Learning Activities
... Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of observing, experimenting, predicting, and validating to think critically. 9-12 Benchmark I: Use accepted scientific methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data and observations and to design ...
... Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of observing, experimenting, predicting, and validating to think critically. 9-12 Benchmark I: Use accepted scientific methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data and observations and to design ...
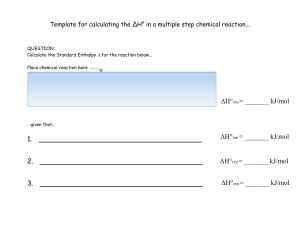
Template for calculating the ΔH° in a multiple step chemical reaction
... 20. _______________ systems can exchange energy and mass, whereas ________________ systems allow the transfer of energy (heat) but not mass. 21. What is the third type of system in Thermochemistry? __________________ 22. LIST three examples of an intensive property: 23. LIST three examples of an ext ...
... 20. _______________ systems can exchange energy and mass, whereas ________________ systems allow the transfer of energy (heat) but not mass. 21. What is the third type of system in Thermochemistry? __________________ 22. LIST three examples of an intensive property: 23. LIST three examples of an ext ...
SUPPORT MATERIAL CLASS – X(science) FIRST TERM
... elements is same on both sides of the arrow is called balanced chemical equation. 4) The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such as— a) Combination reaction – The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance are called combination reaction. For exa ...
... elements is same on both sides of the arrow is called balanced chemical equation. 4) The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such as— a) Combination reaction – The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance are called combination reaction. For exa ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... Neon has an octet of electrons in its outer shell, and - indeed - a full outer shell. We observe that this type of arrangement is associated with stability. (By ‘this type of arrangement’ I mean either a full outer shell or an octet of electrons in the outer shell. Helium has the former, but not the ...
... Neon has an octet of electrons in its outer shell, and - indeed - a full outer shell. We observe that this type of arrangement is associated with stability. (By ‘this type of arrangement’ I mean either a full outer shell or an octet of electrons in the outer shell. Helium has the former, but not the ...
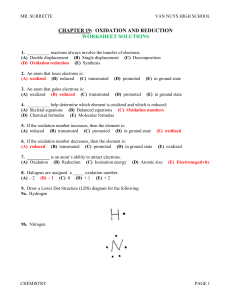
Solutions_C19
... 16. For the above reaction, identify the element that is oxidized and the element that is reduced. 16A. Carbon is oxidized and iodine is reduced. 17. Predict the oxidation numbers for the carbonate ion, CO3-2. 17A. Each oxygen has a – 2 oxidation number. Since there are 3 oxygen atoms in CO3-2, they ...
... 16. For the above reaction, identify the element that is oxidized and the element that is reduced. 16A. Carbon is oxidized and iodine is reduced. 17. Predict the oxidation numbers for the carbonate ion, CO3-2. 17A. Each oxygen has a – 2 oxidation number. Since there are 3 oxygen atoms in CO3-2, they ...
lewis dot diagrams (structures) for atoms and ions predicting
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
Document
... elements is same on both sides of the arrow is called balanced chemical equation. 4) The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such as— a) Combination reaction – The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance are called combination reaction. For exa ...
... elements is same on both sides of the arrow is called balanced chemical equation. 4) The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such as— a) Combination reaction – The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance are called combination reaction. For exa ...
Preparation of spherical DDNP study Liu off on a journey
... Wastewater volume. Pot liquor recycling program was first dispersed picric acid with fresh Water, the second and third pan pot for each half of the first mother liquor with each pot produced Liquor (including some washed with water) by 650 ~ 700kg meter, three pot scrap The total amount of water is ...
... Wastewater volume. Pot liquor recycling program was first dispersed picric acid with fresh Water, the second and third pan pot for each half of the first mother liquor with each pot produced Liquor (including some washed with water) by 650 ~ 700kg meter, three pot scrap The total amount of water is ...
Higher Chemistry Learning Outcomes
... The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms. The second and subsequent ionisation energies refer to the energies required to remove further moles of electrons. The trends in first ionisation energy across periods and down gr ...
... The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms. The second and subsequent ionisation energies refer to the energies required to remove further moles of electrons. The trends in first ionisation energy across periods and down gr ...
matter
... • It is important to understand that when matter undergoes a chemical reaction (a chemical change) it does not disappear or appear – The atoms are rearranged and form new bonds, but no matter is lost nor gained ...
... • It is important to understand that when matter undergoes a chemical reaction (a chemical change) it does not disappear or appear – The atoms are rearranged and form new bonds, but no matter is lost nor gained ...
Chemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Recovery
... add an additional 2 mL 3.0 M NaOH dropwise on top of the floating solid. 19. Decant (pour off) the clear solution with minimal loss of the precipitate. The trick is not to pour a little and then stop; then pour a little more, then stop, etc – this will just stir up the solid in the bottom of the bea ...
... add an additional 2 mL 3.0 M NaOH dropwise on top of the floating solid. 19. Decant (pour off) the clear solution with minimal loss of the precipitate. The trick is not to pour a little and then stop; then pour a little more, then stop, etc – this will just stir up the solid in the bottom of the bea ...
Final Exam Practice Questions for General Chemistry NOTICE TO
... 28. Many classical experiments have given us indirect evidence of the nature of the atom. Which of the experiments listed below did not give the result described? a) The line spectrum of the hydrogen atom implied that the electronic energies are quantized. b) Millikan’s oil drop experiment provided ...
... 28. Many classical experiments have given us indirect evidence of the nature of the atom. Which of the experiments listed below did not give the result described? a) The line spectrum of the hydrogen atom implied that the electronic energies are quantized. b) Millikan’s oil drop experiment provided ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _C__ 47) Which of the following atoms acquires the most negative charge in a covalent bond with hydrogen? a. C b. Na c. O d. S (Oxygen has the highest electronegativity (EN)) _B__ 48) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? (dispersion is just from the moving e-) a. dipole intera ...
... _C__ 47) Which of the following atoms acquires the most negative charge in a covalent bond with hydrogen? a. C b. Na c. O d. S (Oxygen has the highest electronegativity (EN)) _B__ 48) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? (dispersion is just from the moving e-) a. dipole intera ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 66. Know the definitions of Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases and be able to classify a substance as one or more of these based on its dissociation reaction 67. Know what pH means and where acids and bases appear on the pH scale 68. Be able to use the pH equation to calculate pH from hydr ...
... 66. Know the definitions of Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases and be able to classify a substance as one or more of these based on its dissociation reaction 67. Know what pH means and where acids and bases appear on the pH scale 68. Be able to use the pH equation to calculate pH from hydr ...
ionic bond. - cloudfront.net
... ionization energy • Low EN; give up electrons easily. • Metals have luster (shine), are malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). ...
... ionization energy • Low EN; give up electrons easily. • Metals have luster (shine), are malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). ...
1 - Study Hungary
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
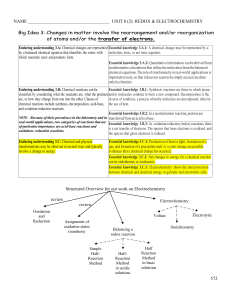
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.