Chapter 2
... Octet rule: Except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their outermost energy level (valence shell) ...
... Octet rule: Except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their outermost energy level (valence shell) ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... A) Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) 2Ag (s) + Cu(NO3 )2 (aq) B) HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → H 2 O (l) + NaCl (aq) C) AgNO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) AgCl (s) + HNO3 (aq) D) Ba(C2 H3O2 )2 (aq) + Na 2SO4 (aq) BaSO4 (s) + 2NaC2 H3O2 (aq) E) H2 CO3 (aq) + Ca(NO3 )2 (aq) 2HNO3 (aq) + CaCO3 (s) 49) Which one of the followin ...
... A) Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) 2Ag (s) + Cu(NO3 )2 (aq) B) HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → H 2 O (l) + NaCl (aq) C) AgNO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) AgCl (s) + HNO3 (aq) D) Ba(C2 H3O2 )2 (aq) + Na 2SO4 (aq) BaSO4 (s) + 2NaC2 H3O2 (aq) E) H2 CO3 (aq) + Ca(NO3 )2 (aq) 2HNO3 (aq) + CaCO3 (s) 49) Which one of the followin ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Revision Themes
... Sodium chloride dissolves to give a colourless solution. Similarly with magnesium chloride. Aluminium chloride also dissolves but is then hydrolysed to give a cloudy, white, solution. The cloudyness is due to insoluble aluminium hydroxide. Silicon, phosphorus and sulphur chlorides are highly reactiv ...
... Sodium chloride dissolves to give a colourless solution. Similarly with magnesium chloride. Aluminium chloride also dissolves but is then hydrolysed to give a cloudy, white, solution. The cloudyness is due to insoluble aluminium hydroxide. Silicon, phosphorus and sulphur chlorides are highly reactiv ...
Chemistr.e1a.chapter.4.new2015
... • The following reaction that you have seen before in class and the laboratory is neither a precipitation reaction nor an acid-base reaction. Cu (s) + ½ O2 (g) " CuO (s) The reaction above is one where electrons are transferred from one element to another during the reaction. This kind of reaction i ...
... • The following reaction that you have seen before in class and the laboratory is neither a precipitation reaction nor an acid-base reaction. Cu (s) + ½ O2 (g) " CuO (s) The reaction above is one where electrons are transferred from one element to another during the reaction. This kind of reaction i ...
File
... 10. Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following molecules or ions. 2pt each a. H2S b. SO2 c. PO3-3 ...
... 10. Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following molecules or ions. 2pt each a. H2S b. SO2 c. PO3-3 ...
Chemical Reactions
... Bellringer, tell me what type of reaction is shown in each problem.Also, take 1 of the ten and work it out completely. ...
... Bellringer, tell me what type of reaction is shown in each problem.Also, take 1 of the ten and work it out completely. ...
chemical reaction
... • Before a reaction can start, molecules of the reactants have to bump into each other, or collide. • The collision must be strong enough. • This means the reactants must smash into each other with a certain amount of energy. • To start any chemical reaction, a minimum amount of energy is needed. • ...
... • Before a reaction can start, molecules of the reactants have to bump into each other, or collide. • The collision must be strong enough. • This means the reactants must smash into each other with a certain amount of energy. • To start any chemical reaction, a minimum amount of energy is needed. • ...
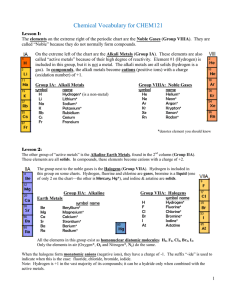
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not ...
... Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not ...
Net ionic equation
... • In the above rxn, Mg(s) loses e-, H+ gains e• Oxidized: atom, molecule, or ion becomes more positively charged. • Reduced: atom, molecule, or ion becomes less positively charged. ...
... • In the above rxn, Mg(s) loses e-, H+ gains e• Oxidized: atom, molecule, or ion becomes more positively charged. • Reduced: atom, molecule, or ion becomes less positively charged. ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... Compare/contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions. Include the following: definition, sign of ΔH, temperature change, where heat is written in a chemical equation, enthalpy of products and reactants, reaction pathway diagram. What is the universe? System? Surroundings? What is entropy? How can y ...
... Compare/contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions. Include the following: definition, sign of ΔH, temperature change, where heat is written in a chemical equation, enthalpy of products and reactants, reaction pathway diagram. What is the universe? System? Surroundings? What is entropy? How can y ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... Ductile: can be pulled out into a long wire Conductivity: ability to transfer heat from one object to another ...
... Ductile: can be pulled out into a long wire Conductivity: ability to transfer heat from one object to another ...
Unit 7: Reduction, Oxidation and Electrochemistry
... - in another words, Reducing Species = Oxidizing Agent (GER-OA) Reducing Agent: - a chemical species that Donates (Lose) Electrons from a Reduced species. - it helps another species to reduce but itself being oxidized (lost electrons or increased in oxidation number). - in another words, Oxidizing S ...
... - in another words, Reducing Species = Oxidizing Agent (GER-OA) Reducing Agent: - a chemical species that Donates (Lose) Electrons from a Reduced species. - it helps another species to reduce but itself being oxidized (lost electrons or increased in oxidation number). - in another words, Oxidizing S ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
General Chemistry Questions
... Reaction (2) is the formation reaction for H2O(l). The reverse of reaction (2) is endothermic. The energy content of H2O(g) is lower than H2O(l). ΔH for the reaction: H2O(l) → H2O(g) is + 44 kJ/mol. ...
... Reaction (2) is the formation reaction for H2O(l). The reverse of reaction (2) is endothermic. The energy content of H2O(g) is lower than H2O(l). ΔH for the reaction: H2O(l) → H2O(g) is + 44 kJ/mol. ...
03. The Theoretic bases of bioenergetics
... 1. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules. Inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity; If a competing molecule blocks the active site or changes its shape, the enzyme's activity is inhibited. If the enzyme's configuration is destroyed (denaturated), its activity is lost. ...
... 1. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules. Inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity; If a competing molecule blocks the active site or changes its shape, the enzyme's activity is inhibited. If the enzyme's configuration is destroyed (denaturated), its activity is lost. ...
Conservation of Energy in chemical reactions, Hess`s Law
... What kind of change is occurring this time, and what elements are involved? What is the critical difference? What would H be in the second reaction? _____ Why does this make sense? ...
... What kind of change is occurring this time, and what elements are involved? What is the critical difference? What would H be in the second reaction? _____ Why does this make sense? ...
1. The compound which could act both as oxidising as well as
... A mixture of Na2C2O4 (A) and KHC2O4 . H2C2O4 (B) required equal volumes of 0.1 M KMnO4 and 0.1 M NaOH, separately. Molar ratio of A and B in this mixture is (a) 1 : 1 (b) 1 : 5.5 (c) 5.5 : 1 (d) 3.1 : 1 3 mole of a mixture of FeSO4 and Fe2(SO4)3 required 100 ml. of 2 M KMnO4 solution in acidic mediu ...
... A mixture of Na2C2O4 (A) and KHC2O4 . H2C2O4 (B) required equal volumes of 0.1 M KMnO4 and 0.1 M NaOH, separately. Molar ratio of A and B in this mixture is (a) 1 : 1 (b) 1 : 5.5 (c) 5.5 : 1 (d) 3.1 : 1 3 mole of a mixture of FeSO4 and Fe2(SO4)3 required 100 ml. of 2 M KMnO4 solution in acidic mediu ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
Chapter 4
... How much of a substance will dissolve in a given amount of water. Usually g/100 mL Varies greatly, but if they do dissolve the ions are separated, and they can move around. Water can also dissolve non-ionic compounds if they have polar bonds. ...
... How much of a substance will dissolve in a given amount of water. Usually g/100 mL Varies greatly, but if they do dissolve the ions are separated, and they can move around. Water can also dissolve non-ionic compounds if they have polar bonds. ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter5
... are not the amounts that would be produced if the reactions were actually done in the laboratory. • In each case, less product would be obtained than was calculated. There are numerous causes. Some materials are lost during transfers from one container to another and side reactions take place that a ...
... are not the amounts that would be produced if the reactions were actually done in the laboratory. • In each case, less product would be obtained than was calculated. There are numerous causes. Some materials are lost during transfers from one container to another and side reactions take place that a ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.