Concept Development Studies in Chemistry
... permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of lead sul de, etc. There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrog ...
... permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of lead sul de, etc. There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrog ...
Oxidation of Fatty Acids Is the Source of Increased
... pH 7.4) (27) at 30°C with glutamate (20 mmol/L) + malate (5 mmol/L), pyruvate (10 mmol/L) + malate, succinate (20 mmol/L) + rotenone (3.75 mmol/L), durohydroquinone (DHQ, 1 mmol/L) + rotenone, N,N,N9,N9-tetramethyl-pphenylenediamine (TMPD) + ascorbate (1:10 mmol/L) + rotenone, palmitoylCoA (0.02 mmo ...
... pH 7.4) (27) at 30°C with glutamate (20 mmol/L) + malate (5 mmol/L), pyruvate (10 mmol/L) + malate, succinate (20 mmol/L) + rotenone (3.75 mmol/L), durohydroquinone (DHQ, 1 mmol/L) + rotenone, N,N,N9,N9-tetramethyl-pphenylenediamine (TMPD) + ascorbate (1:10 mmol/L) + rotenone, palmitoylCoA (0.02 mmo ...
7 rounds of beta oxidation
... Fatty acids (FA) from the diet or from the degradation of triglycerides stored in adipose cells are broken down further to smaller molecules to completely metabolize them and therefore release energy. This process of catabolism of FA includes three major parts: ...
... Fatty acids (FA) from the diet or from the degradation of triglycerides stored in adipose cells are broken down further to smaller molecules to completely metabolize them and therefore release energy. This process of catabolism of FA includes three major parts: ...
Details of the scope analysis for each organism
... (http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/supplementary/1471-2180-5-39-S1.xls) was used with two minor modifications. The following two reactions were changed to be irreversible: ATP + H+ + nicotinate D-ribonucleotide diphosphate + deamino-NAD+ ATP + H+ + pantetheine 4'-phosphate diphosphate + depho ...
... (http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/supplementary/1471-2180-5-39-S1.xls) was used with two minor modifications. The following two reactions were changed to be irreversible: ATP + H+ + nicotinate D-ribonucleotide diphosphate + deamino-NAD+ ATP + H+ + pantetheine 4'-phosphate diphosphate + depho ...
a new equation for calculating the number of atp molecules
... Pharmaceutical Sciences Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, ...
... Pharmaceutical Sciences Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, ...
PDF
... acid sequence, thermal stability and cluster content, obviously suggests a close evolutionary relationship between these proteins. The homology is surprising, however, for two reasons. First, the ferredoxin-dependent metabolic pathways that these two groups of organisms use for sugar oxidation are v ...
... acid sequence, thermal stability and cluster content, obviously suggests a close evolutionary relationship between these proteins. The homology is surprising, however, for two reasons. First, the ferredoxin-dependent metabolic pathways that these two groups of organisms use for sugar oxidation are v ...
Chapter 28 Slides
... • Kinetic controls over catabolic pathways ensure that the [ATP]/[ADP][Pi] ratio stays very high • This allows ATP hydrolysis to serve as the driving force for nearly all biochemical processes Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
... • Kinetic controls over catabolic pathways ensure that the [ATP]/[ADP][Pi] ratio stays very high • This allows ATP hydrolysis to serve as the driving force for nearly all biochemical processes Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
Chapter 8 "Ionic versus Covalent Bonding"
... then E is negative, which means that energy is released when oppositely charged ions are brought together from an infinite distance to form an isolated ion pair. As shown by the green curve in the lower half of Figure 8.1 "A Plot of Potential Energy versus Internuclear Distance for the Interaction b ...
... then E is negative, which means that energy is released when oppositely charged ions are brought together from an infinite distance to form an isolated ion pair. As shown by the green curve in the lower half of Figure 8.1 "A Plot of Potential Energy versus Internuclear Distance for the Interaction b ...
Catabolism of Organic Compounds Chapter 14
... • Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons and organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen can be oxidized anaerobically • The first step in degradation is the addition of oxygen to the molecule through the incorporation of fumarate • Hydrocarbons are oxidized to intermediates that can be catab ...
... • Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons and organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen can be oxidized anaerobically • The first step in degradation is the addition of oxygen to the molecule through the incorporation of fumarate • Hydrocarbons are oxidized to intermediates that can be catab ...
Plant Physiology
... material indicated that doubling the isotopic dilution of leucine resulted in a similar effect on light and dark chloroplasts (Table I), indicating that the curtailed incorporation into dark chloroplasts was not a pool effect. Dithiothreitol, a potent reducing agent, reportedly reactivates various e ...
... material indicated that doubling the isotopic dilution of leucine resulted in a similar effect on light and dark chloroplasts (Table I), indicating that the curtailed incorporation into dark chloroplasts was not a pool effect. Dithiothreitol, a potent reducing agent, reportedly reactivates various e ...
Growing Membranes, Sustaining Cells
... and connected by transporters to other pathways. Instead, some pathways operate across two or more compartments. In other words, some pathways are segmented into pieces operating in different compartments in eukaryotic cells, where membrane transporters become part of the pathway itself, as is well ...
... and connected by transporters to other pathways. Instead, some pathways operate across two or more compartments. In other words, some pathways are segmented into pieces operating in different compartments in eukaryotic cells, where membrane transporters become part of the pathway itself, as is well ...
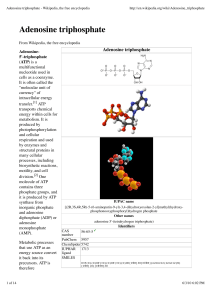
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids, as well as by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and ...
... by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids, as well as by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and ...
Rubisco
... (3) Regeneration of ribulose 1,5bisphosphate from triose phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate is an important branchpoint. Cell can choose to synthesize starch or regenerate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate from F-6-P. Animals do not have these following enzymes so they can not perform photosynthesis: Sedohept ...
... (3) Regeneration of ribulose 1,5bisphosphate from triose phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate is an important branchpoint. Cell can choose to synthesize starch or regenerate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate from F-6-P. Animals do not have these following enzymes so they can not perform photosynthesis: Sedohept ...
FUNCTION IN PHYSARUM POLYCEPHALUM mitochondria of
... body which has been stained with azure B. Figs. ! b and c are electron m i c r o g r a p h s of thin sections of the nonisolated (Fig. 1 b) and isolated mitochondria (Fig. I c), respectively. The morphology of the isolated m i t o c h o n d r i a is very similar to t h a t of nonisolated mitochondri ...
... body which has been stained with azure B. Figs. ! b and c are electron m i c r o g r a p h s of thin sections of the nonisolated (Fig. 1 b) and isolated mitochondria (Fig. I c), respectively. The morphology of the isolated m i t o c h o n d r i a is very similar to t h a t of nonisolated mitochondri ...
1- Glycolysis
... form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to prod ...
... form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to prod ...
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach Molecular Interactions 1
... 102) What makes vegetable oils with trans fats similar in structure to saturated animal fats? Which type of fat is harmful, and in what way? Answer: Trans fats have hydrogen atoms attached to make them more saturated and solid at room temperature, like animal fats. Both vegetable trans fats and satu ...
... 102) What makes vegetable oils with trans fats similar in structure to saturated animal fats? Which type of fat is harmful, and in what way? Answer: Trans fats have hydrogen atoms attached to make them more saturated and solid at room temperature, like animal fats. Both vegetable trans fats and satu ...
Early bioenergetic evolution
... and protein synthesis, which consumes about 75 per cent of the cell’s ATP budget, with RNA monomer and polymer synthesis consuming only about 12 per cent [41]. Because hydrothermal vents present conditions where the synthesis of proteins from H2, CO2 and NH3 would be an exergonic process [14,34], th ...
... and protein synthesis, which consumes about 75 per cent of the cell’s ATP budget, with RNA monomer and polymer synthesis consuming only about 12 per cent [41]. Because hydrothermal vents present conditions where the synthesis of proteins from H2, CO2 and NH3 would be an exergonic process [14,34], th ...
20 Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... group is oxidized to two molecules of CO2, energy is conserved as NADH, FAD(2H), and GTP (Fig. 20.1). NADH and FAD(2H) subsequently donate electrons to O2 via the electron transport chain, with the generation of ATP from oxidative phosphorylation. Thus, the TCA cycle is central to energy generation ...
... group is oxidized to two molecules of CO2, energy is conserved as NADH, FAD(2H), and GTP (Fig. 20.1). NADH and FAD(2H) subsequently donate electrons to O2 via the electron transport chain, with the generation of ATP from oxidative phosphorylation. Thus, the TCA cycle is central to energy generation ...
Electron Transport Chains of Lactic Acid Bacteria
... Most bacteria have a proton driven F1F0 ATPase complex to generate ATP, although some bacteria (and Archaea), such as Acetobacterium woodii, have sodium driven ATPase systems (23, 41). LAB also require the F1F0 ATPase for growth, although they, when fermenting, do not use this protein complex to gen ...
... Most bacteria have a proton driven F1F0 ATPase complex to generate ATP, although some bacteria (and Archaea), such as Acetobacterium woodii, have sodium driven ATPase systems (23, 41). LAB also require the F1F0 ATPase for growth, although they, when fermenting, do not use this protein complex to gen ...
File - Mr. Arnold`s Classes
... extra carbon is released as carbon dioxide. Acetyl CoA can also be produced from fatty acids. When the fatty acid chain contains an even number of carbons, no CO 2 is released. How many Acetyl CoA molecules can be produced with the following fatty acids? a. 23C b. 18C c. 31C ...
... extra carbon is released as carbon dioxide. Acetyl CoA can also be produced from fatty acids. When the fatty acid chain contains an even number of carbons, no CO 2 is released. How many Acetyl CoA molecules can be produced with the following fatty acids? a. 23C b. 18C c. 31C ...
http://doc.rero.ch
... electronic matrix element τHDA. While τFC can be directly calculated from classical simulations,75−78 we will use the expression for its semiclassical limit, τFC = h̅(2λkBT)1/2.79,80 Using reorganization energies in the range of 1.8−2.3 eV (Table 3) we obtain τFC ≈ 2 fs. To calculate the decay time ...
... electronic matrix element τHDA. While τFC can be directly calculated from classical simulations,75−78 we will use the expression for its semiclassical limit, τFC = h̅(2λkBT)1/2.79,80 Using reorganization energies in the range of 1.8−2.3 eV (Table 3) we obtain τFC ≈ 2 fs. To calculate the decay time ...
2015 HSC Chemistry Marking Guidelines
... which would drive the reaction to the right, as according to Le Chatelier’s principle, the reaction would be favoured that produced heat. On the graph, this is clearly shown, as for each pressure, the yield increased at lower temperatures. Maximum yield could be obtained at very low temperatures, ho ...
... which would drive the reaction to the right, as according to Le Chatelier’s principle, the reaction would be favoured that produced heat. On the graph, this is clearly shown, as for each pressure, the yield increased at lower temperatures. Maximum yield could be obtained at very low temperatures, ho ...
Chapter 15
... glycolysis that generates NADPH and pentoses. While it does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. ...
... glycolysis that generates NADPH and pentoses. While it does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. ...
References
... To clarify whether the high and low FRET states include one and two steps, we measured the histogram of the dwell multiplied by [ATP] (Fig. 4). If a state consisted of one or two steps, the histogram of [ATP] would follow equations exp(-Kon[ATP]/) (solid lines in Fig. 4) or exp(-Kon[ATP]/) (d ...
... To clarify whether the high and low FRET states include one and two steps, we measured the histogram of the dwell multiplied by [ATP] (Fig. 4). If a state consisted of one or two steps, the histogram of [ATP] would follow equations exp(-Kon[ATP]/) (solid lines in Fig. 4) or exp(-Kon[ATP]/) (d ...