Abstract
... changing isotope ratios, because heavier isotopes are more difficult to move than lighter ones. Such isotope changes are called mass-dependent fractionation. The large isotope fractionation takes place between two isotopes with a large mass difference. In the case of oxygen, the fractionation in (18 ...
... changing isotope ratios, because heavier isotopes are more difficult to move than lighter ones. Such isotope changes are called mass-dependent fractionation. The large isotope fractionation takes place between two isotopes with a large mass difference. In the case of oxygen, the fractionation in (18 ...
NOMENCLATURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS CHEMISTRY 1411
... Iron is a transition metal ion with an oxidation number of +3. Each chloride has a charge of -1 and there are three chlorides to balnce the overall positive charge of +3. ...
... Iron is a transition metal ion with an oxidation number of +3. Each chloride has a charge of -1 and there are three chlorides to balnce the overall positive charge of +3. ...
Smith Reaction- HW PSI Chemistry
... A) The ways in which atoms are joined together are changed. B) New atoms are formed as products. C) The starting materials are named reactants. D) The bonds of the reactants are broken and new bonds of the products are formed. E) In a word equation representing a chemical reaction, the reactants are ...
... A) The ways in which atoms are joined together are changed. B) New atoms are formed as products. C) The starting materials are named reactants. D) The bonds of the reactants are broken and new bonds of the products are formed. E) In a word equation representing a chemical reaction, the reactants are ...
Slide 1
... a battery of very high voltage V in series with a very large resistance R. Such approximation would supply a current V/R into any load that has a resistance much smaller than R. ...
... a battery of very high voltage V in series with a very large resistance R. Such approximation would supply a current V/R into any load that has a resistance much smaller than R. ...
Matter Key
... Gas – does not have definite volume or definite shape; takes shape of container; not packed at all ...
... Gas – does not have definite volume or definite shape; takes shape of container; not packed at all ...
chemical reaction
... does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tarnishing, rusting, baking ...
... does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tarnishing, rusting, baking ...
Mega avolts and Kil loamps s – The Life of fa Bolt t of
... are equal quantities of the two charges then the object is electrically neutral. Small irregularities in this distribution can lead to the movement of charges because similar charges repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. If a positively charged object approaches another obje ...
... are equal quantities of the two charges then the object is electrically neutral. Small irregularities in this distribution can lead to the movement of charges because similar charges repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. If a positively charged object approaches another obje ...
Semester 1 Final Exam
... (A) 27 protons, 30 neutrons, 24 electrons (B) 27 protons, 30 neutrons, 30 electrons (C) 27 protons, 57 neutrons, 3 electrons (D) 30 protons, 27 neutrons, 3 electrons 13. All of the following describe a neutron EXCEPT: (A) It determines the identity of the atom. (B) It does not carry a charge. (C) It ...
... (A) 27 protons, 30 neutrons, 24 electrons (B) 27 protons, 30 neutrons, 30 electrons (C) 27 protons, 57 neutrons, 3 electrons (D) 30 protons, 27 neutrons, 3 electrons 13. All of the following describe a neutron EXCEPT: (A) It determines the identity of the atom. (B) It does not carry a charge. (C) It ...
oxidationnumbers
... DETERMINING OXIDATION NUMBERS (from Dr. Raynor) If the compound is ionic, first separate it into its component ions. Treat each of the component ions separately, using the rules given below, to assign oxidation numbers to each of the elements in each ion. [Note: the oxidation number is for each indi ...
... DETERMINING OXIDATION NUMBERS (from Dr. Raynor) If the compound is ionic, first separate it into its component ions. Treat each of the component ions separately, using the rules given below, to assign oxidation numbers to each of the elements in each ion. [Note: the oxidation number is for each indi ...
Ch 7: Reactions
... Oxidation Reaction: H2 → 2H+ + 2eSubstance reduced: Fluorine Reduction Reaction: F2 + 2e- → 2F• ****A lot of reactions are redox and another type of reaction from the above list. ...
... Oxidation Reaction: H2 → 2H+ + 2eSubstance reduced: Fluorine Reduction Reaction: F2 + 2e- → 2F• ****A lot of reactions are redox and another type of reaction from the above list. ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... Part I of this test is designed to be taken with a Scantron® answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. Only this Scantron sheet is graded for a score on Part I. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the Scantron sheet should be made available to the student only during the exam ...
... Part I of this test is designed to be taken with a Scantron® answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. Only this Scantron sheet is graded for a score on Part I. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the Scantron sheet should be made available to the student only during the exam ...
Cosmetology Learning Module 12
... Physical and Chemical Changes Physical Change A change in the form or physical properties of a substance without the formation of a new substance No chemical reaction involved No new chemicals are formed Solid ice changes into water Temporary hair color changes the appearance of hair by ...
... Physical and Chemical Changes Physical Change A change in the form or physical properties of a substance without the formation of a new substance No chemical reaction involved No new chemicals are formed Solid ice changes into water Temporary hair color changes the appearance of hair by ...
Chapter 7 Lecture
... Molecular, Complete Ionic, and Net Ionic Equations A molecular equation is a chemical equation showing the complete, neutral formulas for every compound in a reaction. A complete ionic equation is a chemical equation showing all of the species as they are actually present in solution. A net ionic e ...
... Molecular, Complete Ionic, and Net Ionic Equations A molecular equation is a chemical equation showing the complete, neutral formulas for every compound in a reaction. A complete ionic equation is a chemical equation showing all of the species as they are actually present in solution. A net ionic e ...
Final Exam Study Guide Word document
... Chapter 8 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity Learning Objectives: Students should be able to: 30. What element has the electron configuration 1s22s22p5? 31. If an atom’s electron configuration ends in s1 the element is a(n) ___________. ...
... Chapter 8 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity Learning Objectives: Students should be able to: 30. What element has the electron configuration 1s22s22p5? 31. If an atom’s electron configuration ends in s1 the element is a(n) ___________. ...
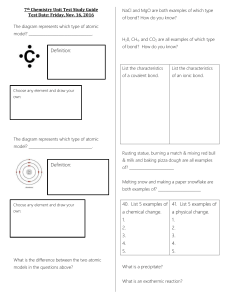
chemical reaction?
... • What is an exothermic reaction? – A chemical reaction in which energy is released to the surroundings – Exothermic reactions often feel __________ because energy is released as heat – An example of an exothermic reaction is _______________ ...
... • What is an exothermic reaction? – A chemical reaction in which energy is released to the surroundings – Exothermic reactions often feel __________ because energy is released as heat – An example of an exothermic reaction is _______________ ...
Bonding Notes
... MgCl2 tells you that these salt crystals have 1 magnesium ion for each two chloride ions In general, for any pair of positive and negative ions there is only one ratio and, thus, one formula that results in overall electrical neutrality. ...
... MgCl2 tells you that these salt crystals have 1 magnesium ion for each two chloride ions In general, for any pair of positive and negative ions there is only one ratio and, thus, one formula that results in overall electrical neutrality. ...
2 - mrstorie
... c. Nitric acid and magnesium hydroxide 10. A solution was made by dissolving 28.5 g of KOH in 0.50 L of water. If 0.250 L of this solution was titrated with 0.136 L of H2SO4, what is the molarity of the acid? 0.938 M ...
... c. Nitric acid and magnesium hydroxide 10. A solution was made by dissolving 28.5 g of KOH in 0.50 L of water. If 0.250 L of this solution was titrated with 0.136 L of H2SO4, what is the molarity of the acid? 0.938 M ...
AP Chem Equations - Speedway High School
... Phosphorus halides react with water to produce an acid of phosphorus (phosphorous acid or phosphoric acid) and a hydrohalic acid. The oxidation number of the phosphorus remains the same in both ...
... Phosphorus halides react with water to produce an acid of phosphorus (phosphorous acid or phosphoric acid) and a hydrohalic acid. The oxidation number of the phosphorus remains the same in both ...
WRITING AP EQUATIONS AP equation sets are found in the free
... Phosphorus halides react with water to produce an acid of phosphorus (phosphorous acid or phosphoric acid) and a hydrohalic acid. The oxidation number of the phosphorus remains the same in both ...
... Phosphorus halides react with water to produce an acid of phosphorus (phosphorous acid or phosphoric acid) and a hydrohalic acid. The oxidation number of the phosphorus remains the same in both ...
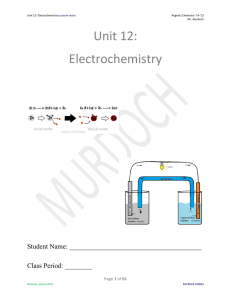
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.