Chemical Equations PowerPoint
... 1. Chemical reaction = process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) ...
... 1. Chemical reaction = process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances (atoms are rearranged) ...
4-Physical Chemistry of SW-Equilibrium-ion
... The effective concentration of a solute is called its activity (ai) and this is not necessarily equal to its molal concentration (it is usually lower). The activity of an ion (ai) is equal to its molality (mi) times an activity coefficient (i), which is the fraction of the ion that is available to ...
... The effective concentration of a solute is called its activity (ai) and this is not necessarily equal to its molal concentration (it is usually lower). The activity of an ion (ai) is equal to its molality (mi) times an activity coefficient (i), which is the fraction of the ion that is available to ...
WEEK 3
... compounds, we expressed the end result of a chemical change called SYNTHESIS. For example combine copper with oxygen to form copper (II) oxide. Cu0 + O20 Cu+2O-2 This is a synthesis reaction. Notice that the net charge equals zero. The zeroes on the left hand side of the equation indicate that neutr ...
... compounds, we expressed the end result of a chemical change called SYNTHESIS. For example combine copper with oxygen to form copper (II) oxide. Cu0 + O20 Cu+2O-2 This is a synthesis reaction. Notice that the net charge equals zero. The zeroes on the left hand side of the equation indicate that neutr ...
Specification
... manner, the size of an object can be described in terms of its ‘length in metres’, rather than its ‘number of metres’. Graph Axes and Table Headings Labelled as: quantity / unit, e.g. c / mol L–1. Only values will then be written on the axes or in a table. ...
... manner, the size of an object can be described in terms of its ‘length in metres’, rather than its ‘number of metres’. Graph Axes and Table Headings Labelled as: quantity / unit, e.g. c / mol L–1. Only values will then be written on the axes or in a table. ...
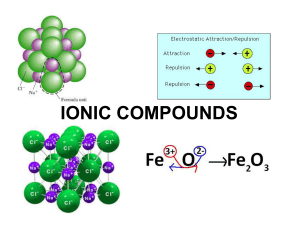
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... • Ionic compounds generally have high melting points and boiling points. ...
... • Ionic compounds generally have high melting points and boiling points. ...
AP Review to Share - Wappingers Central School District
... Exceptions: Oxygen in peroxides is -1 Ex. H2O2 Na2O2 Then, assign hydrogen. The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, but may be –1 when combined with a metal. For example: H in hydrides is -1 Ex. NaH For compounds in which both atoms cannot have the oxidation number which is equal to the char ...
... Exceptions: Oxygen in peroxides is -1 Ex. H2O2 Na2O2 Then, assign hydrogen. The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, but may be –1 when combined with a metal. For example: H in hydrides is -1 Ex. NaH For compounds in which both atoms cannot have the oxidation number which is equal to the char ...
Does electrical double layer formation lead to salt exclusion or to
... to be the case. On the other hand, colloidal particles in aqueous electrolyte solutions acquire their surface charge by preferential uptake of certain ionic species, say H+ and OH− ions for oxidic materials. Such interfaces are continually in adsorption-desorption equilibrium with the solution. We d ...
... to be the case. On the other hand, colloidal particles in aqueous electrolyte solutions acquire their surface charge by preferential uptake of certain ionic species, say H+ and OH− ions for oxidic materials. Such interfaces are continually in adsorption-desorption equilibrium with the solution. We d ...
Read bulletin here
... The universal requirement is water – where there is water, there are bacteria. This is why it is so important to understand the role bacteria play in oil and gas applications that involve water. ...
... The universal requirement is water – where there is water, there are bacteria. This is why it is so important to understand the role bacteria play in oil and gas applications that involve water. ...
Reactions
... Examples of replacement reactions: 1. Replacement of a metal in a compound by a more active metal. Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) ----> FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) 2. Replacement of hydrogen in water by an active metal. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ----> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) Mg(s) + H2O(g) ----> MgO(s) + H2(g) 3. Replacement of hydrogen ...
... Examples of replacement reactions: 1. Replacement of a metal in a compound by a more active metal. Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) ----> FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) 2. Replacement of hydrogen in water by an active metal. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ----> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) Mg(s) + H2O(g) ----> MgO(s) + H2(g) 3. Replacement of hydrogen ...
Document
... and the individual vapor pressure for each component is Pi = (Pi)pure ・ Xi where ((Pi)pure is the vapor pressure of the pure component, Xi is the mole fraction of the component in solution Boiling-point elevation is a colligative property (the properties of dilute solutions of non-volatiles solute w ...
... and the individual vapor pressure for each component is Pi = (Pi)pure ・ Xi where ((Pi)pure is the vapor pressure of the pure component, Xi is the mole fraction of the component in solution Boiling-point elevation is a colligative property (the properties of dilute solutions of non-volatiles solute w ...
Slide 1 - MrCard.Org
... • Are ones in which an element or a compound reacts rapidly with O gas to liberate heat and light energy, compounds combining with O in these reactions are hydrocarbons, fuels like kerosene and gasoline, complete combustion yields CO2 and H2O, if not have enough O combustion will not be complete – C ...
... • Are ones in which an element or a compound reacts rapidly with O gas to liberate heat and light energy, compounds combining with O in these reactions are hydrocarbons, fuels like kerosene and gasoline, complete combustion yields CO2 and H2O, if not have enough O combustion will not be complete – C ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... kool-aid in water. It is an expected color change. It is a chemical change only when it is unexpected- for example mixing two clear liquids and having the substance turn blue. ...
... kool-aid in water. It is an expected color change. It is a chemical change only when it is unexpected- for example mixing two clear liquids and having the substance turn blue. ...
Matter and Measurement
... reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed. First write the chemical formulas of the reactants aqueous Calcium chloride: CaCl2(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate: Na2CO3(aq) Next, determine what the products of the reaction will be and which product is t ...
... reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed. First write the chemical formulas of the reactants aqueous Calcium chloride: CaCl2(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate: Na2CO3(aq) Next, determine what the products of the reaction will be and which product is t ...
File
... A 1.00 gram sample of which of these compounds contains the greatest mass of oxygen? A) Al2O3 B) BeO C) Na2O D) K2O2 2. What is the chemical formula of iron (III) sulfate? A) FeSO4 B) FeSO3 C) Fe(SO4)3 D) Fe2(SO4)3 3 - 4. An experiment is done to determine the density of copper. A sample of copper i ...
... A 1.00 gram sample of which of these compounds contains the greatest mass of oxygen? A) Al2O3 B) BeO C) Na2O D) K2O2 2. What is the chemical formula of iron (III) sulfate? A) FeSO4 B) FeSO3 C) Fe(SO4)3 D) Fe2(SO4)3 3 - 4. An experiment is done to determine the density of copper. A sample of copper i ...
Reactions and Balancing
... Combustion reactions are the ones that burn (or explode!). There are two types of combustion reactions—complete or incomplete reactions. These reactions are identified by their products. They either produce carbon monoxide and water or carbon dioxide and water. ...
... Combustion reactions are the ones that burn (or explode!). There are two types of combustion reactions—complete or incomplete reactions. These reactions are identified by their products. They either produce carbon monoxide and water or carbon dioxide and water. ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... 2. Use the Solubility Rules to determine if each product is soluble or insoluble. – If at least one product is insoluble, a precipitation reaction has occurred. Write the formulas for both products, indicating the precipitate as (s), then balance the equation. – If both products are soluble, write N ...
... 2. Use the Solubility Rules to determine if each product is soluble or insoluble. – If at least one product is insoluble, a precipitation reaction has occurred. Write the formulas for both products, indicating the precipitate as (s), then balance the equation. – If both products are soluble, write N ...
Honors Chemistry
... Careful! Check your activity series. The reactant that is an element must be stronger than the ion it’s replacing! eg. Cu + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag 2Ag + Cu(NO3)2 No Reaction! ...
... Careful! Check your activity series. The reactant that is an element must be stronger than the ion it’s replacing! eg. Cu + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag 2Ag + Cu(NO3)2 No Reaction! ...
Atoms and Molecules
... THIS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT IS VOLUNTARY!!! This assignment is a voluntary activity for those who wish for a bit of review or want to polish off the rust. We will conduct a general review of first-year chemistry material during the first one or two class meetings (typically the first week of school). We ...
... THIS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT IS VOLUNTARY!!! This assignment is a voluntary activity for those who wish for a bit of review or want to polish off the rust. We will conduct a general review of first-year chemistry material during the first one or two class meetings (typically the first week of school). We ...
Ch17-2 Driving Forces of Reactions
... (exothermic or endothermic) in a chemical reaction. Enthalpy: change in energy ...
... (exothermic or endothermic) in a chemical reaction. Enthalpy: change in energy ...
Dynamic modeling of electrochemical systems using linear graph
... can be the currents and voltages, respectively. A summary of possible through and across variable for some common energy domains are summarized in Table A.1. These two quantities are carried along the entire linear graph so that the balance of energy at any point of the graph can be found. This make ...
... can be the currents and voltages, respectively. A summary of possible through and across variable for some common energy domains are summarized in Table A.1. These two quantities are carried along the entire linear graph so that the balance of energy at any point of the graph can be found. This make ...
Chapter 4 - U of L Class Index
... Quantitative analysis is the identification of an unknown substance by subjecting it to chemical reactions and analyzing the resulting products. (What are they? How much of each was made?) Generally, we must already know which elements the unknown contains in order to choose the best reactions. Quan ...
... Quantitative analysis is the identification of an unknown substance by subjecting it to chemical reactions and analyzing the resulting products. (What are they? How much of each was made?) Generally, we must already know which elements the unknown contains in order to choose the best reactions. Quan ...
Atomic Structure - BDJ Engineering
... When the faucet (switch) is off, is there any pressure (voltage)? YES – Pressure (voltage) is pushing against the pipe, tank, and the faucet. When the faucet (switch) is on, is there any pressure (voltage)? YES – Pressure (voltage) pushes flow (current) through the system. ...
... When the faucet (switch) is off, is there any pressure (voltage)? YES – Pressure (voltage) is pushing against the pipe, tank, and the faucet. When the faucet (switch) is on, is there any pressure (voltage)? YES – Pressure (voltage) pushes flow (current) through the system. ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... elements: K, Cl, Mn, Zr, Ne, Ca, Sc, Ti, Fe, Al, Br, Ni, Cu, S, Ag, He, B, O, Na, Mg, Be, Ar, N, V, ...
... elements: K, Cl, Mn, Zr, Ne, Ca, Sc, Ti, Fe, Al, Br, Ni, Cu, S, Ag, He, B, O, Na, Mg, Be, Ar, N, V, ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.