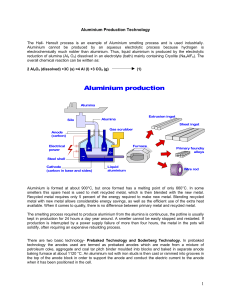
For detailed information on Aluminium Production
... Recycled metal requires only 5 percent of the energy required to make new metal. Blending recycled metal with new metal allows considerable energy savings, as well as the efficient use of the extra heat available. When it comes to quality, there is no difference between primary metal and recycled me ...
... Recycled metal requires only 5 percent of the energy required to make new metal. Blending recycled metal with new metal allows considerable energy savings, as well as the efficient use of the extra heat available. When it comes to quality, there is no difference between primary metal and recycled me ...
How to Balance Chemical Equations
... involved are set and their formulas can not be altered. Hence, any change to the subscripts is NOT allowed. ONLY COEFFICIENTS ARE ALLOWED TO BE CHANGED!! ...
... involved are set and their formulas can not be altered. Hence, any change to the subscripts is NOT allowed. ONLY COEFFICIENTS ARE ALLOWED TO BE CHANGED!! ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... ending second. 3) Add prefixes to both indicating the number of atoms of each element ...
... ending second. 3) Add prefixes to both indicating the number of atoms of each element ...
Introduction - HCC Learning Web
... chemical reactions. Because bonds are formed or broken during a reaction, the properties of product molecules differ from those of reactant molecules. If there is a significant difference, a distant signal that a chemical reaction has occurred can usually be observed. One easily seen signal of a che ...
... chemical reactions. Because bonds are formed or broken during a reaction, the properties of product molecules differ from those of reactant molecules. If there is a significant difference, a distant signal that a chemical reaction has occurred can usually be observed. One easily seen signal of a che ...
Document
... An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, ionizes and increases the concentration of hydrogen ions, H+. HCl → H+ + Cl A base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, OH-. But, Not all bases contain OHNaOH → Na+ + OH- ...
... An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, ionizes and increases the concentration of hydrogen ions, H+. HCl → H+ + Cl A base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, OH-. But, Not all bases contain OHNaOH → Na+ + OH- ...
An experimental set up for detecting Weber`s
... Description of the experimental setup with reference to Fig. 2: - Portion AB and CD are made of two different conducting materials such that they have opposite charges as current carriers or the current carriers has different drift velocities (or both) both). AB-CD is connected to the end of a batte ...
... Description of the experimental setup with reference to Fig. 2: - Portion AB and CD are made of two different conducting materials such that they have opposite charges as current carriers or the current carriers has different drift velocities (or both) both). AB-CD is connected to the end of a batte ...
The collision theory of reactions
... In the Haber process, (reaction between H2 and N2) at 300 K only 1 in 1011 collisions between H2 and N2 results in a reaction! Even at 800 K only 1 in 104 collisions results in a reaction. The collision theory says: Reactions occur when molecules collide with a certain minimum kinetic energy. The mo ...
... In the Haber process, (reaction between H2 and N2) at 300 K only 1 in 1011 collisions between H2 and N2 results in a reaction! Even at 800 K only 1 in 104 collisions results in a reaction. The collision theory says: Reactions occur when molecules collide with a certain minimum kinetic energy. The mo ...
Equilibrium Constant
... Kinetics tells us if the system will actually achieve this state within a reasonable time. ...
... Kinetics tells us if the system will actually achieve this state within a reasonable time. ...
UNIT 1 - StudyGuide.PK
... For the Haber process, the idea of the temperature being a compromise between the high rate but low equilibrium yield at high temperatures, and low rate but high yield at low temperatures. Pressure is a compromise between high yield and rate at high pressures, but at high capital and running costs. ...
... For the Haber process, the idea of the temperature being a compromise between the high rate but low equilibrium yield at high temperatures, and low rate but high yield at low temperatures. Pressure is a compromise between high yield and rate at high pressures, but at high capital and running costs. ...
CHM1 Review for Exam 9 Topics 1. Reaction Types a. Combustion
... a. __ C2H6 (g) + __ O2 (g) __ CO2 (g) + __ H2O (g) b. __ C2H6OH (g) + __ O2 (g) __ CO2 (g) + __ H2O (g) c. __ Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + __ Na3PO4 (aq) __ Ca3(PO4)2 (s) + __ NaNO3 (aq) d. __ CuCl2 (aq) + __ AgNO3 (aq) __ AgCl (s) + __ Cu(NO3)2 (aq) ...
... a. __ C2H6 (g) + __ O2 (g) __ CO2 (g) + __ H2O (g) b. __ C2H6OH (g) + __ O2 (g) __ CO2 (g) + __ H2O (g) c. __ Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + __ Na3PO4 (aq) __ Ca3(PO4)2 (s) + __ NaNO3 (aq) d. __ CuCl2 (aq) + __ AgNO3 (aq) __ AgCl (s) + __ Cu(NO3)2 (aq) ...
IGCSE Revision Guide (Double Award) | PDF
... Say that covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds between the bonding pair of electrons and the nuclei of the atoms involved in the bond. Use dot and cross diagrams to represent single covalent bonds ...
... Say that covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds between the bonding pair of electrons and the nuclei of the atoms involved in the bond. Use dot and cross diagrams to represent single covalent bonds ...
Redox Reactions
... • oxidation-reduction or redox reactions are Electron transfer reactions. • Redox reactions can result in the ...
... • oxidation-reduction or redox reactions are Electron transfer reactions. • Redox reactions can result in the ...
REACTION PREDICTION
... Reactants Products The arrow means “yields” or “produces” (s) = solid (g)= gas (l)= liquid (aq)= aqueous (dissolved in water) or = reversible reaction ...
... Reactants Products The arrow means “yields” or “produces” (s) = solid (g)= gas (l)= liquid (aq)= aqueous (dissolved in water) or = reversible reaction ...
Equilibrium Constant - Faculty Server Contact
... it", just think of it as a partial pressure: it is a strong function of the mole fraction of the component in the gas phase, and of the total pressure of the gas phase, just like a partial pressure; more precisely, remembering that chemical potential is a quantitative measure of the reactivity of a ...
... it", just think of it as a partial pressure: it is a strong function of the mole fraction of the component in the gas phase, and of the total pressure of the gas phase, just like a partial pressure; more precisely, remembering that chemical potential is a quantitative measure of the reactivity of a ...
Chemical Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reac ...
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reac ...
Writing Chemical Equations - Mrs. Procee's Online Classroom
... At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Translate chemical word equations into formula ...
... At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Translate chemical word equations into formula ...
ELECTROLYTES AND NONELECTROLYTES Lec.3
... ♠The situation is different in an aqueous solution of sugar, a nonelectrolyte. The sugar molecules, surrounded by water molecules, are neutral. When a pair of electrodes is placed in this solution, the sugar molecules are not attracted by either electrode. Consequently no electric current flows thro ...
... ♠The situation is different in an aqueous solution of sugar, a nonelectrolyte. The sugar molecules, surrounded by water molecules, are neutral. When a pair of electrodes is placed in this solution, the sugar molecules are not attracted by either electrode. Consequently no electric current flows thro ...
How to Balance Chemical Equations
... The arrow means '______________' In a chemical reaction atoms are rearranged as old chemical bonds are broken and new chemical bonds are formed. The 'law of conservation of __________' is supported as the weight doesn’t change between the mass of the reactants and the mass of the products. 2. How to ...
... The arrow means '______________' In a chemical reaction atoms are rearranged as old chemical bonds are broken and new chemical bonds are formed. The 'law of conservation of __________' is supported as the weight doesn’t change between the mass of the reactants and the mass of the products. 2. How to ...
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations
... PREDICTING WHETHER A SINGLE REPLACEMENT REACTION WILL OCCUR The reactants in a single replacement reaction are an element (by itself) and a compound. Some single replacement reactions will happen, others will not. In order to determine if a single replacement reaction will occur, you must use the Ac ...
... PREDICTING WHETHER A SINGLE REPLACEMENT REACTION WILL OCCUR The reactants in a single replacement reaction are an element (by itself) and a compound. Some single replacement reactions will happen, others will not. In order to determine if a single replacement reaction will occur, you must use the Ac ...
Enthalpy - Mr. Rowley
... Exothermic reactions release heat because the reactants have a higher heat content (enthalpy). The heat released is the ‘excess’ heat. Since CuCl2 has a lower heat content, the extra heat is released to the ...
... Exothermic reactions release heat because the reactants have a higher heat content (enthalpy). The heat released is the ‘excess’ heat. Since CuCl2 has a lower heat content, the extra heat is released to the ...
Class Notes
... a chemical reaction or a physical change mass is conserved; mass is neither created nor destroyed. This implies that the atoms that were there in the reactants (before the chemical change) must be there in the products (after the chemical change) just rearranges somehow. The subscripts in chemical f ...
... a chemical reaction or a physical change mass is conserved; mass is neither created nor destroyed. This implies that the atoms that were there in the reactants (before the chemical change) must be there in the products (after the chemical change) just rearranges somehow. The subscripts in chemical f ...
Document
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.