Artificial Photosynthesis - The Mars Homestead Project
... Photorespiration and C3 vs. C4 plants RuBP carboxylase can promote the reaction of RuBP with either CO2 or O2 When CO2 is low relative to O2, oxidation competes with carboxylation C4 precede the C3 pathway by fixing CO2 into a 4-carbon compound In C4 plants the CO2:O2 ratio remains high, this favou ...
... Photorespiration and C3 vs. C4 plants RuBP carboxylase can promote the reaction of RuBP with either CO2 or O2 When CO2 is low relative to O2, oxidation competes with carboxylation C4 precede the C3 pathway by fixing CO2 into a 4-carbon compound In C4 plants the CO2:O2 ratio remains high, this favou ...
honors chem 6 day review packet
... contains 3 electrons in its sixth and outer main energy level the element that has 2 electrons in the p sublevel in its second main energy level 4s24p5 Be able to locate s, p, d, and f blocks on the periodic table The ___________ ____________ _____________ is the same as the period number. There are ...
... contains 3 electrons in its sixth and outer main energy level the element that has 2 electrons in the p sublevel in its second main energy level 4s24p5 Be able to locate s, p, d, and f blocks on the periodic table The ___________ ____________ _____________ is the same as the period number. There are ...
Substrate Level Phosphorylation Substrate level phosphorylation
... • The substance being reduced actually gets “bigger” because the increased number of electrons allows for more bonds • Glucose oxidation transfers electrons (of hydrogen) to a lower energy state as it bonds with oxygen – Energy released is used in ATP regeneration ...
... • The substance being reduced actually gets “bigger” because the increased number of electrons allows for more bonds • Glucose oxidation transfers electrons (of hydrogen) to a lower energy state as it bonds with oxygen – Energy released is used in ATP regeneration ...
2 - Warner Pacific College
... Glucose (6 C) split into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3C) Uses 2 ATP, produces 4 ATP net yield of 2 ATP Available for immediate energy needs ...
... Glucose (6 C) split into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3C) Uses 2 ATP, produces 4 ATP net yield of 2 ATP Available for immediate energy needs ...
Exam 2 Material Outline MS Word
... View course website animation on Transcription C. Translation – process by which info encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a protein at a ribosome (Fig. 14.2, 14.6, ...
... View course website animation on Transcription C. Translation – process by which info encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a protein at a ribosome (Fig. 14.2, 14.6, ...
From Fig - Jiamusi University
... mol of ATP are formed per atom of oxygen consumed. The malate shuttle system is linked to the NAD –linked respiratory chain, 3 mol of ATP are formed per atom of oxygen consumed. ...
... mol of ATP are formed per atom of oxygen consumed. The malate shuttle system is linked to the NAD –linked respiratory chain, 3 mol of ATP are formed per atom of oxygen consumed. ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Glossary
... Ligase an enzyme which joins fragments of DNA together Metabolites the intermediates and products of metabolic reactions that take place in organisms Migration a process which avoids metabolic adversity by expending energy to relocate to a more suitable environment Mitochondria a structure in the ce ...
... Ligase an enzyme which joins fragments of DNA together Metabolites the intermediates and products of metabolic reactions that take place in organisms Migration a process which avoids metabolic adversity by expending energy to relocate to a more suitable environment Mitochondria a structure in the ce ...
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN (student)
... So what’s the deal with ATP?? • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP • We need to produce 36 ATP in Cell. Resp. • After 3 stages, we have only produced 6 ATP through substrate-level oxidation • Thus, there are 30 ATP left to create – We produce the remaining 30 ATP through oxidative phosphorylation ...
... So what’s the deal with ATP?? • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP • We need to produce 36 ATP in Cell. Resp. • After 3 stages, we have only produced 6 ATP through substrate-level oxidation • Thus, there are 30 ATP left to create – We produce the remaining 30 ATP through oxidative phosphorylation ...
Energy Metabolism - 35-206-202
... Gains electrons by losing oxygen or gaining hydrogen. Electrons are the currency that are passed around to make energy for the cell. ...
... Gains electrons by losing oxygen or gaining hydrogen. Electrons are the currency that are passed around to make energy for the cell. ...
Photosynthesis, key concepts, and understandings
... Part 2: Chemistry of photosynthesis • There are two distinct parts of photosynthesis • Light-dependent (light) reactions: sun energy is absorbed and transformed into chemical energy • Light-independent (dark) reactions: also called the Calvin cycle, chemical energy from the light reactions is used ...
... Part 2: Chemistry of photosynthesis • There are two distinct parts of photosynthesis • Light-dependent (light) reactions: sun energy is absorbed and transformed into chemical energy • Light-independent (dark) reactions: also called the Calvin cycle, chemical energy from the light reactions is used ...
Lecture 12 (3/03/10) "Magnetic Tweezers and (Optical) Microscopes"
... 1. HW (really!) assigned today (Due next Wednesday, 3/10/10). 2. March 15th, 17th, night of 18th: Presentations Reports due night of 18th. ...
... 1. HW (really!) assigned today (Due next Wednesday, 3/10/10). 2. March 15th, 17th, night of 18th: Presentations Reports due night of 18th. ...
Cell Respiration powerpoint slides
... compound, thus forming citric acid. As the citric acid proceeds through the cycle, it is first broken down into a 5-carbon compound, and then into a 4-carbon ...
... compound, thus forming citric acid. As the citric acid proceeds through the cycle, it is first broken down into a 5-carbon compound, and then into a 4-carbon ...
Ch 12
... • If we start with 1M reactants and products, the free energy change of that reaction is called the “standard” free energy • Go’ is a reflection of the chemical potential (stability of bonds) – Negative Go’ means equilibrium ...
... • If we start with 1M reactants and products, the free energy change of that reaction is called the “standard” free energy • Go’ is a reflection of the chemical potential (stability of bonds) – Negative Go’ means equilibrium ...
Catabolism
... Anaerobic conditions Two unifying themes should be kept in mind when microbial fermentation are examined: ...
... Anaerobic conditions Two unifying themes should be kept in mind when microbial fermentation are examined: ...
NAME: : :______ Honors Biology Reading Guide – Chapter 6
... 69. One mole of glucose stores _____kcal of energy which is then utilized by living things when carbohydrates are oxidized in ______________________________________________. Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration 70. Write the overall equation for cellular respiration. ...
... 69. One mole of glucose stores _____kcal of energy which is then utilized by living things when carbohydrates are oxidized in ______________________________________________. Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration 70. Write the overall equation for cellular respiration. ...
MATTER INTO ENERGY ENERGY INTO MATTER - TJ
... ATP & NADPH – Occurs in the thylakoid of the chloroplast (green pancakes) – Light is absorbed and used to split water to make ATP & NADPH • Light energy into chemical energy ...
... ATP & NADPH – Occurs in the thylakoid of the chloroplast (green pancakes) – Light is absorbed and used to split water to make ATP & NADPH • Light energy into chemical energy ...
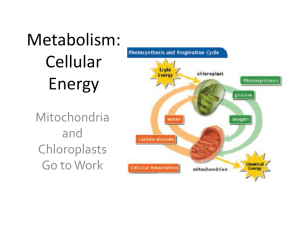
Cellular Energy
... • The extra glucose is stored in the cells of the plant’s leaves. • When needed, the glucose travels to the mitochondria to be used in cellular respiration for the production of ATP. ...
... • The extra glucose is stored in the cells of the plant’s leaves. • When needed, the glucose travels to the mitochondria to be used in cellular respiration for the production of ATP. ...
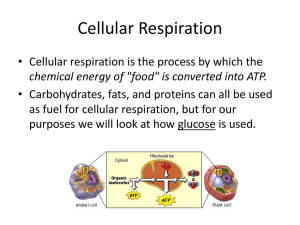
Cellular Respiration
... Electron Transport Chain (ETC) • The electron transport chain (ETC) consists of a series of molecules, mostly proteins, embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. • The electron transport chain captures the electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 and passes them along the membrane. – As the electrons ...
... Electron Transport Chain (ETC) • The electron transport chain (ETC) consists of a series of molecules, mostly proteins, embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. • The electron transport chain captures the electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 and passes them along the membrane. – As the electrons ...
Chapter 9 from Mrs Chou
... Chemiosmosis = H+ gradient across membrane drives cellular work Proton-motive force: use proton (H+) gradient to perform work ...
... Chemiosmosis = H+ gradient across membrane drives cellular work Proton-motive force: use proton (H+) gradient to perform work ...
1 Confusion from last week: Purines and Pyrimidines
... – Too much energy, and bonds inside important molecules (e.g. proteins) can be disrupted, doing damage. ...
... – Too much energy, and bonds inside important molecules (e.g. proteins) can be disrupted, doing damage. ...
Warm-Up
... Chemiosmosis = H+ gradient across membrane drives cellular work Proton-motive force: use proton (H+) gradient to perform work ...
... Chemiosmosis = H+ gradient across membrane drives cellular work Proton-motive force: use proton (H+) gradient to perform work ...
Electron Transport Chain Questions
... 9. What is the purpose of NAD+? What type of reaction is NAD+ involved in? The purpose of NAD+ is to serve as an electron carrier. As bonds are broken in the molecule when it is oxidized (loses electrons and H+ ion), NAD+ collects the energy in the form of electrons and becomes reduced to NADH (oxid ...
... 9. What is the purpose of NAD+? What type of reaction is NAD+ involved in? The purpose of NAD+ is to serve as an electron carrier. As bonds are broken in the molecule when it is oxidized (loses electrons and H+ ion), NAD+ collects the energy in the form of electrons and becomes reduced to NADH (oxid ...
Ch 9 (primary ppt) - Phillips Scientific Methods
... Chemiosmosis = H+ gradient across membrane drives cellular work Proton-motive force: use proton (H+) gradient to perform work ...
... Chemiosmosis = H+ gradient across membrane drives cellular work Proton-motive force: use proton (H+) gradient to perform work ...