Exam 3 Review Sheet
... o Oxidation of a benzylic C-H with chromic acid or potassium permanganate. • Nomenclature – common derivatives, o/m/p usage. • Electrophilic Aromatic subsitution reactions. o General mechanism, high energy intermediate. o Generation of electrophile mechanisms. o Halogenation: X2, FeX3. o Sulfonation ...
... o Oxidation of a benzylic C-H with chromic acid or potassium permanganate. • Nomenclature – common derivatives, o/m/p usage. • Electrophilic Aromatic subsitution reactions. o General mechanism, high energy intermediate. o Generation of electrophile mechanisms. o Halogenation: X2, FeX3. o Sulfonation ...
11 Thermodynamics 9 26 05
... the more that disorder comes into play higher proportion of energy lost to randomness ...
... the more that disorder comes into play higher proportion of energy lost to randomness ...
Fall Exam 4
... ΔHfus = 2.20 kJ/mol ΔHvap = 35.2 kJ/mol Cs of CH3OH(s) = 3.28 J/g·°C Cs of CH3OH(l) = 2.54 J/g·°C Cs of CH3OH(g) = 1.50 J/g·°C How much energy is required to warm 320. g (10.0 mol) of CH3OH(l), initially at −33.0 °C , to CH3OH(g) at 77.0 °C? A. 675 kJ C. 238 kJ B. ...
... ΔHfus = 2.20 kJ/mol ΔHvap = 35.2 kJ/mol Cs of CH3OH(s) = 3.28 J/g·°C Cs of CH3OH(l) = 2.54 J/g·°C Cs of CH3OH(g) = 1.50 J/g·°C How much energy is required to warm 320. g (10.0 mol) of CH3OH(l), initially at −33.0 °C , to CH3OH(g) at 77.0 °C? A. 675 kJ C. 238 kJ B. ...
experiment 3
... As reaction (3-1) progresses, the amount of OH- ions in solution diminishes as CH3COO- ions are produced. It is known that the electrical conductivity of OH- ions is much greater than that of CH3COO- ions. Equivalent ionic conductivity at infinite dilution, at 25oC, for OH- and CH3COO- are 198.6 mho ...
... As reaction (3-1) progresses, the amount of OH- ions in solution diminishes as CH3COO- ions are produced. It is known that the electrical conductivity of OH- ions is much greater than that of CH3COO- ions. Equivalent ionic conductivity at infinite dilution, at 25oC, for OH- and CH3COO- are 198.6 mho ...
king fahd university of petroleum and minerals chemistry
... 16. How many minutes would be required to electroplate (i.e., precipitate) 12.5 grams of chromium (Cr) by passing a constant current of 4.80 amperes through a solution containing CrCl3? A) B) C) D) ...
... 16. How many minutes would be required to electroplate (i.e., precipitate) 12.5 grams of chromium (Cr) by passing a constant current of 4.80 amperes through a solution containing CrCl3? A) B) C) D) ...
Document
... of exergonic reactions that power the work of the cell. The product of each reaction becomes the reactant for the next, so no reaction reaches equilibrium. ...
... of exergonic reactions that power the work of the cell. The product of each reaction becomes the reactant for the next, so no reaction reaches equilibrium. ...
File - Mr Weng`s IB Chemistry
... Can be gaps Low (can occur if metal or graphite is in the structure) Low (except for carbon fibre) ...
... Can be gaps Low (can occur if metal or graphite is in the structure) Low (except for carbon fibre) ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Based on your investigation so far, do you think that energy changes only accompany chemical reactions? Using only the materials from the first two reactions, design an experiment that would test this idea. Propose a procedure and have it approved by your teacher before you continue experimentin ...
... 1. Based on your investigation so far, do you think that energy changes only accompany chemical reactions? Using only the materials from the first two reactions, design an experiment that would test this idea. Propose a procedure and have it approved by your teacher before you continue experimentin ...
Measurements/Unit Cancellation/Significant Figures 1. When
... Concentration: The measure of the quantity of a solute dissolved in a given quantity of solution. Dilute Solution: A solution that contains a small amount of solute relative to the amount that could dissolve. Electrolyte: A substance that conducts a current when it dissolves in water. Empirical form ...
... Concentration: The measure of the quantity of a solute dissolved in a given quantity of solution. Dilute Solution: A solution that contains a small amount of solute relative to the amount that could dissolve. Electrolyte: A substance that conducts a current when it dissolves in water. Empirical form ...
2016
... a.Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. b.How many liters of sulfur dioxide would be produced from 10.0 l of Oxygen? Assume 100% yield and that all gases are measured at the same temperature and pressure. ...
... a.Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. b.How many liters of sulfur dioxide would be produced from 10.0 l of Oxygen? Assume 100% yield and that all gases are measured at the same temperature and pressure. ...
homework assignment - Global Change Program
... calculate residence time. For our current atmosphere, consider that we are at steady state with respect to oxygen. Remember to interpret the residence time in light of the question “what would it take to disturb or change this system?” B. Equation of Photosynthesis and Respiration: CO2 + H2O CH2O ...
... calculate residence time. For our current atmosphere, consider that we are at steady state with respect to oxygen. Remember to interpret the residence time in light of the question “what would it take to disturb or change this system?” B. Equation of Photosynthesis and Respiration: CO2 + H2O CH2O ...
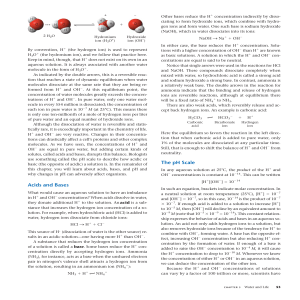
Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... human blood and many other biological solutions. One of these is carbonic acid (H2CO3), formed when CO2 reacts with water in blood plasma. As mentioned earlier, carbonic acid dissociates to yield a bicarbonate ion (HCO3") and a hydrogen ion (H!): ...
... human blood and many other biological solutions. One of these is carbonic acid (H2CO3), formed when CO2 reacts with water in blood plasma. As mentioned earlier, carbonic acid dissociates to yield a bicarbonate ion (HCO3") and a hydrogen ion (H!): ...
Pages from PS 11 Textbook for Lab
... change for a chemical process at constant pressure, which is the thermal energy (heat) produced by the chemical reaction at constant pressure. Because we live, by and large, in a constant pressure world, the state variable enthalpy is a variable of great importance. In fact, ∆H released in a chemica ...
... change for a chemical process at constant pressure, which is the thermal energy (heat) produced by the chemical reaction at constant pressure. Because we live, by and large, in a constant pressure world, the state variable enthalpy is a variable of great importance. In fact, ∆H released in a chemica ...
Hydrogen Peroxide Formation Rates in a PEMFC Anode and Cathode
... potentiodynamic experiments. Though a variety of supporting electrolytes are reported in the literature, anion adsorption on Pt is minimal for only a few electrolytes.23 关e.g., trifluoromethane sulfonic acid 共TFMSA兲 and HClO4兴. In addition, the ultrapure reagent grade HClO4 used in this study is fre ...
... potentiodynamic experiments. Though a variety of supporting electrolytes are reported in the literature, anion adsorption on Pt is minimal for only a few electrolytes.23 关e.g., trifluoromethane sulfonic acid 共TFMSA兲 and HClO4兴. In addition, the ultrapure reagent grade HClO4 used in this study is fre ...
chemistry
... 59 At constant temperature, the relationship between the volume (V) of a given mass of gas and its pressure (P) is ...
... 59 At constant temperature, the relationship between the volume (V) of a given mass of gas and its pressure (P) is ...
Scientific Measurement
... P Copper and zinc are mixed to form brass. P A large piece of copper is chopped in half. C Copper reacts with bromine to form copper (II) bromide. Circle the particle diagram that best represents Substance A after a physical change has occurred. ...
... P Copper and zinc are mixed to form brass. P A large piece of copper is chopped in half. C Copper reacts with bromine to form copper (II) bromide. Circle the particle diagram that best represents Substance A after a physical change has occurred. ...
Topic/Objective - cloudfront.net
... gas laws on the basis of this theory b. Avogadro’s hypothesis and the mole concept c. Dependence of kinetic energy of molecules on temperature d. Deviations from ideal gas laws ...
... gas laws on the basis of this theory b. Avogadro’s hypothesis and the mole concept c. Dependence of kinetic energy of molecules on temperature d. Deviations from ideal gas laws ...
chapter 6: chemical reactions: an introduction
... The starting materials are called reactants and are shown on the left side of the chemical equation. The substances formed in a reaction are called products and are shown on the right side of the equation. The same kinds of atoms must be present before and after a chemical reaction because atoms are ...
... The starting materials are called reactants and are shown on the left side of the chemical equation. The substances formed in a reaction are called products and are shown on the right side of the equation. The same kinds of atoms must be present before and after a chemical reaction because atoms are ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.