L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... 36. Heating potassium chloride makes it dissolve more. On a solubility graph its curve would be __upsweeping It would make a solution colder when it dissolves because it has a net endothermic dissolving process. 37. What is the molality of a solution containing 1.70g of sodium nitrate in 162.6 g of ...
... 36. Heating potassium chloride makes it dissolve more. On a solubility graph its curve would be __upsweeping It would make a solution colder when it dissolves because it has a net endothermic dissolving process. 37. What is the molality of a solution containing 1.70g of sodium nitrate in 162.6 g of ...
Metacognitive Chart_Chapter 33
... 3) Electric potential is electric potential energy per _________________. 4) Lines further apart mean ________________ fields. 5) Electric field lines are drawn away from _________________ charges. 6) Doing work to move a charge will give it _____________ _______________ energy 7) We represent force ...
... 3) Electric potential is electric potential energy per _________________. 4) Lines further apart mean ________________ fields. 5) Electric field lines are drawn away from _________________ charges. 6) Doing work to move a charge will give it _____________ _______________ energy 7) We represent force ...
Section 8.1 - CPO Science
... matter has zero (total) charge, most matter acts as if there is no electric charge at all. • A tiny imbalance in either positive or negative charge is the cause of static electricity. ...
... matter has zero (total) charge, most matter acts as if there is no electric charge at all. • A tiny imbalance in either positive or negative charge is the cause of static electricity. ...
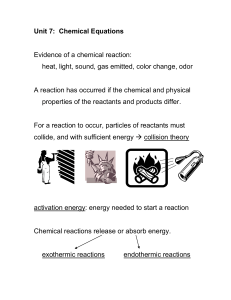
Chemical Equations
... A representation of a substance in which the elements are represented by their symbols and subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element ...
... A representation of a substance in which the elements are represented by their symbols and subscripts represent the number of atoms of each element ...
Chapter 2
... partial charges The atoms are not ions, the partial charges result from the atoms being polar covalently bonded to some other atom. weak bonds, but very important in living systems ...
... partial charges The atoms are not ions, the partial charges result from the atoms being polar covalently bonded to some other atom. weak bonds, but very important in living systems ...
CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm and 34 oC, what is its temperature at 6.11 atm and 235 L? 20. If 12.2 m ...
... 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm and 34 oC, what is its temperature at 6.11 atm and 235 L? 20. If 12.2 m ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Exam Review Chemical Bonds Give
... 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm and 34 oC, what is its temperature at 6.11 atm and 235 L? 20. If 12.2 m ...
... 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm and 34 oC, what is its temperature at 6.11 atm and 235 L? 20. If 12.2 m ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm and 34 oC, what is its temperature at 6.11 atm and 235 L? 20. If 12.2 m ...
... 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm and 34 oC, what is its temperature at 6.11 atm and 235 L? 20. If 12.2 m ...
Old EXAM I - gozips.uakron.edu
... The system must be closed if it contains gaseous products. The forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate. The ratio of products to reactants is constant. ...
... The system must be closed if it contains gaseous products. The forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate. The ratio of products to reactants is constant. ...
Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
... Ionic Charge: when neutral atoms collide, a negative electron is transferred from one atom to another, and both atoms become particles called ions, which have an electrical charge. If an atom has lost electrons the overall charge becomes positive and if it gains electrons the overall charge is negat ...
... Ionic Charge: when neutral atoms collide, a negative electron is transferred from one atom to another, and both atoms become particles called ions, which have an electrical charge. If an atom has lost electrons the overall charge becomes positive and if it gains electrons the overall charge is negat ...
1. Review (MC problems, due Monday) 2. - mvhs
... c) Hybridization: NO2+ is sp, NO2¯ is sp2 also. 2. a. Sucrose: Non conductor because it is a molecular compound. No ions to conduct electricity. Silver Nitrate solution contains Ag+ ions and NO3- ions (ionic compound), ions conduct electricity. b. Solid silver nitrate- Non conductor, ions not free t ...
... c) Hybridization: NO2+ is sp, NO2¯ is sp2 also. 2. a. Sucrose: Non conductor because it is a molecular compound. No ions to conduct electricity. Silver Nitrate solution contains Ag+ ions and NO3- ions (ionic compound), ions conduct electricity. b. Solid silver nitrate- Non conductor, ions not free t ...
Final Exam Review Guide
... ________ 1. Ionic bonds are formed between metals and non-metals ________ 2. Covalent bonds are formed between non-metals and other non-metals. ________ 3. Metals do not form bonds with other metals ________ 4. The transition metals lose electrons to form ions. ________ 5. When comparing degree of p ...
... ________ 1. Ionic bonds are formed between metals and non-metals ________ 2. Covalent bonds are formed between non-metals and other non-metals. ________ 3. Metals do not form bonds with other metals ________ 4. The transition metals lose electrons to form ions. ________ 5. When comparing degree of p ...
ACS Practice Test 1
... 52. The electrical conductance of a solution of Ba(OH)2 slowly decreases upon the addition of H2SO4 to a minimum, and then slowly increases. The best theoretical explanation of this is (A)The Ba(OH)2 solution becomes more dilute since its volume is increased by adding the H2SO4 ...
... 52. The electrical conductance of a solution of Ba(OH)2 slowly decreases upon the addition of H2SO4 to a minimum, and then slowly increases. The best theoretical explanation of this is (A)The Ba(OH)2 solution becomes more dilute since its volume is increased by adding the H2SO4 ...
chemeqohnotes18f2005
... Examples: enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions catalytic converters convert CO into CO2 ...
... Examples: enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions catalytic converters convert CO into CO2 ...
Chapter 19 General Science Electricity and Magnetism 19
... _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ * Thin ...
... _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ * Thin ...
Question Bank Topic 5
... 19.1: Reactions in simple chemical cells 19.2: Simple chemical cells made from different metal couples 19.3: The electrochemical series of metals 19.4: Improving simple chemical cells 19.5: The role of a salt bridge 19.6: The Daniell cell (CDC guide: Simple chemical cells: (a) consisting of two meta ...
... 19.1: Reactions in simple chemical cells 19.2: Simple chemical cells made from different metal couples 19.3: The electrochemical series of metals 19.4: Improving simple chemical cells 19.5: The role of a salt bridge 19.6: The Daniell cell (CDC guide: Simple chemical cells: (a) consisting of two meta ...
Power point types of chemical rxn
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=98JuJ-G1qXY&feature=related See page 264 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=98JuJ-G1qXY&feature=related See page 264 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
Covalent Bonds - WordPress.com
... • An ionic bond is an attracted between ions of opposite charge in an ionic compound • An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine • When sodium and chlorine interection with together.what’ll happen? • After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have charges • A charged atom ...
... • An ionic bond is an attracted between ions of opposite charge in an ionic compound • An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine • When sodium and chlorine interection with together.what’ll happen? • After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have charges • A charged atom ...
Discussion 8
... Both diagrams and graphs are used in chemistry to help represent physical phenomena. The most common graphs show the relationship of two variables, such as distance and time, or frequency and wavelength. Diagrams, however, are a bit tricker. Diagrams can come in a number of different structures and ...
... Both diagrams and graphs are used in chemistry to help represent physical phenomena. The most common graphs show the relationship of two variables, such as distance and time, or frequency and wavelength. Diagrams, however, are a bit tricker. Diagrams can come in a number of different structures and ...
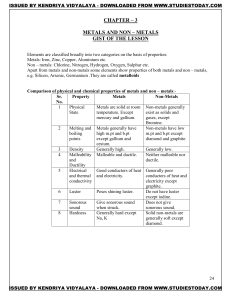
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... 2. Melting point and boiling point:have high M.P and B.P, as large amount of heat energy is required to break strong ionic attraction. 3. Solubility: soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and pertrol. 4. Conduction of electricity:ionic compounds in solid state-----does not conduct electricity. ...
... 2. Melting point and boiling point:have high M.P and B.P, as large amount of heat energy is required to break strong ionic attraction. 3. Solubility: soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and pertrol. 4. Conduction of electricity:ionic compounds in solid state-----does not conduct electricity. ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.