Mock Exam 2 1. Which of the following s
... b. To produce NAD+ in order to continue glycolysis c. To produce NADH in order to continue glycolysis d. To prevent further increases in oxygen debt If an enzyme solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain an even faster yield of products is to a. Add more of the enzyme b. ...
... b. To produce NAD+ in order to continue glycolysis c. To produce NADH in order to continue glycolysis d. To prevent further increases in oxygen debt If an enzyme solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain an even faster yield of products is to a. Add more of the enzyme b. ...
Document
... • Absorb light with a maximum at 680 nm All photosynthetic cells have P700. Both are present in O2 evolving organisms higher plants, algae and cyanobacteria. ...
... • Absorb light with a maximum at 680 nm All photosynthetic cells have P700. Both are present in O2 evolving organisms higher plants, algae and cyanobacteria. ...
Cellular Respiration PPT
... Aerobic Process = Only if oxygen is present!! Occurs in the MATRIX of the mitochondria Pyruvic Acid from Glycolysis enters to form 1 ATP 3 NADH 1 FADH2 CO2 (which is released when we exhale!!) AKA….Citric Acid Cycle ...
... Aerobic Process = Only if oxygen is present!! Occurs in the MATRIX of the mitochondria Pyruvic Acid from Glycolysis enters to form 1 ATP 3 NADH 1 FADH2 CO2 (which is released when we exhale!!) AKA….Citric Acid Cycle ...
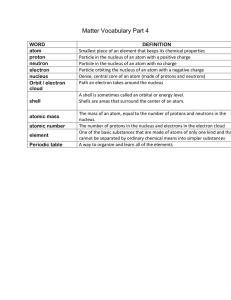
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
ch04_sec3_as - LCMR School District
... electrons are located. Each energy level may contain only a certain number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below shows how many electrons can be found in each of the first four e ...
... electrons are located. Each energy level may contain only a certain number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below shows how many electrons can be found in each of the first four e ...
Section 3: Modern Atomic Theory Atoms Section 3
... electrons are located. Each energy level may contain only a certain number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below shows how many electrons can be found in each of the first four e ...
... electrons are located. Each energy level may contain only a certain number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below shows how many electrons can be found in each of the first four e ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Test Bluff Questions
... 13. During aerobic respiration, the breakdown of 1 molecule of glucose will make how many ATP? a. 38 14. During anaerobic respiration, the breakdown of 1 molecule of glucose will make how many ATP? a. 2 15. Most of the energy used by life on Earth comes from where? a. Sun 16. Where do heterotrophs g ...
... 13. During aerobic respiration, the breakdown of 1 molecule of glucose will make how many ATP? a. 38 14. During anaerobic respiration, the breakdown of 1 molecule of glucose will make how many ATP? a. 2 15. Most of the energy used by life on Earth comes from where? a. Sun 16. Where do heterotrophs g ...
MICR 201 Microbiology for Health Related Sciences
... ATP contains energy that can be easily released (highenergy or unstable energy bond) Required for anabolic reactions Produced by ...
... ATP contains energy that can be easily released (highenergy or unstable energy bond) Required for anabolic reactions Produced by ...
Microbial Metabolism
... anabolic reactions. – . Energy harvested from catabolic reactions are stored in ATP molecules. ATP molecules are used to drive many anabolic reactions. ...
... anabolic reactions. – . Energy harvested from catabolic reactions are stored in ATP molecules. ATP molecules are used to drive many anabolic reactions. ...
Photosynthesis Review Worksheet
... from sunlight to transform CO2 from the air with water from the ground into glucose. This process, called photosynthesis, occurs in the chloroplast of the plant cell. During this process, oxygen (O2) is created as a waste product and is released into the air for us to breathe. The formula for photos ...
... from sunlight to transform CO2 from the air with water from the ground into glucose. This process, called photosynthesis, occurs in the chloroplast of the plant cell. During this process, oxygen (O2) is created as a waste product and is released into the air for us to breathe. The formula for photos ...
Assignment 6 Cell Respiration
... chain and give the electrons (from whom?) to the first molecule of the chain (reducing it), who passes the electrons to its neighbor reducing the neighbor while oxidizing itself. This electron passing continues through the rest of the transport molecules. The FADH2’s have to drop off their electrons ...
... chain and give the electrons (from whom?) to the first molecule of the chain (reducing it), who passes the electrons to its neighbor reducing the neighbor while oxidizing itself. This electron passing continues through the rest of the transport molecules. The FADH2’s have to drop off their electrons ...
Chem 331 ETS OxPhos Notes - University of San Diego Home Pages
... protein changes conformation redox state - most likely leads to proton pumping - resulting pKa changes in aas in complex I probably leads to loss and gain of protons * 2 e- are transferred from NADH and 4 H+ are pumped Complex II * Succinate dehydrogenase and other FADH producing enzymes are linked ...
... protein changes conformation redox state - most likely leads to proton pumping - resulting pKa changes in aas in complex I probably leads to loss and gain of protons * 2 e- are transferred from NADH and 4 H+ are pumped Complex II * Succinate dehydrogenase and other FADH producing enzymes are linked ...
Chapter 1 - TeacherWeb
... Cellular respiration – name four phases, starting reactants/ending products of each phase, location of each process, general understanding of each process, number of ATP & product at each stage produced by 1 glucose molecule Role of NAD+, FAD, Coenzyme A Similarities and differences between aerobic ...
... Cellular respiration – name four phases, starting reactants/ending products of each phase, location of each process, general understanding of each process, number of ATP & product at each stage produced by 1 glucose molecule Role of NAD+, FAD, Coenzyme A Similarities and differences between aerobic ...
Study Guide
... glycolysis and produces two ATP molecules. 9. A small, high-energy molecule that can be used by cells. It is the by-product of glucose breakdown. 10. A series of reactions used by all living things that allows the breakdown of food in order to obtain its stored energy. 12. The amount of energy requi ...
... glycolysis and produces two ATP molecules. 9. A small, high-energy molecule that can be used by cells. It is the by-product of glucose breakdown. 10. A series of reactions used by all living things that allows the breakdown of food in order to obtain its stored energy. 12. The amount of energy requi ...
Microbial Metabolism Notes
... (b) transfer e- and H+ from NADH & FADH2 to O2 resulting in H2O (i) O2 is considered the final electron acceptor (c) redox energy is used to pump H+ into the cell (i) creates a higher concentration in ICF (d) H+ is moved out through ATPsynthase creating ATP as it moves out (e) each NADH has enough e ...
... (b) transfer e- and H+ from NADH & FADH2 to O2 resulting in H2O (i) O2 is considered the final electron acceptor (c) redox energy is used to pump H+ into the cell (i) creates a higher concentration in ICF (d) H+ is moved out through ATPsynthase creating ATP as it moves out (e) each NADH has enough e ...
cellular respiration - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● During cellular respiration, the fuel (such as glucose) is oxidized and oxygen is reduced: ...
... ● During cellular respiration, the fuel (such as glucose) is oxidized and oxygen is reduced: ...
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reactions Calvin Cycle Observe the animations
... highlighted above ...
... highlighted above ...
C3.2 Leaf and Photos..
... main purpose is to carry out or support the process of photosynthesis. • There are special organelles responsible for this. What are the organelles called? CHLOROPLASTS ...
... main purpose is to carry out or support the process of photosynthesis. • There are special organelles responsible for this. What are the organelles called? CHLOROPLASTS ...
Document
... Also known as the Calvin-Benson cycle. In this process high energy molecules made by light (ATP + NADPH) are used to drive the reduction of CO2. This is sometimes called the dark reaction, as light is not directly used, but the ATP etc are very short lived and in practice this cycle only happens in ...
... Also known as the Calvin-Benson cycle. In this process high energy molecules made by light (ATP + NADPH) are used to drive the reduction of CO2. This is sometimes called the dark reaction, as light is not directly used, but the ATP etc are very short lived and in practice this cycle only happens in ...
Table showing examples of Complex ions with their bond
... bound and readily enter into metallic bond formation. The metallic radius decreased in passing from Sc to Ni. Addition of electrons might be expected to result in an increase in radius, but the electrons are being added to an inner orbital and it is the increased in nuclear charge in passing from Sc ...
... bound and readily enter into metallic bond formation. The metallic radius decreased in passing from Sc to Ni. Addition of electrons might be expected to result in an increase in radius, but the electrons are being added to an inner orbital and it is the increased in nuclear charge in passing from Sc ...
Chapter 8 Summary
... Metabolic pathways consist of many interrelated, enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions. These pathways can be categorized as either catabolic or anabolic. Anabolic pathways promote the synthesis of new compounds and energy storage, whereas catabolic pathways promote the mobilization of stored energy a ...
... Metabolic pathways consist of many interrelated, enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions. These pathways can be categorized as either catabolic or anabolic. Anabolic pathways promote the synthesis of new compounds and energy storage, whereas catabolic pathways promote the mobilization of stored energy a ...
The Periodic Table - Mrs Molchany`s Webpage
... positive (less energy released). Reason: Moving down a group the average distance between the added electron and the nucleus steadily increases, causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease. The orbital that holds the outermost electron is increasingly spread out, however, proceeding down the ...
... positive (less energy released). Reason: Moving down a group the average distance between the added electron and the nucleus steadily increases, causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease. The orbital that holds the outermost electron is increasingly spread out, however, proceeding down the ...