Topic 3 Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Bonding and
... 2) dissociate chlorine molecules 3) ionize the sodium 4) form ions from the chlorine atoms 5) bring the ions together to form solid NaCl ...
... 2) dissociate chlorine molecules 3) ionize the sodium 4) form ions from the chlorine atoms 5) bring the ions together to form solid NaCl ...
CHEM 30
... - assigning oxidation states to elements in compounds and equations; - balancing redox equations using oxidation states; - recognizing oxidized, reduced species, oxidizing agents and reducing agents; - predicting spontaneity of reactions and E0 values for redox reactions - understanding how an elect ...
... - assigning oxidation states to elements in compounds and equations; - balancing redox equations using oxidation states; - recognizing oxidized, reduced species, oxidizing agents and reducing agents; - predicting spontaneity of reactions and E0 values for redox reactions - understanding how an elect ...
AQA Additional Sci C2 Revision Guide
... Atoms joined by covalent bonds can also form giant structures or macromolecules. Diamond and graphite (forms of carbon) and silicon dioxide (silica) are examples of giant covalent structures (lattices) of atoms. All of the atoms in these structures are linked to other atoms by strong covalent bonds ...
... Atoms joined by covalent bonds can also form giant structures or macromolecules. Diamond and graphite (forms of carbon) and silicon dioxide (silica) are examples of giant covalent structures (lattices) of atoms. All of the atoms in these structures are linked to other atoms by strong covalent bonds ...
First, there are several issues regarding this course need to be
... ∆solvGө(Br-, aq) - ∆solvGө (Cl-, aq) = - (1/196 – 1/181)*6.86*104 kJ mol-1 = 29.00 kJ mol-1 (The calculated result is slightly larger than the experimental value). Quite often, we do not have to go through the above process in order to know the standard Gibbs energy of formation or standard reaction ...
... ∆solvGө(Br-, aq) - ∆solvGө (Cl-, aq) = - (1/196 – 1/181)*6.86*104 kJ mol-1 = 29.00 kJ mol-1 (The calculated result is slightly larger than the experimental value). Quite often, we do not have to go through the above process in order to know the standard Gibbs energy of formation or standard reaction ...
Final exam questions for Chemical Engineer BSc
... 15. Thermodynamic properties of ions in solution: Standard functions of formation of ions. Activity of ions in solution. Mean activity coefficients. The Debey–Hückel limiting law. Ionic strength of solutions. Solubility equilibria and solubility constant of salts. 16. Equilibrium electrochemistry: E ...
... 15. Thermodynamic properties of ions in solution: Standard functions of formation of ions. Activity of ions in solution. Mean activity coefficients. The Debey–Hückel limiting law. Ionic strength of solutions. Solubility equilibria and solubility constant of salts. 16. Equilibrium electrochemistry: E ...
Kémiai technológia I
... 15. Thermodynamic properties of ions in solution: Standard functions of formation of ions. Activity of ions in solution. Mean activity coefficients. The Debey–Hückel limiting law. Ionic strength of solutions. Solubility equilibria and solubility constant of salts. 16. Equilibrium electrochemistry: E ...
... 15. Thermodynamic properties of ions in solution: Standard functions of formation of ions. Activity of ions in solution. Mean activity coefficients. The Debey–Hückel limiting law. Ionic strength of solutions. Solubility equilibria and solubility constant of salts. 16. Equilibrium electrochemistry: E ...
File
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
Document
... together as one ion. • When molecular compounds dissolve in water, the only ones that can form ions in solution are acids and bases. The rest will just dissolve as the complete molecule (if that molecule is soluble in water) ...
... together as one ion. • When molecular compounds dissolve in water, the only ones that can form ions in solution are acids and bases. The rest will just dissolve as the complete molecule (if that molecule is soluble in water) ...
Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... compounds, acids and bases on the basis of their properties; i.e., conductivity, pH, solubility, state • predict whether an ionic compound is relatively soluble in water, using a solubility chart • relate the molecular structure of simple substances to their properties (e.g., describe how the proper ...
... compounds, acids and bases on the basis of their properties; i.e., conductivity, pH, solubility, state • predict whether an ionic compound is relatively soluble in water, using a solubility chart • relate the molecular structure of simple substances to their properties (e.g., describe how the proper ...
Unit 3 Revision Notes 213.00KB 2017-03-01 18
... 2) Scum is formed with soap. 3) Lime scale forms in kettles, pipes etc. Hard water contains Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions in solution. These ions react with soap to form ...
... 2) Scum is formed with soap. 3) Lime scale forms in kettles, pipes etc. Hard water contains Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions in solution. These ions react with soap to form ...
File
... 6 = hex 3 = prop 7 = hept 4 = but 8 = oct Suffix is determined by the type of bond Alkane CnH2n+2 (all bonds are single) Alkene CnH2n (one bond is a double) Alkyne CnH2n-2 (one bond is a triple) ...
... 6 = hex 3 = prop 7 = hept 4 = but 8 = oct Suffix is determined by the type of bond Alkane CnH2n+2 (all bonds are single) Alkene CnH2n (one bond is a double) Alkyne CnH2n-2 (one bond is a triple) ...
What is Weathering
... A. Describe three kinds of chemical reactions. B. In the chemical reaction described on page 379, magnesium reacts with oxygen gas. What kind of chemical reaction is this? Explain. C. How can chemical properties be used to separate substances in a mixture or compound? D. A water molecule is made up ...
... A. Describe three kinds of chemical reactions. B. In the chemical reaction described on page 379, magnesium reacts with oxygen gas. What kind of chemical reaction is this? Explain. C. How can chemical properties be used to separate substances in a mixture or compound? D. A water molecule is made up ...
Slide 1
... charge Q is given by the equation on the right. 1. The zero potential is taken at (a) the center of the sphere (b) the surface of the sphere (c) infinite distance from the sphere +Q ...
... charge Q is given by the equation on the right. 1. The zero potential is taken at (a) the center of the sphere (b) the surface of the sphere (c) infinite distance from the sphere +Q ...
chemical reactions
... gauze covering the beaker. Use a document camera, or similar, to project the reaction on a screen. Repeat this using small pieces of Na and K. When cutting Li, Na and K from a larger piece, do that under the document camera to show the silvery surface of the metal. Add one or two drops of phenolphth ...
... gauze covering the beaker. Use a document camera, or similar, to project the reaction on a screen. Repeat this using small pieces of Na and K. When cutting Li, Na and K from a larger piece, do that under the document camera to show the silvery surface of the metal. Add one or two drops of phenolphth ...
Sample Questions
... 3. The average mass of a carbon atom is 12.011. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon unit, the chances that you would randomly get one with a mass of 12.011 is 4. Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the bod ...
... 3. The average mass of a carbon atom is 12.011. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon unit, the chances that you would randomly get one with a mass of 12.011 is 4. Iron is biologically important in the transport of oxygen by red blood cells from the lungs to the various organs of the bod ...
elements of chemistry unit
... One type of chemical reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one species (species means atoms or groups of atoms) to another. These reactions are called oxidation reduction reactions. The species that loses electrons is oxidized and the species gaining electrons is reduced. Oxidation reduct ...
... One type of chemical reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one species (species means atoms or groups of atoms) to another. These reactions are called oxidation reduction reactions. The species that loses electrons is oxidized and the species gaining electrons is reduced. Oxidation reduct ...
Unit 3 - Salina USD 305
... Each player selects a game piece. Play begins with the student with the longest name. The student rolls a cation dice and an anion dice. Based on what the dice land on, the student will say the formula and the name for the compound. It is up to the other members of the group to determine if the name ...
... Each player selects a game piece. Play begins with the student with the longest name. The student rolls a cation dice and an anion dice. Based on what the dice land on, the student will say the formula and the name for the compound. It is up to the other members of the group to determine if the name ...
doc
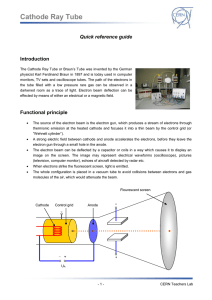
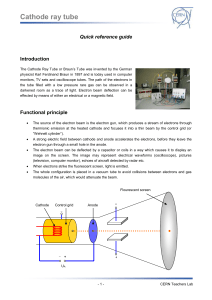
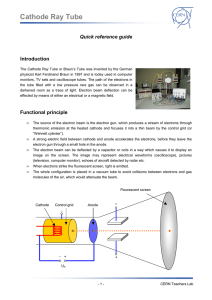
... Cathode Ray Tube 9. Magnetic deflection of the electron beam can be demonstrated by approaching the pole of a bar magnet to the cathode ray tube. We can provide magnetic field to the tube by using another power supply. The tension that this device provides is DC, so the deflection caused to the lig ...
... Cathode Ray Tube 9. Magnetic deflection of the electron beam can be demonstrated by approaching the pole of a bar magnet to the cathode ray tube. We can provide magnetic field to the tube by using another power supply. The tension that this device provides is DC, so the deflection caused to the lig ...
chem eng-problems
... 4) Write the net ionic equation for the precipitation reaction that may occur when solutions of calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 and sodium acetate (CH3COONa) are mixed. Write the balanced molecular equation, Check the solubility of products and determine the spectator ions ...
... 4) Write the net ionic equation for the precipitation reaction that may occur when solutions of calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 and sodium acetate (CH3COONa) are mixed. Write the balanced molecular equation, Check the solubility of products and determine the spectator ions ...
cathode-ray-tube-qrg
... The Cathode Ray Tube or Braun’s Tube was invented by the German physicist Karl Ferdinand Braun in 1897 and is today used in computer monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of li ...
... The Cathode Ray Tube or Braun’s Tube was invented by the German physicist Karl Ferdinand Braun in 1897 and is today used in computer monitors, TV sets and oscilloscope tubes. The path of the electrons in the tube filled with a low pressure rare gas can be observed in a darkened room as a trace of li ...
1 In which way is the electric force similar to the gravitational force
... 5 A negatively charged object is brought close to the surface of a conductor, whose opposite side is then grounded. What is this process of charging called? A Charging by contact B Charging by induction C Charging by conduction D Charging by polarization ...
... 5 A negatively charged object is brought close to the surface of a conductor, whose opposite side is then grounded. What is this process of charging called? A Charging by contact B Charging by induction C Charging by conduction D Charging by polarization ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.