Final Exam - W09
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
PowerPoint - New Mexico FFA
... several chemical processes to occur within the plant for survival. These reactions allow the plant to produce food, expel waste, and regulate plant temperature. Three of the most important reactions that occur within a tree are photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration. ...
... several chemical processes to occur within the plant for survival. These reactions allow the plant to produce food, expel waste, and regulate plant temperature. Three of the most important reactions that occur within a tree are photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration. ...
Periodic Trends & the Periodic Table
... • The elements in Groups 3 through 12 of the periodic table are called the transition elements. • All transition elements are metals. • Many transition metals can have more than one charge ...
... • The elements in Groups 3 through 12 of the periodic table are called the transition elements. • All transition elements are metals. • Many transition metals can have more than one charge ...
BENCHMARK SC.912.L.1 CO2 + H2O + Energy =→ C6H12O6 + O2
... Students will explain how photosynthesis stores energy and cellular respiration releases energy. Photosynthesis stores in energy in the bond of the sugar molecule Cellular respiration releases the energy from the bonds in the sugar molecules Students will identify the reactants, products and/or the ...
... Students will explain how photosynthesis stores energy and cellular respiration releases energy. Photosynthesis stores in energy in the bond of the sugar molecule Cellular respiration releases the energy from the bonds in the sugar molecules Students will identify the reactants, products and/or the ...
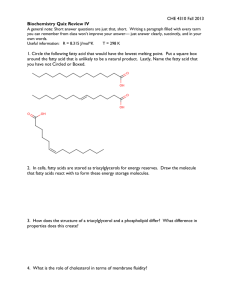
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 15. In glycolysis there are two reactions that require one ATP each and two reactions that produce one ATP each. What are these four reactions? This being the case, how can fermentation of glucose to lactate lead to the net production of two ATP molecules per glucose? ...
... 15. In glycolysis there are two reactions that require one ATP each and two reactions that produce one ATP each. What are these four reactions? This being the case, how can fermentation of glucose to lactate lead to the net production of two ATP molecules per glucose? ...
ATP - Coach Blair`s Biology Website
... • Energy is the ability to move or change matter (light, heat, chemical, electrical, etc.) • Energy can be stored or released by chemical reactions. • Energy from the sunlight flows through living systems, from autotrophs to heterotrophs. • Cellular respiration and photosynthesis form a cycle becaus ...
... • Energy is the ability to move or change matter (light, heat, chemical, electrical, etc.) • Energy can be stored or released by chemical reactions. • Energy from the sunlight flows through living systems, from autotrophs to heterotrophs. • Cellular respiration and photosynthesis form a cycle becaus ...
Filled in Notes
... When input of energy is required to move materials through the cell membrane, active transport takes place. The process of taking substances into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane is called endocytosis. Some one-celled organisms take in food this way. Exocytosis occurs in the opposite ...
... When input of energy is required to move materials through the cell membrane, active transport takes place. The process of taking substances into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane is called endocytosis. Some one-celled organisms take in food this way. Exocytosis occurs in the opposite ...
CH395 G Exam 3 Fall 2004 - Multiple Choice 1. Which of the
... a. binding a proton on the acidic side of the membrane, diffusing through the membrane, and releasing the proton on the alkaline side of the membrane. b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the membrane permeable to protons. c. binding to F0 of ATP synthase thereby blo ...
... a. binding a proton on the acidic side of the membrane, diffusing through the membrane, and releasing the proton on the alkaline side of the membrane. b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the membrane permeable to protons. c. binding to F0 of ATP synthase thereby blo ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Occurs in all eukaryotes and some bacteria • Glycolysis occurs in cytosol of ALL cells • The rest of respiration occurs in ...
... • Occurs in all eukaryotes and some bacteria • Glycolysis occurs in cytosol of ALL cells • The rest of respiration occurs in ...
Review Questions for Advanced Biochemistry Course
... 20. Which of the following statements does NOT help explain the chemiosmotic theory? A. Protons move down a concentration gradient with negative free energy change B. ADP and Pi combine to form ATP, this reaction has a positive change in free energy C. The inner mitochondria membrane is impermeable ...
... 20. Which of the following statements does NOT help explain the chemiosmotic theory? A. Protons move down a concentration gradient with negative free energy change B. ADP and Pi combine to form ATP, this reaction has a positive change in free energy C. The inner mitochondria membrane is impermeable ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 30: Ion pumps in the membrane
... hydrolyses ATP and pumps H+ through Fo towards the exterior face of the membrane. This is actually a normal role when bacteria grow anaerobically, because the H+ gradient is not being provided by electron transport, but is still needed for symport of nutrients. In mitochondria, ATP hydrolysis only o ...
... hydrolyses ATP and pumps H+ through Fo towards the exterior face of the membrane. This is actually a normal role when bacteria grow anaerobically, because the H+ gradient is not being provided by electron transport, but is still needed for symport of nutrients. In mitochondria, ATP hydrolysis only o ...
Cellular respiration
... Although there is a theoretical yield of 38 ATP molecules per glucose during cellular respiration, such conditions are generally not realized due to losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are actively ...
... Although there is a theoretical yield of 38 ATP molecules per glucose during cellular respiration, such conditions are generally not realized due to losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are actively ...
The Process That Feeds the Biosphere Plants are photoautotrophs
... make their own food (using sun E, CO2, and H2O) Also called producers of the biosphere Exs = green plants and Ps protist groups (fig 10.2) Heterotrophs - get E from organic compounds produced by other organisms Also called consumers of the biosphere ...
... make their own food (using sun E, CO2, and H2O) Also called producers of the biosphere Exs = green plants and Ps protist groups (fig 10.2) Heterotrophs - get E from organic compounds produced by other organisms Also called consumers of the biosphere ...
Cellular Respiration
... matrix where they are converted into 2 Acetyl CoA (C2). Multienzyme complex: – 1st: each Pyruvate releases CO2 to form Acetate. – 2nd: Acetate is oxidized and gives electrons and H+ ions to 2 NAD+ → 2 NADH. – 3rd Acetate is combined with Coenzyme A to produce 2 Acetyl CoA molecules. ...
... matrix where they are converted into 2 Acetyl CoA (C2). Multienzyme complex: – 1st: each Pyruvate releases CO2 to form Acetate. – 2nd: Acetate is oxidized and gives electrons and H+ ions to 2 NAD+ → 2 NADH. – 3rd Acetate is combined with Coenzyme A to produce 2 Acetyl CoA molecules. ...
Cellular Respiration Introduction Energy flow Overall Equation for
... Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be used as the fuel, but it is traditional to start learning with glucose. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) The catabolism of glucose is exergonic with a delta G of - 686 kcal per mole of glucose. Some of this energy is used to produce ...
... Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be used as the fuel, but it is traditional to start learning with glucose. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) The catabolism of glucose is exergonic with a delta G of - 686 kcal per mole of glucose. Some of this energy is used to produce ...
Preliminary Syllabus -- Biol 501, Principles of
... Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is not used for cellular respiration, but instead is used by the plant to synthesize other molecules such as starch, cellulose and amino acids. At night, starch molecules can be broken down to provide glucose for cellular respiration. Other molecules su ...
... Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is not used for cellular respiration, but instead is used by the plant to synthesize other molecules such as starch, cellulose and amino acids. At night, starch molecules can be broken down to provide glucose for cellular respiration. Other molecules su ...
File - hs science @ cchs
... Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is not used for cellular respiration, but instead is used by the plant to synthesize other molecules such as starch, cellulose and amino acids. At night, starch molecules can be broken down to provide glucose for cellular respiration. Other molecules su ...
... Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is not used for cellular respiration, but instead is used by the plant to synthesize other molecules such as starch, cellulose and amino acids. At night, starch molecules can be broken down to provide glucose for cellular respiration. Other molecules su ...
Using Models to Understand Photosynthesis
... A chemical equation is one type of model of photosynthesis. In the box below, the first version of the chemical equation for photosynthesis shows the chemical formula for each type of molecule, and th ...
... A chemical equation is one type of model of photosynthesis. In the box below, the first version of the chemical equation for photosynthesis shows the chemical formula for each type of molecule, and th ...
Metabolism Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions within an
... isolated from RBCs care must be taken to minimize the opportunities for hemolysis. Hemolysis may arise because of. ...
... isolated from RBCs care must be taken to minimize the opportunities for hemolysis. Hemolysis may arise because of. ...
Photosynthesis - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... • The grana stacks are joined to each other by membranous extensions of the thylakoids called lamella. • Photosynthetic pigments, enzymes and carrier molecules are embedded in the thylakoid membranes. • The clear fluid in the chloroplast is called stroma. ...
... • The grana stacks are joined to each other by membranous extensions of the thylakoids called lamella. • Photosynthetic pigments, enzymes and carrier molecules are embedded in the thylakoid membranes. • The clear fluid in the chloroplast is called stroma. ...
Final Exam - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... c) (6 points) You saw in part b that enzymes can both increase and decrease the value of KM. Which of these inhibitors makes enzyme substrate-binding tighter? How can an inhibitor make enzyme-substrate binding tighter? Explain using three sentences or fewer. d) (6 points) Trypsin us a serine proteas ...
... c) (6 points) You saw in part b that enzymes can both increase and decrease the value of KM. Which of these inhibitors makes enzyme substrate-binding tighter? How can an inhibitor make enzyme-substrate binding tighter? Explain using three sentences or fewer. d) (6 points) Trypsin us a serine proteas ...
Chemistry - Delhi Public School, Faridabad
... An element A combines with element B. An atom of A contains two electrons in its outermost shell whereas that of B has six electrons in its outermost shell. Two electrons are transferred from the atom A to the atom B. a. What is the nature of bond between A and B? ...
... An element A combines with element B. An atom of A contains two electrons in its outermost shell whereas that of B has six electrons in its outermost shell. Two electrons are transferred from the atom A to the atom B. a. What is the nature of bond between A and B? ...