CHAPTER 9 HYDROGEN Position of Hydrogen in Periodic Table
... Half life period is 0.3 sec and therefore, it immediately gets converted into the molecular form liberating a large amount of energy which is used for cutting and welding purposes. ...
... Half life period is 0.3 sec and therefore, it immediately gets converted into the molecular form liberating a large amount of energy which is used for cutting and welding purposes. ...
Oxidation Reactions of Lanthanide Cations with N2O and O2
... The lanthanide cations all have positive affinities for O atoms and are summarized in Table 1. Values for OA(Ln+) in Table 1 are based on values for ∆Hfo(LnO) tabulated in ref 19 and values for ∆Hfo(Ln), ∆Hfo(O), IE(Ln), and IE(LnO) found in ref 20. They range from 88.1 ( 5.9 kcal mol-1 for Yb+ to 2 ...
... The lanthanide cations all have positive affinities for O atoms and are summarized in Table 1. Values for OA(Ln+) in Table 1 are based on values for ∆Hfo(LnO) tabulated in ref 19 and values for ∆Hfo(Ln), ∆Hfo(O), IE(Ln), and IE(LnO) found in ref 20. They range from 88.1 ( 5.9 kcal mol-1 for Yb+ to 2 ...
Are diglycolamide ligands hard or soft Lewis bases?
... donated by the ligand (Lewis base) to the central metal ion (Lewis acid) in the complex. Hard ligands donate little electron density, and interact with the metal ion mainly via electrostatic attraction, forming the M–L bonds of mainly ionic character. Soft ligands donate much more electron density, ...
... donated by the ligand (Lewis base) to the central metal ion (Lewis acid) in the complex. Hard ligands donate little electron density, and interact with the metal ion mainly via electrostatic attraction, forming the M–L bonds of mainly ionic character. Soft ligands donate much more electron density, ...
CHAPTER 2
... form a ______________. Since not _____________ bonds need to be _____________, the different substances that make up a mixture can be ___________________ using physical _______________ ________________. A solution is a ___________________ mixture (consisting of at least one ________ and one ______ ...
... form a ______________. Since not _____________ bonds need to be _____________, the different substances that make up a mixture can be ___________________ using physical _______________ ________________. A solution is a ___________________ mixture (consisting of at least one ________ and one ______ ...
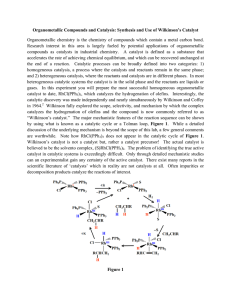
Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis
... Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis and Use of Wilkinson’s Catalyst Organometallic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds which contain a metal carbon bond. Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industria ...
... Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis and Use of Wilkinson’s Catalyst Organometallic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds which contain a metal carbon bond. Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industria ...
Honors Chemistry
... We don’t count solids or liquid water in K expressions, so… Ksp = Ksp = solubility product constant (only for products) K = more soluble For… Ag2SO4(s) ...
... We don’t count solids or liquid water in K expressions, so… Ksp = Ksp = solubility product constant (only for products) K = more soluble For… Ag2SO4(s) ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 7. What does it mean when an equilibrium system is described as a dynamic system? Explain. Dynamic is a term that refers to a process that never stops – the forward process & reverse processes occur at the same rate giving the appearance that the process has stopped, but that is NOT the case. 8. Dra ...
... 7. What does it mean when an equilibrium system is described as a dynamic system? Explain. Dynamic is a term that refers to a process that never stops – the forward process & reverse processes occur at the same rate giving the appearance that the process has stopped, but that is NOT the case. 8. Dra ...
the Language of Chemistry
... Some questions that I have been often asked by the students and parents alike have been—“What do we do by learning Chemistry?” “For a student of Literature or even History what role can Chemistry play?” But the answers came very simply. A mother administering her child a tablet for fever should know ...
... Some questions that I have been often asked by the students and parents alike have been—“What do we do by learning Chemistry?” “For a student of Literature or even History what role can Chemistry play?” But the answers came very simply. A mother administering her child a tablet for fever should know ...
practice exercise - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Solution Elements that are in the same group of the periodic table are most likely to exhibit similar chemical and physical properties. We therefore expect that Ca and Mg should be most alike because they are in the same group (2A, the alkaline earth metals). ...
... Solution Elements that are in the same group of the periodic table are most likely to exhibit similar chemical and physical properties. We therefore expect that Ca and Mg should be most alike because they are in the same group (2A, the alkaline earth metals). ...
Polarizability
... proton in the nucleus, so their polarizability is usually quite small. Only larger positively charged ions can be easily polarizable. Negative ions are easily polarizable because they have a larger electron cloud that tends to be more polarizable. Small, positively charged ions can easily distort th ...
... proton in the nucleus, so their polarizability is usually quite small. Only larger positively charged ions can be easily polarizable. Negative ions are easily polarizable because they have a larger electron cloud that tends to be more polarizable. Small, positively charged ions can easily distort th ...
CHEMISTRY NOTES – CHAPTERS 20 AND 21
... If the pH is less than 7 the solution is considered to be acidic ([H+] >1.0 x 10-7 and [OH-]<1.0 x 10-7) and if the pH is above 7 the solution is considered to be basic, or alkaline ([H+]<1.0 x 10-7 and [OH-]>1.0 x 10-7). If the hydrogen ion (H+) ion increases the hydroxide ion (OH-) will decrease a ...
... If the pH is less than 7 the solution is considered to be acidic ([H+] >1.0 x 10-7 and [OH-]<1.0 x 10-7) and if the pH is above 7 the solution is considered to be basic, or alkaline ([H+]<1.0 x 10-7 and [OH-]>1.0 x 10-7). If the hydrogen ion (H+) ion increases the hydroxide ion (OH-) will decrease a ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... 4. A physical change results in the rearrangement of existing particles in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on w ...
... 4. A physical change results in the rearrangement of existing particles in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on w ...
formula writing and nomenclature of inorganic - Parkway C-2
... As an example, consider the formation of sodium chloride, table salt, from its elements: 2 Na + Cl2 → 2 Na+ClIn this reaction, each sodium atom is considered to have transferred one electron to each chlorine atom forming, as a result, charged atoms or ions. Since each sodium atom has lost one electr ...
... As an example, consider the formation of sodium chloride, table salt, from its elements: 2 Na + Cl2 → 2 Na+ClIn this reaction, each sodium atom is considered to have transferred one electron to each chlorine atom forming, as a result, charged atoms or ions. Since each sodium atom has lost one electr ...
Unit 3: Chemical Kinetics
... topics that we need to first examine - reaction mechanisms and the concept of threshold energy. ...
... topics that we need to first examine - reaction mechanisms and the concept of threshold energy. ...
Test 4 Review
... Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass, and the chemical properties. He arranged the cards in order of increasing atomic mass and noticed a pattern: MENDELEEV'S PERIODIC LAW – When the elements are ...
... Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass, and the chemical properties. He arranged the cards in order of increasing atomic mass and noticed a pattern: MENDELEEV'S PERIODIC LAW – When the elements are ...
1 Unit 11-12: Equilibrium and Acid/Bases Notes Colligative
... ‐ more moles (therefore particles) available to react in a 6.0M solution vs. a 0.10M solution ‐ copper will react faster with 6.0 M acid than 0.10 M. ...
... ‐ more moles (therefore particles) available to react in a 6.0M solution vs. a 0.10M solution ‐ copper will react faster with 6.0 M acid than 0.10 M. ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.