Electric Potential I - Galileo and Einstein
... • Taking the Bohr model for the ground state of the H atom, the electron circles at a radius of 0.53x10-10m, at which V(r) = 27.2 V. • The natural energy unit here is the electron volt : the work needed to take one electron from rest up a one volt hill. But in H the electron already has KE = 13.6eV, ...
... • Taking the Bohr model for the ground state of the H atom, the electron circles at a radius of 0.53x10-10m, at which V(r) = 27.2 V. • The natural energy unit here is the electron volt : the work needed to take one electron from rest up a one volt hill. But in H the electron already has KE = 13.6eV, ...
Unit 3 Notes
... 3. Set up a boiling tube fitted with a bung and delivery tube, to collect gas over water in an inverted measuring cylinder. Add the weighed solid to the boiling tube. Add 10 cm3 of 2 mol l-1 H2SO4 , quickly stopper the boiling tube and collect the gas. ...
... 3. Set up a boiling tube fitted with a bung and delivery tube, to collect gas over water in an inverted measuring cylinder. Add the weighed solid to the boiling tube. Add 10 cm3 of 2 mol l-1 H2SO4 , quickly stopper the boiling tube and collect the gas. ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 3. What 2 temperatures measure the same amount during a phase change of a liquid pure solvent to a solid? 4. Know how to read phase diagrams. Sketch a quick diagram locating the triple point, critical point, the melting point /freezing point line and the boiling point/condensation point line. Also l ...
... 3. What 2 temperatures measure the same amount during a phase change of a liquid pure solvent to a solid? 4. Know how to read phase diagrams. Sketch a quick diagram locating the triple point, critical point, the melting point /freezing point line and the boiling point/condensation point line. Also l ...
IB:Enthalpy Review Questions
... b) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? c) Explain what this implies in terms of the chemical potential energy contained in the reactants and products. d) Draw an energy level diagram for this reaction. Clearly label the reactant side, product side, the enthalpy of reaction, and the activation ...
... b) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? c) Explain what this implies in terms of the chemical potential energy contained in the reactants and products. d) Draw an energy level diagram for this reaction. Clearly label the reactant side, product side, the enthalpy of reaction, and the activation ...
Unit 8 Test Review
... Apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to get the same number of atoms of every element on each side of the equation. Tip: Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant and product. Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balance ...
... Apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to get the same number of atoms of every element on each side of the equation. Tip: Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant and product. Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balance ...
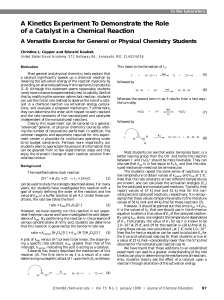
JCE0198 p0087 A Kinetics Experiment To Demonstrate the Role of
... Most students can see that water, being less basic, is a better leaving group than the OH{ and hence the reaction between I{ and H3O 2+ should be more favorable. They can also see that kcat is in fact equal to K1 kH and that the catalyzed mechanism need not be termolecular. The students repeat the s ...
... Most students can see that water, being less basic, is a better leaving group than the OH{ and hence the reaction between I{ and H3O 2+ should be more favorable. They can also see that kcat is in fact equal to K1 kH and that the catalyzed mechanism need not be termolecular. The students repeat the s ...
Combined
... 1. (a) Sodium hydroxide solution reacts with carbon dioxide gas [1] in air to form sodium carbonate: 2NaOH(aq) + CO2(g) Na2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) [1] The sodium carbonate formed reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid [1] to give colourless bubbles of carbon dioxide gas: Na2CO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + ...
... 1. (a) Sodium hydroxide solution reacts with carbon dioxide gas [1] in air to form sodium carbonate: 2NaOH(aq) + CO2(g) Na2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) [1] The sodium carbonate formed reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid [1] to give colourless bubbles of carbon dioxide gas: Na2CO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + ...
Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... electrons - it is Positively Charged ➲ If an atom has more electrons than protons it is Negatively Charged. ➲ Atoms of opposite charge are attracted to each other. ➲ There are three types of chemical bonds. Ionic bonds, Covalent Bonds, & Hydrogen bonds. ...
... electrons - it is Positively Charged ➲ If an atom has more electrons than protons it is Negatively Charged. ➲ Atoms of opposite charge are attracted to each other. ➲ There are three types of chemical bonds. Ionic bonds, Covalent Bonds, & Hydrogen bonds. ...
Single Replacement Reactions - Tri
... • Determined by the amount of oxygen. • Incomplete combustion occurs when there isn't enough oxygen to allow the fuel (usually a hydrocarbon) to react completely. • Carbon monoxide and pure carbon will be produced in addition to carbon dioxide and water in incomplete combustion. ...
... • Determined by the amount of oxygen. • Incomplete combustion occurs when there isn't enough oxygen to allow the fuel (usually a hydrocarbon) to react completely. • Carbon monoxide and pure carbon will be produced in addition to carbon dioxide and water in incomplete combustion. ...
Quiz Samples
... Gas occupies all the volume available T F Calculate the final pressure formed after the containers 1 and 2 were connected: Total volume= 1L+2L=3L; total amount of gas Container 1, 1L under 2 atm of gas Container 2, 2L under 1 atm of gas at normal pressure= 4L*atm (2 L in Container 1 and 2 L in Conta ...
... Gas occupies all the volume available T F Calculate the final pressure formed after the containers 1 and 2 were connected: Total volume= 1L+2L=3L; total amount of gas Container 1, 1L under 2 atm of gas Container 2, 2L under 1 atm of gas at normal pressure= 4L*atm (2 L in Container 1 and 2 L in Conta ...
The Periodic Table
... the core of an atom, called the nucleus The number of protons and neutrons add together to give the mass of the atom – each is designated a mass of 1 amu ...
... the core of an atom, called the nucleus The number of protons and neutrons add together to give the mass of the atom – each is designated a mass of 1 amu ...
2011-2012 Paper 1
... 6. Chlorine has a relative atomic mass of 35.5 and has two isotopes with relative isotopic masses of 35 and 37. Which of the following statements about chlorine are CORRECT? (1) The isotopes have same atomic number. (2) It contains the two isotopes, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, in a ratio of 1:3. (3 ...
... 6. Chlorine has a relative atomic mass of 35.5 and has two isotopes with relative isotopic masses of 35 and 37. Which of the following statements about chlorine are CORRECT? (1) The isotopes have same atomic number. (2) It contains the two isotopes, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, in a ratio of 1:3. (3 ...
Ms - cloudfront.net
... Bonding 18. Describe how a cation and an anion is formed. 19. What do metals typically do when they become ions? What about nonmetals? 20. What type of elements bond together in ionic bonds? covalent bonds? metallic bonds? 21. How do electrons in ionic bonding interact? Covalent bonding? 22. How doe ...
... Bonding 18. Describe how a cation and an anion is formed. 19. What do metals typically do when they become ions? What about nonmetals? 20. What type of elements bond together in ionic bonds? covalent bonds? metallic bonds? 21. How do electrons in ionic bonding interact? Covalent bonding? 22. How doe ...
Chem 106 Week 10.2017
... Write a complete balanced chemical equation for the reaction by adding products and stoichiometric coefficients from the above reactants. ...
... Write a complete balanced chemical equation for the reaction by adding products and stoichiometric coefficients from the above reactants. ...
Equations - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... In the exam, you will be asked to write, or complete, word equations and chemical equations (balanced symbol equations), and you might need to add state symbols to an equation. This unit will help you to write these types of equation and to get information from equations. ...
... In the exam, you will be asked to write, or complete, word equations and chemical equations (balanced symbol equations), and you might need to add state symbols to an equation. This unit will help you to write these types of equation and to get information from equations. ...
Gr.8. Curriculum Document - Taryam American private School
... Describe the relationship between voltage and electric current Describe the relationship between resistance and electric current Identify the parts of an electric circuit Explain how to draw a circuit diagram Distinguish between series and parallel circuits Describe some devices that mak ...
... Describe the relationship between voltage and electric current Describe the relationship between resistance and electric current Identify the parts of an electric circuit Explain how to draw a circuit diagram Distinguish between series and parallel circuits Describe some devices that mak ...
Chemistry A - Montgomery County Public Schools
... compare solutions to suspensions and colloids. differentiate among elements, compounds, mixtures and solutions. distinguish between physical and chemical changes. Formula Writing determine the number and types of atoms represented by a given formula. write names and formulas for ionic and ...
... compare solutions to suspensions and colloids. differentiate among elements, compounds, mixtures and solutions. distinguish between physical and chemical changes. Formula Writing determine the number and types of atoms represented by a given formula. write names and formulas for ionic and ...
Metals
... Many compounds, particularly ionic compounds (eg: NaCl) exist as an array of ions or atoms bound to each other but with no recognisable molecules. The formula NaCl instead tells us that throughout a sample of NaCl sodium and chlorine atoms are present in the ratio 1:1. Because ionic compounds do not ...
... Many compounds, particularly ionic compounds (eg: NaCl) exist as an array of ions or atoms bound to each other but with no recognisable molecules. The formula NaCl instead tells us that throughout a sample of NaCl sodium and chlorine atoms are present in the ratio 1:1. Because ionic compounds do not ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.