sandwich. 2. Using the ratios for the above process (reaction), show the balance ...
... Classwork – Chemical Quantities (Stoichiometry) 1. Using sandwich making as an analogy to chemical reactions, show the balanced equation that requires 2 pieces of bread, 3 slices of meat and on slice of cheese to make 1 sandwich. 2. Using the ratios for the above process (reaction), show the balance ...
chemistry 110 lecture
... Keys: 1. Know the physical states of the elements (g) (l) (s) (aq) 2. Know solubility rules 3. Balancing equations a) Count and compare the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. b) Balance each element individually by placing whole numbers in front of the chemical formula c) ...
... Keys: 1. Know the physical states of the elements (g) (l) (s) (aq) 2. Know solubility rules 3. Balancing equations a) Count and compare the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. b) Balance each element individually by placing whole numbers in front of the chemical formula c) ...
Midterm Review Date
... experiment” and the resulting model of the atom? A) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. B) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. C) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. D) An atom has hardly any e ...
... experiment” and the resulting model of the atom? A) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. B) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. C) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. D) An atom has hardly any e ...
Atomic number
... Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated into other substances. ...
... Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated into other substances. ...
Camp 1 - drjosephryan.com Home Page
... Five important types of redox reactions – combustion: burning in air. The products of complete ...
... Five important types of redox reactions – combustion: burning in air. The products of complete ...
CHEMISTRY
... Hopefully you realize the importance of knowing the many patterns that exist in the periodic table. Patterns help reduce the amount of things we need to memorize and also allow us to acquire information quickly. For example, knowing that an element is in group 2 tells us a lot about that element. We ...
... Hopefully you realize the importance of knowing the many patterns that exist in the periodic table. Patterns help reduce the amount of things we need to memorize and also allow us to acquire information quickly. For example, knowing that an element is in group 2 tells us a lot about that element. We ...
Learning Outcomes
... and copper atoms. These exceptions are due to special stability associated with all the d orbitals being half filled or completely filled. When transition metals form ions it is the s electrons which are lost first rather than the d electrons. ...
... and copper atoms. These exceptions are due to special stability associated with all the d orbitals being half filled or completely filled. When transition metals form ions it is the s electrons which are lost first rather than the d electrons. ...
CHEMISTRY 110 LECTURE
... e. How many moles of sodium sulfate are produced when 177 g of water is formed? ...
... e. How many moles of sodium sulfate are produced when 177 g of water is formed? ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... They are good conductors of heat and electricity. Examples include; iron (Fe), aluminum (Al), and sodium (Na). Metalloids- Appear alon the bolded line on the Periodic Table. They conduct electricity under some conditions. Examples include; boron (B) and silicon (Si). They are important to the semi ...
... They are good conductors of heat and electricity. Examples include; iron (Fe), aluminum (Al), and sodium (Na). Metalloids- Appear alon the bolded line on the Periodic Table. They conduct electricity under some conditions. Examples include; boron (B) and silicon (Si). They are important to the semi ...
Charge to mass ratio of electron
... Every set of magnet current, accelerating voltage and orbit radius provides an independent measurement of e/m. You should also estimate the uncertainties on your measurements of the directly measured quantities V, I, r, and a, and from these determine an uncertainty for every individual measurement ...
... Every set of magnet current, accelerating voltage and orbit radius provides an independent measurement of e/m. You should also estimate the uncertainties on your measurements of the directly measured quantities V, I, r, and a, and from these determine an uncertainty for every individual measurement ...
Microsoft Word
... Strong acids are HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI Weak acids include HF, CH3COOH, HCOOH, H2C2O4, H3PO4 ...
... Strong acids are HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI Weak acids include HF, CH3COOH, HCOOH, H2C2O4, H3PO4 ...
Document
... free to move about within the liquid or solution. Passing an electric current through ionic substances that are molten, for example lead bromide, or in solution breaks them down into elements. This process is called electrolysis and the substance that is broken down is called the electrolyte. During ...
... free to move about within the liquid or solution. Passing an electric current through ionic substances that are molten, for example lead bromide, or in solution breaks them down into elements. This process is called electrolysis and the substance that is broken down is called the electrolyte. During ...
Document
... Butyric acid (also known as butanoic acid, C4H8O2) is one of many compounds found in milk fat. First isolated from rancid butter in 1869, burtyic acid has received a great deal of attention in recent years as a potential anticancer agent. Write a balanced equation for the metabolism of butyric acid. ...
... Butyric acid (also known as butanoic acid, C4H8O2) is one of many compounds found in milk fat. First isolated from rancid butter in 1869, burtyic acid has received a great deal of attention in recent years as a potential anticancer agent. Write a balanced equation for the metabolism of butyric acid. ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents Exam
... 1. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms are bonded together. Breaking a chemical bond is an endothermic process. Forming a chemical bond is an exothermic process. Compounds have less potential energy than the individual atoms they are formed from. 2. Two major categories of compounds are i ...
... 1. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms are bonded together. Breaking a chemical bond is an endothermic process. Forming a chemical bond is an exothermic process. Compounds have less potential energy than the individual atoms they are formed from. 2. Two major categories of compounds are i ...
Need
... 1. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms are bonded together. Breaking a chemical bond is an endothermic process. Forming a chemical bond is an exothermic process. Compounds have less potential energy than the individual atoms they are formed from. 2. Two major categories of compounds are i ...
... 1. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms are bonded together. Breaking a chemical bond is an endothermic process. Forming a chemical bond is an exothermic process. Compounds have less potential energy than the individual atoms they are formed from. 2. Two major categories of compounds are i ...
Current Electricity Static Electricity The Laws of Electrical Charges
... moving a conducting wire through a magnetic field by moving it back and forth through the field, Faraday created the first electricityproducing generator, which could generate electrical current. Massive coils of wire rotating in huge generators can produce enough electricity to power an entire city ...
... moving a conducting wire through a magnetic field by moving it back and forth through the field, Faraday created the first electricityproducing generator, which could generate electrical current. Massive coils of wire rotating in huge generators can produce enough electricity to power an entire city ...
Day 72 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... • Chemical reactions result in chemical changes. – Chemical changes occur when new substances are created. – The original substance(s), called reactants, change into new substance(s) called products. ...
... • Chemical reactions result in chemical changes. – Chemical changes occur when new substances are created. – The original substance(s), called reactants, change into new substance(s) called products. ...
chemical reaction - MRS. STOTTS CHEMISTRY
... separates from the solution is known as a precipitate. 4. Color change ...
... separates from the solution is known as a precipitate. 4. Color change ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.