Cellular Respiration - LaPazColegioWiki2013-2014
... After a few modifications and a handful of reactions (Ch. ...
... After a few modifications and a handful of reactions (Ch. ...
D-Glucose is a carbohydrate which can be classified as which of the
... A. Lower the Vmax and not affect the Km B. Raise the Vmax and not affect the Km C. Raise the Vmax and lower the Km D. Raise the Vmax and raise the Km E. Lower the Vmax and raise the Km 11. The side chain for the amino acid Serine (Ser) is –CH2-OH. The side chain for the amino acid Lysine (Lys) is –C ...
... A. Lower the Vmax and not affect the Km B. Raise the Vmax and not affect the Km C. Raise the Vmax and lower the Km D. Raise the Vmax and raise the Km E. Lower the Vmax and raise the Km 11. The side chain for the amino acid Serine (Ser) is –CH2-OH. The side chain for the amino acid Lysine (Lys) is –C ...
No Slide Title
... but will allow other wavelengths to pass through it. A colored image of the cell is obtained that is visible in the normal bright-field microscope. (B) Light passing through an unstained cell undergoes very little change in amplitude, and the structural details cannot be seen even if the image is hi ...
... but will allow other wavelengths to pass through it. A colored image of the cell is obtained that is visible in the normal bright-field microscope. (B) Light passing through an unstained cell undergoes very little change in amplitude, and the structural details cannot be seen even if the image is hi ...
Light and Pigments
... What type of light do we see? What is a pigment? What are the names of the pigments in leaves? Why are pigments important in photosynthesis? ...
... What type of light do we see? What is a pigment? What are the names of the pigments in leaves? Why are pigments important in photosynthesis? ...
Basic Chemistry
... when long chains of simple sugars are hooked together Glycogen - storage form of glucose in animals Starch - storage form of glucose in plants ...
... when long chains of simple sugars are hooked together Glycogen - storage form of glucose in animals Starch - storage form of glucose in plants ...
Chapter 8: Photosynthesis: Energy from the Sun
... Chapter 8: Photosynthesis: Energy from the Sun ...
... Chapter 8: Photosynthesis: Energy from the Sun ...
File - Pomp
... What is another name for the Calvin Cycle? What are the reactants of photosynthesis? What are the products of photosynthesis? What is the role of energy carriers in photosynthesis? How is energy transformed in photosynthesis? Is photosynthesis energy absorbing or energy releasing? What is the form o ...
... What is another name for the Calvin Cycle? What are the reactants of photosynthesis? What are the products of photosynthesis? What is the role of energy carriers in photosynthesis? How is energy transformed in photosynthesis? Is photosynthesis energy absorbing or energy releasing? What is the form o ...
Lesson Plan 5
... Photosynthesis comes from the root words “photo”, meaning light, and “synthesis” meaning to build or make. So, photosynthesis is a reaction that occurs in plants in the presence of light where light energy is used to make food. Photosynthesis is probably the most important chemical reaction on the p ...
... Photosynthesis comes from the root words “photo”, meaning light, and “synthesis” meaning to build or make. So, photosynthesis is a reaction that occurs in plants in the presence of light where light energy is used to make food. Photosynthesis is probably the most important chemical reaction on the p ...
energy - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... • Free energy of the bond between phosphate groups is much higher than the energy of the O—H bond that forms after hydrolysis. ...
... • Free energy of the bond between phosphate groups is much higher than the energy of the O—H bond that forms after hydrolysis. ...
Biology – Unit 3 Review
... Photosynthesis Certain organisms (plants, cyanobacteria, and photosynthetic protests) can capture light energy and use it to ultimately create food that can be used by their own organism or other organisms that may consume them. Light energy, carbon dioxide and water are needed for the organism to p ...
... Photosynthesis Certain organisms (plants, cyanobacteria, and photosynthetic protests) can capture light energy and use it to ultimately create food that can be used by their own organism or other organisms that may consume them. Light energy, carbon dioxide and water are needed for the organism to p ...
ATP - cloudfront.net
... B. Photosynthesis • Complex process in which visible sunlight is converted into chemical energy in carbohydrate (glucose) molecules ...
... B. Photosynthesis • Complex process in which visible sunlight is converted into chemical energy in carbohydrate (glucose) molecules ...
Chemiosmotic Theory of Energy Transfer Introduction
... enzymes, to derive energy from their environment, to convert it into a biologically useful form, and to utilize it for driving various energy requiring processes. Cells of green plants as well as certain bacteria and algae can capture energy by means of chlorophyll directly from sunlight - the ultim ...
... enzymes, to derive energy from their environment, to convert it into a biologically useful form, and to utilize it for driving various energy requiring processes. Cells of green plants as well as certain bacteria and algae can capture energy by means of chlorophyll directly from sunlight - the ultim ...
Leaf notes
... It is a ________________by which plants _____________ ____________and __________________ _________________ in the presence of _______________ and ______________ and produce carbohydrates and release ________________. ...
... It is a ________________by which plants _____________ ____________and __________________ _________________ in the presence of _______________ and ______________ and produce carbohydrates and release ________________. ...
Chemosynthesis
... • the conversion of chemicals into food in the absence of sunlight • Example organisms: extremeophiles (bacteria, protists) ...
... • the conversion of chemicals into food in the absence of sunlight • Example organisms: extremeophiles (bacteria, protists) ...
Metabolism: Basic concepts
... B. One reactions forms an ionic gradient across a membrane. This drives another reaction that uses the gradient to render it exergonic. Are these reactions coupled? ...
... B. One reactions forms an ionic gradient across a membrane. This drives another reaction that uses the gradient to render it exergonic. Are these reactions coupled? ...
Energy and Glycolysis
... –Autotrophs – make their own food. • Photosynthesis – Uses energy from the sun to make glucose. It’s carried out by plants and some microbes. ...
... –Autotrophs – make their own food. • Photosynthesis – Uses energy from the sun to make glucose. It’s carried out by plants and some microbes. ...
Cell Respiration - Hollidaysburg Area School District
... used to pump _____ ions across the membrane from the matrix to the intermembrane space of the ____________. _____ ions build up in the intermembrane space, making it __________ charged and the outside __________ charged. ...
... used to pump _____ ions across the membrane from the matrix to the intermembrane space of the ____________. _____ ions build up in the intermembrane space, making it __________ charged and the outside __________ charged. ...
Photosynthesis Notes Gresham
... The light dependent reactions can be split into the following specific steps: 1. Light absorption & splitting of water. 2. Production of ATP. 3. Movement of electrons through electron acceptors to power a hydrogen pump. 4. Re-energizing electrons so they can produce NADPH. ...
... The light dependent reactions can be split into the following specific steps: 1. Light absorption & splitting of water. 2. Production of ATP. 3. Movement of electrons through electron acceptors to power a hydrogen pump. 4. Re-energizing electrons so they can produce NADPH. ...
Chapter 9—Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Are composed of electron-carrier molecules built into the inner mitochondrial membrane Accept energy-rich electrons from reduced coenzymes and during a series of redox reactions, pass these electrons down the chain to oxygen, the final electron acceptor, The electronegative oxygen accepts these ...
... Are composed of electron-carrier molecules built into the inner mitochondrial membrane Accept energy-rich electrons from reduced coenzymes and during a series of redox reactions, pass these electrons down the chain to oxygen, the final electron acceptor, The electronegative oxygen accepts these ...
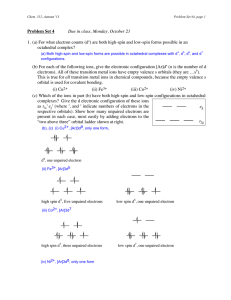
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
Cellular Respiration - Mr. Fusco's Brookdale Weblog
... The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules This released energy is used to make ATP Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants are called oxidation-reduction reactions, or In oxidation, a substance , or is oxidized In r ...
... The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules This released energy is used to make ATP Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants are called oxidation-reduction reactions, or In oxidation, a substance , or is oxidized In r ...
Ch 5
... • Aerobic respiration: The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen (O2). • Anaerobic respiration: The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is not O2. Yields less energy than aerobic respiration because only part of the Krebs cycles operations un ...
... • Aerobic respiration: The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen (O2). • Anaerobic respiration: The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is not O2. Yields less energy than aerobic respiration because only part of the Krebs cycles operations un ...