PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... drawings, which should be done in pencil. You may use scrap paper to work out the answers to the questions, but be sure to record all your answers on your separate answer sheet or in your answer booklet as directed. When you have completed the examination, you must sign the statement printed on your ...
... drawings, which should be done in pencil. You may use scrap paper to work out the answers to the questions, but be sure to record all your answers on your separate answer sheet or in your answer booklet as directed. When you have completed the examination, you must sign the statement printed on your ...
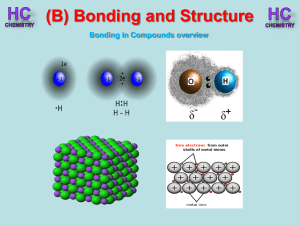
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Copper sulphate contains the Cu2+ and the SO42- ions. There is, therefore, covalent bonding and ionic bonding in copper sulphate A solution of copper sulphate can conduct electricity. Molten ionic compounds can also conduct electricity. ...
... Copper sulphate contains the Cu2+ and the SO42- ions. There is, therefore, covalent bonding and ionic bonding in copper sulphate A solution of copper sulphate can conduct electricity. Molten ionic compounds can also conduct electricity. ...
r - Personal.psu.edu
... opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field ...
... opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field ...
File
... m) Non-metal: any element that is found on the right-hand side of the staircase line on the Periodic Table; tends to gain or share electrons to complete a stable octet electron arrangement. n) Metalloid: an element that is found close to the staircase line on the Periodic Table and has properties o ...
... m) Non-metal: any element that is found on the right-hand side of the staircase line on the Periodic Table; tends to gain or share electrons to complete a stable octet electron arrangement. n) Metalloid: an element that is found close to the staircase line on the Periodic Table and has properties o ...
CHEMSTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS (Form B)
... ST 0.278 kJ mol-1 K 1 (c) Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔHo, That occurs when 0.256 mol sample of NF3(g) is formed from N2(g) and F2(g) at 1.0 atm and 298K. From the chemical equation, -264 kJ standard enthalpy change occurs when 2 moles of NF3(g) are produced at 1.0 atm and 298 K, ...
... ST 0.278 kJ mol-1 K 1 (c) Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔHo, That occurs when 0.256 mol sample of NF3(g) is formed from N2(g) and F2(g) at 1.0 atm and 298K. From the chemical equation, -264 kJ standard enthalpy change occurs when 2 moles of NF3(g) are produced at 1.0 atm and 298 K, ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has high ionization energy, its electron affinity is also high. 35. (a) An electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric current when it is dissolved in water. (b) Ionic compounds are electrolytes because they separate into ...
... small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has high ionization energy, its electron affinity is also high. 35. (a) An electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric current when it is dissolved in water. (b) Ionic compounds are electrolytes because they separate into ...
quiz questions chapters 1
... Which of the following is true about the scientific method? A) A hypothesis is a set of observations that are explained by an experiment. B) Researchers design experiments to prove the conclusions they have already reached. C) The purpose of performing an experiment is to confirm or contradict a hyp ...
... Which of the following is true about the scientific method? A) A hypothesis is a set of observations that are explained by an experiment. B) Researchers design experiments to prove the conclusions they have already reached. C) The purpose of performing an experiment is to confirm or contradict a hyp ...
Assignment CHE-04 TMA-01,02 Year 2005
... 7. 50 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas occupies a volume of 0.8314 m3 at 1.50×105 Pa and 3.00×102 K. The gas undergoes expansion and the final pressure is 7.50×104 Pa. Calculate the final volume of the gas, assuming that it proceeds through (i) reversible isothermal process and (ii) reversible adiabat ...
... 7. 50 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas occupies a volume of 0.8314 m3 at 1.50×105 Pa and 3.00×102 K. The gas undergoes expansion and the final pressure is 7.50×104 Pa. Calculate the final volume of the gas, assuming that it proceeds through (i) reversible isothermal process and (ii) reversible adiabat ...
chapter 4 review: types of chemical reactions and solution
... (a) potassium chloride (aq) + lead (II) nitrate (aq) (b) silver nitrate (aq) + magnesium bromide (aq) (c) calcium hydroxide (aq) + ferric chloride (aq) Write molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations. 4. Aqueous nickel (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide molecular: ...
... (a) potassium chloride (aq) + lead (II) nitrate (aq) (b) silver nitrate (aq) + magnesium bromide (aq) (c) calcium hydroxide (aq) + ferric chloride (aq) Write molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations. 4. Aqueous nickel (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide molecular: ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – The Basics of
... (think H-NOF). These bonds are usually depicted with a dotted line. Because they occur between two different molecules and not within one molecule (like ionic or covalent bonds) and they occur between partial (not full) charges, hydrogen bonds are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. 16. Chemical re ...
... (think H-NOF). These bonds are usually depicted with a dotted line. Because they occur between two different molecules and not within one molecule (like ionic or covalent bonds) and they occur between partial (not full) charges, hydrogen bonds are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. 16. Chemical re ...
AP Chem
... If this reaction occurs at STP, approximately how many liters of O2 is required to produce 70g of FeO? A. 22 B. 33 C. 44 D. 55 E. 66 19. A beaker containing 150ml of .2M Pb(NO3)2 is added to a beaker containing 50ml of .2M MgCl2. What is the final concentration of Pb2+ ions in the solution? A. .2M B ...
... If this reaction occurs at STP, approximately how many liters of O2 is required to produce 70g of FeO? A. 22 B. 33 C. 44 D. 55 E. 66 19. A beaker containing 150ml of .2M Pb(NO3)2 is added to a beaker containing 50ml of .2M MgCl2. What is the final concentration of Pb2+ ions in the solution? A. .2M B ...
Sherbert
... reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates; chemical reactions may be represented by balanced chemical equations. ...
... reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates; chemical reactions may be represented by balanced chemical equations. ...
Semester 2 Review
... 50. What is a catalyst? How is an enzyme like a catalyst? How do catalysts work? ...
... 50. What is a catalyst? How is an enzyme like a catalyst? How do catalysts work? ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... When electricity is applied to liquid water, it decomposes into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Mercury(II) oxide is heated to produce solid mercury and gaseous oxygen. Aqueous potassium iodide and aqueous lead(II) nitrate react to produce solid lead(II) iodide and a solution of potassium nitrate. Soli ...
... When electricity is applied to liquid water, it decomposes into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Mercury(II) oxide is heated to produce solid mercury and gaseous oxygen. Aqueous potassium iodide and aqueous lead(II) nitrate react to produce solid lead(II) iodide and a solution of potassium nitrate. Soli ...
File - Mc Guckin Science
... o) Electron Configuration: a way of showing where the electrons are found in an atom. Includes the number of electrons found in each quantum level of the atom, arranged in order from lowest to highest energy. p) Orbital: a region in three-dimensional space around the nucleus of an atom where there i ...
... o) Electron Configuration: a way of showing where the electrons are found in an atom. Includes the number of electrons found in each quantum level of the atom, arranged in order from lowest to highest energy. p) Orbital: a region in three-dimensional space around the nucleus of an atom where there i ...
Document
... b) Mixing of Mn(VII) compounds with Mn(IV) compounds to form Mn(VI) compounds in alkaline medium. 2 MnO4- + MnO2 + 4 OH- ...
... b) Mixing of Mn(VII) compounds with Mn(IV) compounds to form Mn(VI) compounds in alkaline medium. 2 MnO4- + MnO2 + 4 OH- ...
Potential Energy and Potential W5D1
... A. The total flux entering a surface is equal to the charge on the other side of the surface divided by e0 . B. The flux leaving a volume is equal to the charge inside multiplied by e0 C. The flux leaving a closed volume multiplied by e0 is equal to the charge enclosed in the volume. D. None of thes ...
... A. The total flux entering a surface is equal to the charge on the other side of the surface divided by e0 . B. The flux leaving a volume is equal to the charge inside multiplied by e0 C. The flux leaving a closed volume multiplied by e0 is equal to the charge enclosed in the volume. D. None of thes ...
Introduction to Chemistry and the Metric System
... Lewis Structures for atoms, ions, and molecular (covalent) compounds shared pair of electrons, unshared pair, single bond, double bond, triple bond VSEPR Theory, hybrid orbitals, shapes of molecules, sigma bonds, pi bonds, polarity Intermolecular Forces (in order from weakest to strongest): ...
... Lewis Structures for atoms, ions, and molecular (covalent) compounds shared pair of electrons, unshared pair, single bond, double bond, triple bond VSEPR Theory, hybrid orbitals, shapes of molecules, sigma bonds, pi bonds, polarity Intermolecular Forces (in order from weakest to strongest): ...
full text - pdf 452 kB
... increasing temperature. Most isocoulombic reactions where an ion reacts with a neutral species have smaller absolute values of AC, and positive AS values (11,14). These negative values indicate that the water structure becomes more organized with the formation of the complex. One possible explanatio ...
... increasing temperature. Most isocoulombic reactions where an ion reacts with a neutral species have smaller absolute values of AC, and positive AS values (11,14). These negative values indicate that the water structure becomes more organized with the formation of the complex. One possible explanatio ...
Thermochemistry - Ars
... The enthalpy of a reaction from the thermochemical equation is a conversion factor that can be used to calculate the amount of heat generated or absorbed by a reaction for an amount different than the stoichiometric amounts from the balanced chemical equation. The conversion factors are based on the ...
... The enthalpy of a reaction from the thermochemical equation is a conversion factor that can be used to calculate the amount of heat generated or absorbed by a reaction for an amount different than the stoichiometric amounts from the balanced chemical equation. The conversion factors are based on the ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.