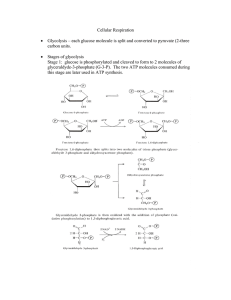
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
... • This is an oxidation reaction where 2 hydrogen atoms (or 2 hydrogen ions and 2 electrons) are removed from the organic metabolite. When electrons are transferred from a metabolite by NAD+, NAD+ additionally removes two protons, hydrogen ions, H+ MH2 + NAD+ → NADH + H+ + M + energy This converts NA ...
... • This is an oxidation reaction where 2 hydrogen atoms (or 2 hydrogen ions and 2 electrons) are removed from the organic metabolite. When electrons are transferred from a metabolite by NAD+, NAD+ additionally removes two protons, hydrogen ions, H+ MH2 + NAD+ → NADH + H+ + M + energy This converts NA ...
No Slide Title
... •Chemical Evolution, simple molecules condense to form more complex forms (polymers) ...
... •Chemical Evolution, simple molecules condense to form more complex forms (polymers) ...
EXTRA
... respire oxygen in their metabolism. Many aerobes can even tolerate elevated concentrations of oxygen (hyperbaric oxygen>21% O2). The process of energy production involves glycolysis, the Krebs’ cycle and the electron transport system for which O2 acts as a terminal electron acceptor. Energy is gener ...
... respire oxygen in their metabolism. Many aerobes can even tolerate elevated concentrations of oxygen (hyperbaric oxygen>21% O2). The process of energy production involves glycolysis, the Krebs’ cycle and the electron transport system for which O2 acts as a terminal electron acceptor. Energy is gener ...
Cellular Respiration
... molecules break down during cellular respiration. Much of the energy released during this process is used to make ATP. ATP is an energy storage molecule. Cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of cells. This process requires oxygen and produces water and carbon dioxide as wast ...
... molecules break down during cellular respiration. Much of the energy released during this process is used to make ATP. ATP is an energy storage molecule. Cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of cells. This process requires oxygen and produces water and carbon dioxide as wast ...
Sum total of all chemical reactions that occur within an
... or proton motive force converted to chemical bond energy in ATP Racker and Stoeckenius confirmed ATP uses an H+ electrochemical gradient Rotary machine that makes ATP as it spins ...
... or proton motive force converted to chemical bond energy in ATP Racker and Stoeckenius confirmed ATP uses an H+ electrochemical gradient Rotary machine that makes ATP as it spins ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 Part A
... 1. What are cytochromes? 2. Write a note on the amphoteric nature of proteins. 3. Comment on the following: (i) Isomerization (ii) Tautomerization. 4. What is called line Weaker Burk equation? 5. What is V-Max? 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto ox ...
... 1. What are cytochromes? 2. Write a note on the amphoteric nature of proteins. 3. Comment on the following: (i) Isomerization (ii) Tautomerization. 4. What is called line Weaker Burk equation? 5. What is V-Max? 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto ox ...
Chapter 27 Bioenergetics: How the Body Converts Food to Energy
... and reduced cofactors, NADH and FADH2. ATP may be used directly for energy, but the cofactors must be oxidized to recover their energy. The reduced cofactors are oxidized by the electron transport chain that transfers the electrons to molecular oxygen. The energy released by the oxidation is used to ...
... and reduced cofactors, NADH and FADH2. ATP may be used directly for energy, but the cofactors must be oxidized to recover their energy. The reduced cofactors are oxidized by the electron transport chain that transfers the electrons to molecular oxygen. The energy released by the oxidation is used to ...
Chapter 9
... complex I). • The electrons continue along the chain which includes several cytochrome proteins and one lipid carrier Ubiquinone • The final electron acceptor is: OXYGEN because it is MOST electronegative • The product is WATER and ……. (its not over) ...
... complex I). • The electrons continue along the chain which includes several cytochrome proteins and one lipid carrier Ubiquinone • The final electron acceptor is: OXYGEN because it is MOST electronegative • The product is WATER and ……. (its not over) ...
File
... Q10 What is transamination and how do amino acids enter the Krebs cycle? The removal of amine groups from the amino acid is transamination. Amino acids undergo the process of deamination, oxidative deamination and other changes to become one of the intermediates in Glycolosis or the Krebs cycle Q11 ...
... Q10 What is transamination and how do amino acids enter the Krebs cycle? The removal of amine groups from the amino acid is transamination. Amino acids undergo the process of deamination, oxidative deamination and other changes to become one of the intermediates in Glycolosis or the Krebs cycle Q11 ...
Exam 3 - Chemistry Courses: About
... developed antidote functions to bypass the problem by taking the place of cytochrome c in the chain. This compound accepts electrons just like cytochrome c, but then donates the electrons directly to oxygen without the aid of Complex 4. With reference to your figure from part A, explain why this ant ...
... developed antidote functions to bypass the problem by taking the place of cytochrome c in the chain. This compound accepts electrons just like cytochrome c, but then donates the electrons directly to oxygen without the aid of Complex 4. With reference to your figure from part A, explain why this ant ...
A and P Practice Exam 01 (pdf 86.08kb)
... a. Sodium-potassium pump b. Endocytosis c. Exocytosis d. Bulk flow 49. Which of the following is not a form of passive transport? a. Osmosis b. Passive transport c. Bulk flow d. Exocytosis 50. O2, CO2, H2O, and other small, electrically neutral molecules move across the cell membrane by________. a. ...
... a. Sodium-potassium pump b. Endocytosis c. Exocytosis d. Bulk flow 49. Which of the following is not a form of passive transport? a. Osmosis b. Passive transport c. Bulk flow d. Exocytosis 50. O2, CO2, H2O, and other small, electrically neutral molecules move across the cell membrane by________. a. ...
Photosynthesis
... The photosystem II complex (i.e. the reaction centre and the light-harvesting proteins) is made of several different redox components and more than 20 different polypeptides that are a mixture of chloroplast and nuclear gene products. These intricately assembled polypeptides bind and precisely orient ...
... The photosystem II complex (i.e. the reaction centre and the light-harvesting proteins) is made of several different redox components and more than 20 different polypeptides that are a mixture of chloroplast and nuclear gene products. These intricately assembled polypeptides bind and precisely orient ...
Unit 10 Photosynthesis
... • Plants use energy from the sun and convert it to chemical energy – Glucose ...
... • Plants use energy from the sun and convert it to chemical energy – Glucose ...
Cellular Respiration
... The rest come from an electron transport chain that gets the remaining energy from NADH & FADH2. The ETC also produces 2 water molecules that are released. The ETC makes a total of about 32-34 ATP. O2 is the final e- acceptor. ...
... The rest come from an electron transport chain that gets the remaining energy from NADH & FADH2. The ETC also produces 2 water molecules that are released. The ETC makes a total of about 32-34 ATP. O2 is the final e- acceptor. ...
Cell Respiration - Biology Junction
... two electrons and a hydrogen ion (H+); this results in NADH + H+. 3. Electrons received by NAD+ and FAD are high-energy electrons and are usually carried to the electron transport chain. 4. NAD+ is a coenzyme of oxidation-reduction since it both accepts and gives up electrons; thus, NAD+ is sometime ...
... two electrons and a hydrogen ion (H+); this results in NADH + H+. 3. Electrons received by NAD+ and FAD are high-energy electrons and are usually carried to the electron transport chain. 4. NAD+ is a coenzyme of oxidation-reduction since it both accepts and gives up electrons; thus, NAD+ is sometime ...
BIO 212 SI Kukday--Energetics (2) Review 2/7
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
CH`s 8 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the proton, ATP synthase. ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP. This is ...
... Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the proton, ATP synthase. ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP. This is ...
Mitochondria
... By now we’ve encountered a wide variety of chemical reactions that require the presence of enzymes, specialized proteins that keep the reactions occurring at a rapid pace. These reactions would occur much too slowly to be effective if they were not pepped up by specific enzymes. The enzymes that cat ...
... By now we’ve encountered a wide variety of chemical reactions that require the presence of enzymes, specialized proteins that keep the reactions occurring at a rapid pace. These reactions would occur much too slowly to be effective if they were not pepped up by specific enzymes. The enzymes that cat ...
Revision topic 1-3
... the wavelengths or frequencies of visible light. An absorption spectrum is produced where some colours are missing ( those that are absorbed by hydrogen). A corresponding emission line spectrum has only certain wavelegths or frequencies of visible light.The lines correspond to the light of particula ...
... the wavelengths or frequencies of visible light. An absorption spectrum is produced where some colours are missing ( those that are absorbed by hydrogen). A corresponding emission line spectrum has only certain wavelegths or frequencies of visible light.The lines correspond to the light of particula ...
sample
... are more electron carriers, which increases ATP synthesis. The reduced coenzymes, NADH 2 and FADH 2, produced during glycolysis, the link reaction and the Krebs cycle act as a source of electrons and protons. Figure 9 shows the electron carriers at progressively lower energy levels. As electrons pas ...
... are more electron carriers, which increases ATP synthesis. The reduced coenzymes, NADH 2 and FADH 2, produced during glycolysis, the link reaction and the Krebs cycle act as a source of electrons and protons. Figure 9 shows the electron carriers at progressively lower energy levels. As electrons pas ...
Lecture 20
... NADH produced must be converted back to NAD+ 1. Under anaerobic conditions in muscle NADH reduces pyruvate to lactate (homolactic fermentation). 2. Under anaerobic conditions in yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to yield CO2 and acetaldehyde and the latter is reduced by NADH to ethanol and NAD+ is ...
... NADH produced must be converted back to NAD+ 1. Under anaerobic conditions in muscle NADH reduces pyruvate to lactate (homolactic fermentation). 2. Under anaerobic conditions in yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to yield CO2 and acetaldehyde and the latter is reduced by NADH to ethanol and NAD+ is ...
How do all the parts of photosynthesis work together
... compared to the absorbed quantum flux: the absorbed energy cannot be dissipated via metabolism. d. the environment is dynamic and unpredictable e. imbalances will result in the build-up of driving forces (³chl and reductant) that will drive ROS formation. Thursday, 2 April 2009 ...
... compared to the absorbed quantum flux: the absorbed energy cannot be dissipated via metabolism. d. the environment is dynamic and unpredictable e. imbalances will result in the build-up of driving forces (³chl and reductant) that will drive ROS formation. Thursday, 2 April 2009 ...
Cell Respiration Practice Packet
... 3. What happens to the molecules of glycolysis when oxygen is available? 4. Where is the electron transport chain located? ...
... 3. What happens to the molecules of glycolysis when oxygen is available? 4. Where is the electron transport chain located? ...























