Photosynthesis - Chicagoland Jewish High School
... 3. Wavelength not absorbed by chlorophylls reflected as green 4. Chlorophyll absorbs in a narrow range, but with great efficiency c. xanthrophyll ...
... 3. Wavelength not absorbed by chlorophylls reflected as green 4. Chlorophyll absorbs in a narrow range, but with great efficiency c. xanthrophyll ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... P.S. The Dark Cycle Does Not Happen in the Dark It is dependent on the products of the light reaction (ATP and NADPH) So when the lights go out…it has no energy to continue. ...
... P.S. The Dark Cycle Does Not Happen in the Dark It is dependent on the products of the light reaction (ATP and NADPH) So when the lights go out…it has no energy to continue. ...
Transport and Metabolism Group work
... o The catabolic processes that you would find being used by these bacteria (summarized in Part A). o Note that enzymes are carrying out these metabolic reactions! o How energy is stored during these processes ATP • Substrate-level phosphorylation and/or • Oxidative phosphorylation Proton motive ...
... o The catabolic processes that you would find being used by these bacteria (summarized in Part A). o Note that enzymes are carrying out these metabolic reactions! o How energy is stored during these processes ATP • Substrate-level phosphorylation and/or • Oxidative phosphorylation Proton motive ...
Exam 2 Practice - Nicholls State University
... mitochondrial membrane c. because NADH produced in glycolysis cannot be used to produce ATP d. because cells seldom receive enough oxygen to be 100% efficient 24. Which statement about B-oxidation is correct? a. deamination is required before it begins b. it ultimately yields fewer ATP molecules per ...
... mitochondrial membrane c. because NADH produced in glycolysis cannot be used to produce ATP d. because cells seldom receive enough oxygen to be 100% efficient 24. Which statement about B-oxidation is correct? a. deamination is required before it begins b. it ultimately yields fewer ATP molecules per ...
What do we call a substance with more than one kind of atom
... 42. Within a period, the atomic radius __________ as the atomic number increases. 43. As a nonmetal becomes an ion, its radius _________ 44. The ______________ are the family that contain the most reactive metals. 45. Examine the following electron configuration for element X and use it to answer th ...
... 42. Within a period, the atomic radius __________ as the atomic number increases. 43. As a nonmetal becomes an ion, its radius _________ 44. The ______________ are the family that contain the most reactive metals. 45. Examine the following electron configuration for element X and use it to answer th ...
Handout
... NADH enters at first protein – ejects 2 hydrogen ions (one pair of H+) from the inner membrane of the mitochondria Ejects two more pairs of H+ at the next two steps in the chain A total of 3 pairs of H+ have been ejected when an NADH completes it’s passage along the chain Each pair of H+ ions passes ...
... NADH enters at first protein – ejects 2 hydrogen ions (one pair of H+) from the inner membrane of the mitochondria Ejects two more pairs of H+ at the next two steps in the chain A total of 3 pairs of H+ have been ejected when an NADH completes it’s passage along the chain Each pair of H+ ions passes ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... • What keeps the electrons coming down the Electron transport chain? • O2 at the bottom pulls electrons down the energy hill. • What happens to the energy of the electrons as it falls down the electron transport chain? • The energy is used to pump H+ against their gradient which then come back thro ...
... • What keeps the electrons coming down the Electron transport chain? • O2 at the bottom pulls electrons down the energy hill. • What happens to the energy of the electrons as it falls down the electron transport chain? • The energy is used to pump H+ against their gradient which then come back thro ...
Photosynthesis Review
... 5. What are the raw materials of photosynthesis? 6. What are the products of photosynthesis? 7. Why is light energy written on the left side of the equation? 8. Where does photosynthesis generally occur? ...
... 5. What are the raw materials of photosynthesis? 6. What are the products of photosynthesis? 7. Why is light energy written on the left side of the equation? 8. Where does photosynthesis generally occur? ...
Cellular Energy
... store more energy for future use • Many proteins have spots where ATP attaches to provide energy for the protein to do its job, then the ADP is released for recycling ...
... store more energy for future use • Many proteins have spots where ATP attaches to provide energy for the protein to do its job, then the ADP is released for recycling ...
Krebs Cycle - WordPress.com
... The Krebs cycle completes the breakdown of sugar In the Krebs cycle, Pyruvate from glycolysis is first “prepped” into a usable form, Acetyl-CoA ...
... The Krebs cycle completes the breakdown of sugar In the Krebs cycle, Pyruvate from glycolysis is first “prepped” into a usable form, Acetyl-CoA ...
Root Structure and Function
... The intensity where PSN=Resp is called _______________ At higher intensities ________________________________ At lower intensities ________________________________ A sun-loving has a_________________ compensation point. A shade-tolerant plant is _______________ efficient at PSN. ...
... The intensity where PSN=Resp is called _______________ At higher intensities ________________________________ At lower intensities ________________________________ A sun-loving has a_________________ compensation point. A shade-tolerant plant is _______________ efficient at PSN. ...
Respiration - Biology Innovation
... must find another way to convert NADH back into NAD, this process is called fermentation. Lactate fermentation occurs in mammals when there is a deficiency of oxygen. It has many advantages including strenuous exercise and oxygen demand under water. It works by each pyruvate molecule produced taking ...
... must find another way to convert NADH back into NAD, this process is called fermentation. Lactate fermentation occurs in mammals when there is a deficiency of oxygen. It has many advantages including strenuous exercise and oxygen demand under water. It works by each pyruvate molecule produced taking ...
Document
... are catalyzed by dehydrogenases that transfer pairs of electrons fron substrates to coenzymes, NADH and FADH2 → electron-transport chain • 2. NADH and FADH2 dehydrogenase are located in the inner membrane of ...
... are catalyzed by dehydrogenases that transfer pairs of electrons fron substrates to coenzymes, NADH and FADH2 → electron-transport chain • 2. NADH and FADH2 dehydrogenase are located in the inner membrane of ...
Introductory Microbiology Chap. 5 Chapter Outlines/Notes I
... 1) Occurs simultaneously with the electron transport chain (they are coupled) to transfer the energy to form ATP from ADP and phosphate (ADP phosphorylation). 2) At certain points along the electron transport chain, the hydrogen atom is ‘split’; the electron and the proton are separated. Remember, s ...
... 1) Occurs simultaneously with the electron transport chain (they are coupled) to transfer the energy to form ATP from ADP and phosphate (ADP phosphorylation). 2) At certain points along the electron transport chain, the hydrogen atom is ‘split’; the electron and the proton are separated. Remember, s ...
How does it occur (con`t)?
... How does it occur? Molecules of glucose are chemically “chopped up” in a series of chemical reactions, which produces CO2 and water molecules. Breaking the bonds in glucose is used to make ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), the cell’s energy molecule. ATP is a type of nucleotide. ...
... How does it occur? Molecules of glucose are chemically “chopped up” in a series of chemical reactions, which produces CO2 and water molecules. Breaking the bonds in glucose is used to make ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), the cell’s energy molecule. ATP is a type of nucleotide. ...
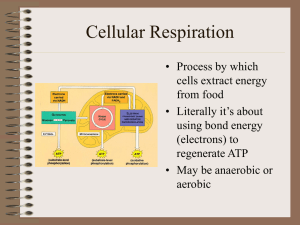
Cellular Respiration
... • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
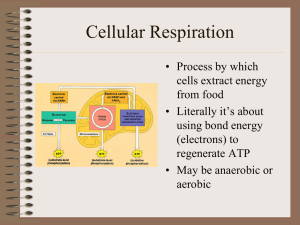
SCI_7726_files/Cellular Respiration
... • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
The Kreb`s Cycle - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Glycolysis, which occurs in the cytosol, begins the degradation process by breaking down glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate. • The citric acid cycle, which takes place in the mitochondrial matrix, completes the breakdown of glucose by oxidizing a derivative of pyruvate to car ...
... • Glycolysis, which occurs in the cytosol, begins the degradation process by breaking down glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate. • The citric acid cycle, which takes place in the mitochondrial matrix, completes the breakdown of glucose by oxidizing a derivative of pyruvate to car ...
Bio102 Problems
... C. This allows the organelle to have more copies of photosystems I and II and ATP synthase. D. The larger membrane improves its fluidity. E. This makes a more effective barrier to prevent protons from leaking through. 2. At the end of the electron transport chain found in the thylakoid membrane, the ...
... C. This allows the organelle to have more copies of photosystems I and II and ATP synthase. D. The larger membrane improves its fluidity. E. This makes a more effective barrier to prevent protons from leaking through. 2. At the end of the electron transport chain found in the thylakoid membrane, the ...
Atomic Structure
... • Electron affinity - The energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. • Electronegativity - a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. ...
... • Electron affinity - The energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. • Electronegativity - a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. ...
No Slide Title
... Sites of photosynthesis in plants & algae. Concentrated in mesophyll cells of most plants. ...
... Sites of photosynthesis in plants & algae. Concentrated in mesophyll cells of most plants. ...
Ans 518_class 4
... Electrons are transported along the membrane, through a series of protein carriers ...
... Electrons are transported along the membrane, through a series of protein carriers ...
Name: Date: Hour: Capstone 1B Review: Describe the overall
... “A maple tree can make all of the substances it needs. It builds up carbohydrates by the process of __a__. In this process it combines __b__ from the soil with __c__ from the air to form __d__. The energy needed for this process is __e__ which is absorbed by chlorophyll in a chloroplast” a. Photosyn ...
... “A maple tree can make all of the substances it needs. It builds up carbohydrates by the process of __a__. In this process it combines __b__ from the soil with __c__ from the air to form __d__. The energy needed for this process is __e__ which is absorbed by chlorophyll in a chloroplast” a. Photosyn ...
Biochemistry 6/e
... Complex III? First of all, Complex III takes up two protons on the matrix side of the inner membrane and releases four protons on the cytoplasmic side for each pair of electrons that passes through the Q cycle. The apparent imbalance of two protons in for four protons out is offset by proton translo ...
... Complex III? First of all, Complex III takes up two protons on the matrix side of the inner membrane and releases four protons on the cytoplasmic side for each pair of electrons that passes through the Q cycle. The apparent imbalance of two protons in for four protons out is offset by proton translo ...
ATP, Photosynthesis and Respiration
... higher energy level. They are captured by a primary electron acceptor. Photolysis: H2O gets split apart into 2 e- , 2 H+, and one oxygen atom.. The ereplace those lost by ChloroA. 2 oxygen molecules combine and is released into the air. H+ are released into the inner thylakoid space, which creates a ...
... higher energy level. They are captured by a primary electron acceptor. Photolysis: H2O gets split apart into 2 e- , 2 H+, and one oxygen atom.. The ereplace those lost by ChloroA. 2 oxygen molecules combine and is released into the air. H+ are released into the inner thylakoid space, which creates a ...