PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all parts of this examination according to the dir ...
... This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all parts of this examination according to the dir ...
syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of the balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effe ...
... Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of the balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effe ...
Effects of antioxidants for the degradation of flame
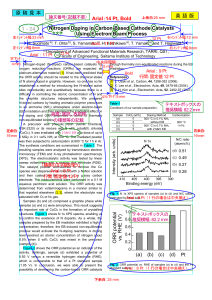
... species was dispersed in a mixture with a Nafion solution and then coated on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode. The measurements were performed in a 0.1 M aqueous perchloric acid solution. The ORR activity was determined from voltammograms in a manner similar to that reported elsewhere [2, 3] ...
... species was dispersed in a mixture with a Nafion solution and then coated on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode. The measurements were performed in a 0.1 M aqueous perchloric acid solution. The ORR activity was determined from voltammograms in a manner similar to that reported elsewhere [2, 3] ...
Physical Science: Study Guide
... The three forms that matter usually takes: solid, liquid, and gas. ...
... The three forms that matter usually takes: solid, liquid, and gas. ...
Name
... 18. Sulfur in gasoline can produce sulfuric acid, H2SO4, according to the two-step process shown below. For each 125g of sulfur in gasoline, how many moles of H2SO4 will be produced? S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 2H2SO4(aq) a. 4.5mol b. 2.1mol c. 3.9mol d. 1.4mol 19. How many at ...
... 18. Sulfur in gasoline can produce sulfuric acid, H2SO4, according to the two-step process shown below. For each 125g of sulfur in gasoline, how many moles of H2SO4 will be produced? S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 2H2SO4(aq) a. 4.5mol b. 2.1mol c. 3.9mol d. 1.4mol 19. How many at ...
Formulae/ Equations homework - St Peter the Apostle High School
... 10. Write word equations from the following descriptions of chemical reactions: (a) When zinc metal burns, it reacts with oxygen in the air to form zinc oxide, a grey solid. (b) Sodium metal reacts violently with water producing hydrogen gas and a solution of sodium hydroxide. (c) When iron is produ ...
... 10. Write word equations from the following descriptions of chemical reactions: (a) When zinc metal burns, it reacts with oxygen in the air to form zinc oxide, a grey solid. (b) Sodium metal reacts violently with water producing hydrogen gas and a solution of sodium hydroxide. (c) When iron is produ ...
Worksheet on Ionic and Atomic Size Trends
... 12. The sodium ion is smaller than the atom, because when sodium loses its valence electron to form an ion, it also loses its 3rd energy level. 13. The chlorine ion is larger than the chlorine atom, because adding an additional electron to the 3 rd energy level causes the energy level to expand beca ...
... 12. The sodium ion is smaller than the atom, because when sodium loses its valence electron to form an ion, it also loses its 3rd energy level. 13. The chlorine ion is larger than the chlorine atom, because adding an additional electron to the 3 rd energy level causes the energy level to expand beca ...
KEY_Reaction Types WS
... hydroxide to form a salt plus water. Alternatively, the acid may react with ammonia (NH3) to form an ammonium salt (but no water). These are proton transfer reactions in which H+ (the proton) is transferred from the acid to the base. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: These are reactions in which one ty ...
... hydroxide to form a salt plus water. Alternatively, the acid may react with ammonia (NH3) to form an ammonium salt (but no water). These are proton transfer reactions in which H+ (the proton) is transferred from the acid to the base. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: These are reactions in which one ty ...
In Situ Vanadium K-Edge and Tungsten LIII-Edge X
... Polyoxometalate Synthesis. K4PVW11O40 and Cs6PV3W9O40, and H3PW12O40 were prepared and purified according to the procedures outlined in refs 9 and 10, respectively, and subsequently characterized by IR and UV-visible spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. Electrode Preparation. a. In situ XAFS. For th ...
... Polyoxometalate Synthesis. K4PVW11O40 and Cs6PV3W9O40, and H3PW12O40 were prepared and purified according to the procedures outlined in refs 9 and 10, respectively, and subsequently characterized by IR and UV-visible spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. Electrode Preparation. a. In situ XAFS. For th ...
Spectrum05
... Reversible Reactions 2H2O(g) + energy 2H2O(g) + energy H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2(g) ...
... Reversible Reactions 2H2O(g) + energy 2H2O(g) + energy H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2(g) ...
Final Review
... 4. What is the relationship between atmospheric pressure and the boiling point of a liquid? 5. Water has a high heat of fusion (6.009 KJ/mol) and a high heat of vaporization (40.79 KJ/mol). Explain what this means in terms of attraction between particles. 6. Using the values given in #5, calculate t ...
... 4. What is the relationship between atmospheric pressure and the boiling point of a liquid? 5. Water has a high heat of fusion (6.009 KJ/mol) and a high heat of vaporization (40.79 KJ/mol). Explain what this means in terms of attraction between particles. 6. Using the values given in #5, calculate t ...
Trends in Physical Properties
... Deduce the half-equation for the reduction of the MnO4− ions in acidified solution to manganese(II) ions and water. ...
... Deduce the half-equation for the reduction of the MnO4− ions in acidified solution to manganese(II) ions and water. ...
Document
... Standard enthalpy of formation of a compound, Hof, is the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of compound with all substances in their standard states. If there is more than one state for a substance under standard conditions, the more stable one is used. Example: When dealing with carbon we ...
... Standard enthalpy of formation of a compound, Hof, is the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of compound with all substances in their standard states. If there is more than one state for a substance under standard conditions, the more stable one is used. Example: When dealing with carbon we ...
CHEM_Review - Kenston Local Schools
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... Examples: CH4, NH3, H2O, NH4 +, H3O+, BF3, C2H4, SO2, C2H2 and CO2. Aim 7: Simulations are available to study the three dimensional structures of these and the structures in 4.2.9( diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene) and 4.2.10 ( silicon and silicon dioxide). Predict whether or not a molecule is po ...
... Examples: CH4, NH3, H2O, NH4 +, H3O+, BF3, C2H4, SO2, C2H2 and CO2. Aim 7: Simulations are available to study the three dimensional structures of these and the structures in 4.2.9( diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene) and 4.2.10 ( silicon and silicon dioxide). Predict whether or not a molecule is po ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.