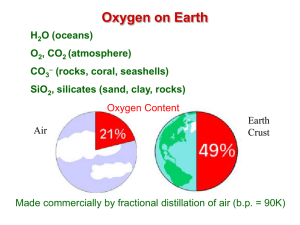
Honors Unit 3 - Stoichiometry
... 1. Zinc metal and aqueous lead (II) nitrate react to form aqueous zinc nitrate and solid lead. ...
... 1. Zinc metal and aqueous lead (II) nitrate react to form aqueous zinc nitrate and solid lead. ...
Final Exam Study Guide Chapters 1-12
... b. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) c. 2H2O(aq) + 2Na(s) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) d. Cl2(g) 2Cl(g) ____ 88. Which of the following would be investigated in reaction stoichiometry? a. the masses of hydrogen and oxygen in water b. the amount of energy released in chemical reactions c. the mass of p ...
... b. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) c. 2H2O(aq) + 2Na(s) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) d. Cl2(g) 2Cl(g) ____ 88. Which of the following would be investigated in reaction stoichiometry? a. the masses of hydrogen and oxygen in water b. the amount of energy released in chemical reactions c. the mass of p ...
Energy and Matter in Chemical Change Science 10
... • A hypothesis is an educated guess about how things work. • Your hypothesis should be something that you can actually test, what's called a testable hypothesis. • In other words, you need to be able to measure both "what you do" and "what will happen." ...
... • A hypothesis is an educated guess about how things work. • Your hypothesis should be something that you can actually test, what's called a testable hypothesis. • In other words, you need to be able to measure both "what you do" and "what will happen." ...
Large Gate Modulation in the Current of a Room Temperature
... junctions (Figure 1a).7 A large gate field is achieved using an electrochemical gate in which the gate voltage is applied between the source and a gate in the electrolyte.8 Since the gate voltage falls across the double layers at the electrode-electrolyte interfaces, which are only a few ions thick, ...
... junctions (Figure 1a).7 A large gate field is achieved using an electrochemical gate in which the gate voltage is applied between the source and a gate in the electrolyte.8 Since the gate voltage falls across the double layers at the electrode-electrolyte interfaces, which are only a few ions thick, ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... State the Law of Conservation of Mass and explain its relationship to stoichiometry. ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ ...
... State the Law of Conservation of Mass and explain its relationship to stoichiometry. ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
Electrical Energy Potential
... Capacitance • A capacitor is a device that temporarily stores electrical energy that can be reclaimed at a later time. It consists of two parallel metal plates separated by a distance d, each connected to one of the terminals of an electrical source. The plate connected to the +ve terminal losses e ...
... Capacitance • A capacitor is a device that temporarily stores electrical energy that can be reclaimed at a later time. It consists of two parallel metal plates separated by a distance d, each connected to one of the terminals of an electrical source. The plate connected to the +ve terminal losses e ...
C:\exams\June\June_06\chemistry\final\Chemistry 3202 June 2006
... the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 g of a substance 1.0 oC the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 g of a substance 100.0 oC the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 mol of a substance 1.0 oC the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 mol of a substan ...
... the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 g of a substance 1.0 oC the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 g of a substance 100.0 oC the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 mol of a substance 1.0 oC the energy required to raise the temperature of 1.0 mol of a substan ...
New Title
... a. H2 + O2 H2O b. Mg + O2 MgO c. Na + O2 Na2O d. 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 17. A number placed in front of a chemical formula in a chemical equation is called a(n) 18. What does a coefficient tell you? ...
... a. H2 + O2 H2O b. Mg + O2 MgO c. Na + O2 Na2O d. 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 17. A number placed in front of a chemical formula in a chemical equation is called a(n) 18. What does a coefficient tell you? ...
Review Session Handout from 10/6
... 38. 0.750 g of Mg is reacted with 25.0 g H2O Mg(s) + H2O(l) Mg(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) If the H2 is collected over water, what is the total volume that could be produced if the experiment was done at 25 C and 750 torr? ...
... 38. 0.750 g of Mg is reacted with 25.0 g H2O Mg(s) + H2O(l) Mg(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) If the H2 is collected over water, what is the total volume that could be produced if the experiment was done at 25 C and 750 torr? ...
Chapter 04
... the aqueous species are represented as follows: Na2SO4(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + SO42–(aq) Ba(OH)2(aq) → Ba2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) NaOH(aq) → Na+(aq) + OH–(aq) In an ionic equation compounds that exist completely or predominately as ions in solution are represented as those ions. 2Na+(aq) + SO42– (aq) + Ba2+(aq) + ...
... the aqueous species are represented as follows: Na2SO4(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + SO42–(aq) Ba(OH)2(aq) → Ba2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) NaOH(aq) → Na+(aq) + OH–(aq) In an ionic equation compounds that exist completely or predominately as ions in solution are represented as those ions. 2Na+(aq) + SO42– (aq) + Ba2+(aq) + ...
Unit 1: Matter and Energy HW Packet
... Part 16: Match the following types of energy with the correct description. 1. __________ Chemical a. energy of motion 2. __________ Electrical b. stored energy or energy due to position 3. __________ Electromagnetic c. energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms 4. __________ Kinetic d. energy tha ...
... Part 16: Match the following types of energy with the correct description. 1. __________ Chemical a. energy of motion 2. __________ Electrical b. stored energy or energy due to position 3. __________ Electromagnetic c. energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms 4. __________ Kinetic d. energy tha ...
Physical Chemistry of Colloids and Surfaces – Final Exam Review 4-30-02
... adsorbed layers repel each other by entropic and EDL interactions. They are potent electrostatic flocculants since they raise the ionic strength of the solution by adding polymer and counterions. The persistence length of polyelectrolytes is inversely related to the salt concentration due to Debye s ...
... adsorbed layers repel each other by entropic and EDL interactions. They are potent electrostatic flocculants since they raise the ionic strength of the solution by adding polymer and counterions. The persistence length of polyelectrolytes is inversely related to the salt concentration due to Debye s ...
Effect Of Convection For Gaseous Hydrochloride
... and 60% of scrap, containing number of different metals. Some of them, Ni, Cr, V make steel better etc., however metals like Zn, Cd, Pb are unwelcome. In modern steelmaking equipment using oxygen atmosphere in presence of lime, C is removed as CO gas, Si, P and S form slag. Small percentage of Fe is ...
... and 60% of scrap, containing number of different metals. Some of them, Ni, Cr, V make steel better etc., however metals like Zn, Cd, Pb are unwelcome. In modern steelmaking equipment using oxygen atmosphere in presence of lime, C is removed as CO gas, Si, P and S form slag. Small percentage of Fe is ...
18. REASONING The electric potential at a distance r from a point
... voltage V is q CV (Equation 19.8). The capacitance C is C 0 (Equation 19.10), d where κ is the dielectric constant of the material between the plates, ε0 is the permittivity of free space, A is the area of each plate, and d is the distance between the plates. Once the capacitor is charged and di ...
... voltage V is q CV (Equation 19.8). The capacitance C is C 0 (Equation 19.10), d where κ is the dielectric constant of the material between the plates, ε0 is the permittivity of free space, A is the area of each plate, and d is the distance between the plates. Once the capacitor is charged and di ...
2002 Final Exam for Practice - Department of Chemistry | Oregon
... Sketch a 1s orbital and a 4p orbital side by side, with correct relative scale. ...
... Sketch a 1s orbital and a 4p orbital side by side, with correct relative scale. ...
Chemicals: What`s in? What`s out?
... The following chemicals can be considered for use in handson middle school science programs. However, the teacher should review the character of each chemical or compound by consulting the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet. Appropriate precautions, such as PPE and ventilation, are an absolute m ...
... The following chemicals can be considered for use in handson middle school science programs. However, the teacher should review the character of each chemical or compound by consulting the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet. Appropriate precautions, such as PPE and ventilation, are an absolute m ...
Chem 171 Review Exam 2
... definitions of oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent identify an oxidation/reduction reaction based on changes in oxidation states write oxidation and reduction half reactions determine oxidation numbers of elements within species and a reaction identify oxidizing and reducing ag ...
... definitions of oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent identify an oxidation/reduction reaction based on changes in oxidation states write oxidation and reduction half reactions determine oxidation numbers of elements within species and a reaction identify oxidizing and reducing ag ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.