AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... atm and the temperature is 33˚C? 77. On a warm day, an amusement park balloon is filled with 47.8 g He. The temperature is 33˚C and the pressure in the balloon is 2.25 atm. Calculate the volume of the balloon. 78. A drum use to transport crude oil has a volume of 162 L. How many water molecules, as ...
... atm and the temperature is 33˚C? 77. On a warm day, an amusement park balloon is filled with 47.8 g He. The temperature is 33˚C and the pressure in the balloon is 2.25 atm. Calculate the volume of the balloon. 78. A drum use to transport crude oil has a volume of 162 L. How many water molecules, as ...
Chemical Stability
... Chemical Bonding • Chemical Bonding occurs to achieve Chemical Stability. • Atoms gain, lose or share valence electrons. Why do Atoms Bond? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JOL-nUt_vfo&feature=youtu.be&app=desktop ...
... Chemical Bonding • Chemical Bonding occurs to achieve Chemical Stability. • Atoms gain, lose or share valence electrons. Why do Atoms Bond? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JOL-nUt_vfo&feature=youtu.be&app=desktop ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
... solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
Spring 2002 - Kwantlen Polytechnic University
... The triple point of water is at 4.58 mm Hg and +0.01°C. Some H2O at -50°C is heated to 120°C at a constant pressure of 2.05 mm Hg. The changes of state(s) occuring in this process are: a. solid to gas b. solid to liquid to gas c. liquid to gas d. solid to liquid e. no change in state occurs at const ...
... The triple point of water is at 4.58 mm Hg and +0.01°C. Some H2O at -50°C is heated to 120°C at a constant pressure of 2.05 mm Hg. The changes of state(s) occuring in this process are: a. solid to gas b. solid to liquid to gas c. liquid to gas d. solid to liquid e. no change in state occurs at const ...
Environmental Chemistry
... These non-metal oxides are all gases Their acidic products all contribute to the acidity of rain. Note: strong acids completely dissociate to their ions, so that a monoprotic acid will have the same hydronium ion concentration as the original concentration of the acid. ...
... These non-metal oxides are all gases Their acidic products all contribute to the acidity of rain. Note: strong acids completely dissociate to their ions, so that a monoprotic acid will have the same hydronium ion concentration as the original concentration of the acid. ...
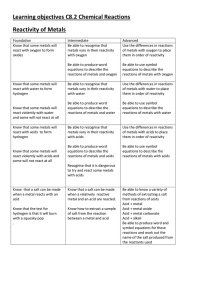
Chapter 8 Chemical Equations and Reactions
... The relative amounts of reactants and products represented in the equation must be adjusted so that the numbers and types of atoms are the same on both sides of the equation. This process is called Balancing an Equation and is carried out by ...
... The relative amounts of reactants and products represented in the equation must be adjusted so that the numbers and types of atoms are the same on both sides of the equation. This process is called Balancing an Equation and is carried out by ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of t ...
... energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of t ...
Formula and The Mole
... 14. The __________ electrons in metals are free to move and so metals can conduct electricity. 15. Covalent substances ________ conduct electricity. 16. Electricity is carried by __________ ions in ionic compounds, therefore the only conduct in __________ or as a ________ when the ions are ______ __ ...
... 14. The __________ electrons in metals are free to move and so metals can conduct electricity. 15. Covalent substances ________ conduct electricity. 16. Electricity is carried by __________ ions in ionic compounds, therefore the only conduct in __________ or as a ________ when the ions are ______ __ ...
Final Exam - Seattle Central College
... – For small values of Kc or Kp (<10-3), the reaction does not occur to any significant degree. → The equilibrium mixture consists mostly of reactants (reactant favored) → The equilibrium lies to the left. – For intermediate values (10-3 < Kc or Kp < 103), the equilibrium mixture contains appreciable ...
... – For small values of Kc or Kp (<10-3), the reaction does not occur to any significant degree. → The equilibrium mixture consists mostly of reactants (reactant favored) → The equilibrium lies to the left. – For intermediate values (10-3 < Kc or Kp < 103), the equilibrium mixture contains appreciable ...
Describing Chemical Reactions
... produce water. The reverse of this reaction can also occur. In other words, water can be broken down to make hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The breakdown of water is a decomposition reaction. The unbalanced equation for this reaction is shown below. H 2O H2 ...
... produce water. The reverse of this reaction can also occur. In other words, water can be broken down to make hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The breakdown of water is a decomposition reaction. The unbalanced equation for this reaction is shown below. H 2O H2 ...
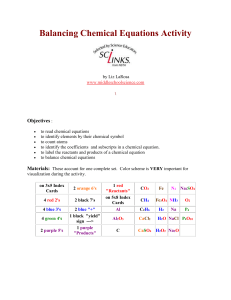
Balancing Chemical Equations Activity by Liz LaRosa www
... Print activity cards on card stock instead of making index cards for quicker set up. The color coding is very important for visualization. It is easier and quicker to locate the elements that you are trying to balance. If everything is in black ink, its harder to distinguish the equation contents. I ...
... Print activity cards on card stock instead of making index cards for quicker set up. The color coding is very important for visualization. It is easier and quicker to locate the elements that you are trying to balance. If everything is in black ink, its harder to distinguish the equation contents. I ...
Organometallic Chemistry at the Magnesium− Tris (8
... formation, gives rise to the observed N(1s) BE shift.12 Reduced charge delocalization in 2 (compared with a fully delocalized ligand radical anion8) results in only small changes in core binding energies for the carbon atoms before and after reduction, and detection of these changes is not possible, ...
... formation, gives rise to the observed N(1s) BE shift.12 Reduced charge delocalization in 2 (compared with a fully delocalized ligand radical anion8) results in only small changes in core binding energies for the carbon atoms before and after reduction, and detection of these changes is not possible, ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Key Concept 13: Single Replacement Explanation: Reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of another element in a compound. ...
... Key Concept 13: Single Replacement Explanation: Reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of another element in a compound. ...
Bio 102 Lecture - chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
... The Octet Rule for Distribution of Electrons 8-electron configuration is stable because this atom is having 8 valence electrons. ...
... The Octet Rule for Distribution of Electrons 8-electron configuration is stable because this atom is having 8 valence electrons. ...
CHEM 20 FINAL EXAM: STUDY HEADINGS Jan 2012
... Physical Chemistry: Solutions and Gases (Ch 14, 20, 21, 15, 18, 19) characteristics of the 3 phases of matter: solids, liquids, gases characteristics of phase changes: fusion, vaporization, liquefaction qualitative aspects of the kinetic theory: behavior of gases – pressure, volume Avogadro’s hypoth ...
... Physical Chemistry: Solutions and Gases (Ch 14, 20, 21, 15, 18, 19) characteristics of the 3 phases of matter: solids, liquids, gases characteristics of phase changes: fusion, vaporization, liquefaction qualitative aspects of the kinetic theory: behavior of gases – pressure, volume Avogadro’s hypoth ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.