4-H Virtual Forest User`s Guide Photosynthesis
... breathe through an interesting process called photosynthesis.” Photosynthesis means “putting together with light.” During photosynthesis, trees and plants use energy from the sun to change carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. Throughout the module, the user advances to the next frame by ...
... breathe through an interesting process called photosynthesis.” Photosynthesis means “putting together with light.” During photosynthesis, trees and plants use energy from the sun to change carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. Throughout the module, the user advances to the next frame by ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Rubin Risto Gulaboski
... • Used primarily in the cell as an electron carrier to mediate numerous reactions ...
... • Used primarily in the cell as an electron carrier to mediate numerous reactions ...
Preliminary Syllabus -- Biol 501, Principles of Biological Science
... be transferred to ATP molecules which provide the energy for cellular processes. In addition, plant cells use some of the sugar molecules to synthesize other needed molecules such as cellulose and amino acids. All biological organisms use ATP to provide energy for many of the molecular and cellular ...
... be transferred to ATP molecules which provide the energy for cellular processes. In addition, plant cells use some of the sugar molecules to synthesize other needed molecules such as cellulose and amino acids. All biological organisms use ATP to provide energy for many of the molecular and cellular ...
Unit 3 (Bioenergetics) Objectives and Essay Samples
... Explain how cell metabolize foods other than carbohydrates ...
... Explain how cell metabolize foods other than carbohydrates ...
Cellular respiration
... The negative ΔG indicates that the products of the chemical process store less energy than the reactants and the reaction can happen spontaneously; In other words, without an input of energy. The reducing potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with o ...
... The negative ΔG indicates that the products of the chemical process store less energy than the reactants and the reaction can happen spontaneously; In other words, without an input of energy. The reducing potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with o ...
9 biological oxidation, electron transfer chain and oxidative
... reactions in the oxidative pathways of metabolism, particularly in glycolysis, in the citric acid cycle, and in the respiratory chain of mitochondria. NADP-linked dehydrogenases are found characteristically in reductive syntheses, as in the extramitochondrial pathway of fatty acid synthesis and ster ...
... reactions in the oxidative pathways of metabolism, particularly in glycolysis, in the citric acid cycle, and in the respiratory chain of mitochondria. NADP-linked dehydrogenases are found characteristically in reductive syntheses, as in the extramitochondrial pathway of fatty acid synthesis and ster ...
Metabolism: Introduction
... In phototrophs, light energy is transformed into the light energy of ATP In heterotrophs, catabolism produces ATP, which drives activities of cells ATP cycle carries energy from photosynthesis or catabolism to the energy-requiring processes of cells ...
... In phototrophs, light energy is transformed into the light energy of ATP In heterotrophs, catabolism produces ATP, which drives activities of cells ATP cycle carries energy from photosynthesis or catabolism to the energy-requiring processes of cells ...
Medical Biochemistry
... Animal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) which oxidizes ethanol to acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is oxidized to acetate by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (AcDH). Acetaldehyde and acetate are toxic leading to the many side effects (the hangover) that are associated with alcohol consumption. The ADH ...
... Animal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) which oxidizes ethanol to acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is oxidized to acetate by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (AcDH). Acetaldehyde and acetate are toxic leading to the many side effects (the hangover) that are associated with alcohol consumption. The ADH ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... Since glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate molecules from each glucose molecule, both of which are then converted to acetyl CoA, one glucose molecule will drive two turns of the Krebs Cycle, producing a total of 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2. So far, cellular respiration has produced from one glucose molecu ...
... Since glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate molecules from each glucose molecule, both of which are then converted to acetyl CoA, one glucose molecule will drive two turns of the Krebs Cycle, producing a total of 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2. So far, cellular respiration has produced from one glucose molecu ...
Which statement is false? A. Potential energy is associated with the
... A. Potential energy is associated with the position or composition of an object. B. Kinetic energy is associated with the motion of an of an object. ✓C. Chemical energy is created during a chemical reaction. D. Thermal energy is associated with molecular motion. ...
... A. Potential energy is associated with the position or composition of an object. B. Kinetic energy is associated with the motion of an of an object. ✓C. Chemical energy is created during a chemical reaction. D. Thermal energy is associated with molecular motion. ...
Disciplina: SLC0673 Ciclos energéticos vitais
... (TPP), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), coenzyme A (CoA, sometimes denoted CoA-SH, to emphasize the role of the OSH group), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), and lipoate. Four different vitamins are required in human nutrition are vital components of this system: thiamine (in TPP), riboflav ...
... (TPP), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), coenzyme A (CoA, sometimes denoted CoA-SH, to emphasize the role of the OSH group), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), and lipoate. Four different vitamins are required in human nutrition are vital components of this system: thiamine (in TPP), riboflav ...
Background Terminology Chemistry- word document
... remainder of the explanation will focus on acids since they are what we will encounter most with living systems. Acids are compounds that release H+ when dropped in water. So, if you took a bunch of dry HCl (hydrochloric acid) molecules, they'd probably look like a powder, and they'd be bound toget ...
... remainder of the explanation will focus on acids since they are what we will encounter most with living systems. Acids are compounds that release H+ when dropped in water. So, if you took a bunch of dry HCl (hydrochloric acid) molecules, they'd probably look like a powder, and they'd be bound toget ...
The Chemical Level of Organization
... Potential energy is stored energy (stretched spring or charged battery) ○ Energy cannot be destroyed, it can only be converted During each conversion some energy is released as heat (an increase in random molecular motion) The temperature of an object is directly related to the average kinetic ...
... Potential energy is stored energy (stretched spring or charged battery) ○ Energy cannot be destroyed, it can only be converted During each conversion some energy is released as heat (an increase in random molecular motion) The temperature of an object is directly related to the average kinetic ...
SCCS AP Biology Summer 2016 Assignment Welcome to AP
... have those two. 3. 3.1: What are the 4 types of biomolecules? 4. 3.1: List 3 characteristics of a carbon atom that make it such a great ...
... have those two. 3. 3.1: What are the 4 types of biomolecules? 4. 3.1: List 3 characteristics of a carbon atom that make it such a great ...
Ch6
... catabolism that can be used in anabolism • Serve as carbon skeletons for building macromolecules • E.g., pyruvate can be converted into amino acids alanine, leucine, or valine ...
... catabolism that can be used in anabolism • Serve as carbon skeletons for building macromolecules • E.g., pyruvate can be converted into amino acids alanine, leucine, or valine ...
02_Lecture_Presentation
... another electronegative atom • In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
... another electronegative atom • In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
energy essentials
... 9. CELL RESPIRATION BREAKS CHEMICAL BONDS IN GLUCOSE TO RELEASE THE POTENTIAL ENERGY SO IT CAN BE USED BY CELLS. THIS WOULD BE AN EXAMPLE OF _________. A. ANABOLIC B. CATABOLIC ...
... 9. CELL RESPIRATION BREAKS CHEMICAL BONDS IN GLUCOSE TO RELEASE THE POTENTIAL ENERGY SO IT CAN BE USED BY CELLS. THIS WOULD BE AN EXAMPLE OF _________. A. ANABOLIC B. CATABOLIC ...
Cellular Respiration
... •Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
... •Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
A Mad Scientist`s Chemistry Presentation
... • First, the reactants must have enough energy for the reaction to occur. • This amount of energy is known as the activation energy. Second, the reactant molecules must collide with the proper ...
... • First, the reactants must have enough energy for the reaction to occur. • This amount of energy is known as the activation energy. Second, the reactant molecules must collide with the proper ...
Cellular Respiration What is Cellular Respiration?
... •Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
... •Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
chapter 25 tortora
... • Breakdown of larger molecules through Hydrolysis • Exergonic (energy can be used to drive anabolic pathways) • Example: oxidation (breakdown) of glucose in cellular ...
... • Breakdown of larger molecules through Hydrolysis • Exergonic (energy can be used to drive anabolic pathways) • Example: oxidation (breakdown) of glucose in cellular ...
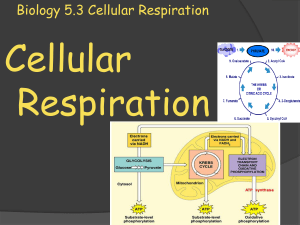
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration
... Hydrogen ions diffuse back into the inner compartment through a carrier protein that adds a phosphate group to ADP, making ATP. At the end of the electron chain, hydrogen ions and spent electrons combine with oxygen molecules (O2) forming water molecules (H20) ...
... Hydrogen ions diffuse back into the inner compartment through a carrier protein that adds a phosphate group to ADP, making ATP. At the end of the electron chain, hydrogen ions and spent electrons combine with oxygen molecules (O2) forming water molecules (H20) ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Unit 4 Ch. 5b, 6, 7 Energy, Respiration and Photosynthesis
... #1. How do cells use metabolic pathways to provide energy? ATP, Enzymes and Buffers A. I can list the basic components of an ATP molecule and draw them properly connected. I can demonstrate how an ATP molecule (serves as an energy shuttle in the cell. / is made and broken down for energy.) b. I can ...
... #1. How do cells use metabolic pathways to provide energy? ATP, Enzymes and Buffers A. I can list the basic components of an ATP molecule and draw them properly connected. I can demonstrate how an ATP molecule (serves as an energy shuttle in the cell. / is made and broken down for energy.) b. I can ...