Slide 1
... Capacitance is basically the ability of an electric conductor to store an electric charge, and is usually defined as the total electric charge placed on the object divided by the potential of the object, C=Q/V with the capacitance “C” in Farads (F), the charge “Q” in Coulombs (C), and the potential ...
... Capacitance is basically the ability of an electric conductor to store an electric charge, and is usually defined as the total electric charge placed on the object divided by the potential of the object, C=Q/V with the capacitance “C” in Farads (F), the charge “Q” in Coulombs (C), and the potential ...
A-level Chemistry Modified question paper Unit 01
... the least polar bond and is formed by chemical combination of two of the elements from TABLE 3. [1 mark] ...
... the least polar bond and is formed by chemical combination of two of the elements from TABLE 3. [1 mark] ...
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... In a laboratory investigation, a student constructs a voltaic cell with iron and copper electrodes. Another student constructs a voltaic cell with zinc and iron electrodes. Testing the cells during operation enables the students to write the balanced ionic equations below. Cell with iron and copper ...
... In a laboratory investigation, a student constructs a voltaic cell with iron and copper electrodes. Another student constructs a voltaic cell with zinc and iron electrodes. Testing the cells during operation enables the students to write the balanced ionic equations below. Cell with iron and copper ...
Paper 3 - TheAllPapers
... (b) Impure copper is extracted from the ore. This copper is refined by electrolysis. (i) Name; the material used for the positive electrode (anode), ...
... (b) Impure copper is extracted from the ore. This copper is refined by electrolysis. (i) Name; the material used for the positive electrode (anode), ...
Optional Extra Credit Exercise
... a, V at a point is the electric potential energy per unit charge at that point. b, We are normally only interested in difference in potential. c, V is a vector so it s direction must be considered. d, The units of V may be expressed as Joule/Coulomb. My answer was D and the other students got C. Dis ...
... a, V at a point is the electric potential energy per unit charge at that point. b, We are normally only interested in difference in potential. c, V is a vector so it s direction must be considered. d, The units of V may be expressed as Joule/Coulomb. My answer was D and the other students got C. Dis ...
1. Potentiometric determination of the dissociation constant of week
... consists of a single phase, or we may say the solution is a one-phase system. The components which constitutes the largest proportion of the solution is called the solvent, while the other, the dissolved substance, is referred to as the solute. A solution may be gaseous, liquid or solid. This treatm ...
... consists of a single phase, or we may say the solution is a one-phase system. The components which constitutes the largest proportion of the solution is called the solvent, while the other, the dissolved substance, is referred to as the solute. A solution may be gaseous, liquid or solid. This treatm ...
3. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is
... As you learned in health and biology, food energy typically comes from carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The amount of energy that the body can use per gram of these substances is not the same. The following balanced exothermic reaction represents combustion (respiration) of glucose (a carbohydrate) ...
... As you learned in health and biology, food energy typically comes from carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The amount of energy that the body can use per gram of these substances is not the same. The following balanced exothermic reaction represents combustion (respiration) of glucose (a carbohydrate) ...
Chemical Kinetics
... easy matter to replace the units moles/liter by any other units (e.g., pressure in atmospheres) to obtain the proper units for the rate constants if quantities other than concentration are being measured Half-Life and Shelf Life The half-life is the time required for one-half of the material to disa ...
... easy matter to replace the units moles/liter by any other units (e.g., pressure in atmospheres) to obtain the proper units for the rate constants if quantities other than concentration are being measured Half-Life and Shelf Life The half-life is the time required for one-half of the material to disa ...
File
... 6. What is the effect of adding more CO2 to the following equilibrium reaction? CO2 + H2O↔ H2CO3 a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More H2O is produced. c. The equilibrium d. No Change 7. Two opposing reactions (A + B ↔C + D) occurring simultaneously at the same rate is an example of: a. reversibility. ...
... 6. What is the effect of adding more CO2 to the following equilibrium reaction? CO2 + H2O↔ H2CO3 a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More H2O is produced. c. The equilibrium d. No Change 7. Two opposing reactions (A + B ↔C + D) occurring simultaneously at the same rate is an example of: a. reversibility. ...
ACP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam - Doc-U-Ment
... A) the sharing of electrons. B) the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. D) the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms. E) the attraction between 2 metal atoms. 7) Determine the name for aqueous HBr. A) bromic acid B) bromo ...
... A) the sharing of electrons. B) the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. D) the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms. E) the attraction between 2 metal atoms. 7) Determine the name for aqueous HBr. A) bromic acid B) bromo ...
ch-4-earth-chemistry
... Chemical formula – a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound. Also, shows the numbers of atoms of each element required to make up a molecule of a compound. ...
... Chemical formula – a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound. Also, shows the numbers of atoms of each element required to make up a molecule of a compound. ...
2A6
... some molecules had broken into two identical ball-shaped protrusions. The S-S bond of a single (CH3S)2 molecule on both Cu(111) and Ag(111) is dissociated to produce two CH3S molecules through vibrational excitation of the S-S stretching mode by injecting tunneling electrons (> 0.36 eV) from the STM ...
... some molecules had broken into two identical ball-shaped protrusions. The S-S bond of a single (CH3S)2 molecule on both Cu(111) and Ag(111) is dissociated to produce two CH3S molecules through vibrational excitation of the S-S stretching mode by injecting tunneling electrons (> 0.36 eV) from the STM ...
Chemical reaction model:
... Irradiation of UHMWPE in air results in the formation of free alkyl radicals. Irradiation produces radicals randomly and uniformly throughout the polymer, irrespective of the crystal morphology [7]. The initial radicals formed are essentially alkyl radicals that react with oxygen to degrade to allyl ...
... Irradiation of UHMWPE in air results in the formation of free alkyl radicals. Irradiation produces radicals randomly and uniformly throughout the polymer, irrespective of the crystal morphology [7]. The initial radicals formed are essentially alkyl radicals that react with oxygen to degrade to allyl ...
Document
... chemical, can be prepared by heating hexane (C6H14) at 800°C. C6H14 C2H4 + other products If the yield of ethylene production is 42.5 percent, what mass of hexane must be reacted to produce 481 g of ethylene? ...
... chemical, can be prepared by heating hexane (C6H14) at 800°C. C6H14 C2H4 + other products If the yield of ethylene production is 42.5 percent, what mass of hexane must be reacted to produce 481 g of ethylene? ...
Chem 12 Prov Exam PLO Review
... describe the activated complex in terms of its potential energy (PE), stability and structure define activation energy describe the relationship between activation energy and rate of reaction describe the changes in KE and PE as reactant molecules approach each other draw and label PE diagrams for b ...
... describe the activated complex in terms of its potential energy (PE), stability and structure define activation energy describe the relationship between activation energy and rate of reaction describe the changes in KE and PE as reactant molecules approach each other draw and label PE diagrams for b ...
Semester Exam Review
... (ii) the volume of the H2O(g) released, measured at 220.C and 735 mm Hg. (c) A 0.345 g sample of anhydrous BeC2O4, which contains an inert impurity, was dissolved in sufficient water to produce 100. mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of the solution was titrated with KMnO4(aq). The balanced equation ...
... (ii) the volume of the H2O(g) released, measured at 220.C and 735 mm Hg. (c) A 0.345 g sample of anhydrous BeC2O4, which contains an inert impurity, was dissolved in sufficient water to produce 100. mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of the solution was titrated with KMnO4(aq). The balanced equation ...
Ion Sources
... – KN (3.7 MV) and JN (1.5 MV) are “singleended”, meaning the ion source is inside the terminal, producing positively charged beams. – FN (10.6 MV) is a “tandem” accelerator, with the terminal electrode in the center of the accelerator, requiring negatively charged beams external to the accelerator. ...
... – KN (3.7 MV) and JN (1.5 MV) are “singleended”, meaning the ion source is inside the terminal, producing positively charged beams. – FN (10.6 MV) is a “tandem” accelerator, with the terminal electrode in the center of the accelerator, requiring negatively charged beams external to the accelerator. ...
UG_Lab_Course_Ion_Sources
... – KN (3.7 MV) and JN (1.5 MV) are “singleended”, meaning the ion source is inside the terminal, producing positively charged beams. – FN (10.6 MV) is a “tandem” accelerator, with the terminal electrode in the center of the accelerator, requiring negatively charged beams external to the accelerator. ...
... – KN (3.7 MV) and JN (1.5 MV) are “singleended”, meaning the ion source is inside the terminal, producing positively charged beams. – FN (10.6 MV) is a “tandem” accelerator, with the terminal electrode in the center of the accelerator, requiring negatively charged beams external to the accelerator. ...
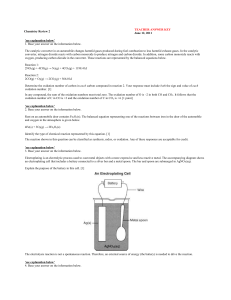
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.