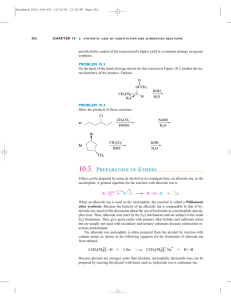
10.3 PREPARATION OF ETHERS
... Ethers can be prepared by using an alcohol or its conjugate base, an alkoxide ion, as the nucleophile. A general equation for the reaction with alkoxide ion is ...
... Ethers can be prepared by using an alcohol or its conjugate base, an alkoxide ion, as the nucleophile. A general equation for the reaction with alkoxide ion is ...
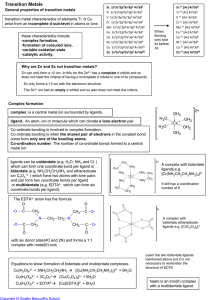
Transition Metals
... absorbed is transmitted to give the substance colour The energy needed to excite electrons to a higher level depends on the oxidation state of the metal and the type of ligand. ...
... absorbed is transmitted to give the substance colour The energy needed to excite electrons to a higher level depends on the oxidation state of the metal and the type of ligand. ...
7.1 Equilibrium PPT equilibrium1
... The equilibrium constant is a measure of the amount of products at equilibrium compared with the amount of ...
... The equilibrium constant is a measure of the amount of products at equilibrium compared with the amount of ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
Chemistry 120
... liquids such as acetone, hexane, benzene or ether or water. Water is the most important solvent. The oceans cover ~ ¾ of the surface of the planet and every cell is mainly composed of water. Solutions in water are termed aqueous solutions and species are written as E(aq). ...
... liquids such as acetone, hexane, benzene or ether or water. Water is the most important solvent. The oceans cover ~ ¾ of the surface of the planet and every cell is mainly composed of water. Solutions in water are termed aqueous solutions and species are written as E(aq). ...
m5zn_1ed95c16cede0b1
... 3. Pressure Factor i) Solids/Liquids - Very little effect Solids and Liquids are already close together, extra pressure will not increase solubility. ii) gas - Solubility increases with Pressure. Increase pressure squeezes gas solute into solvent. ...
... 3. Pressure Factor i) Solids/Liquids - Very little effect Solids and Liquids are already close together, extra pressure will not increase solubility. ii) gas - Solubility increases with Pressure. Increase pressure squeezes gas solute into solvent. ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Forward and reverse reactions taking place at equal rates It is a dynamic state - reactions are constantly occurring ...
... Forward and reverse reactions taking place at equal rates It is a dynamic state - reactions are constantly occurring ...
Year 2 Chemistry Contents Guide
... Virtual experiment exploring the effect of changing pH on amino acids Animation illustrating the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids • Hydrolysis of peptide bonds Animation illustrating the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins • The types of bonds in prot ...
... Virtual experiment exploring the effect of changing pH on amino acids Animation illustrating the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids • Hydrolysis of peptide bonds Animation illustrating the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins • The types of bonds in prot ...
PIB - Unit 6 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
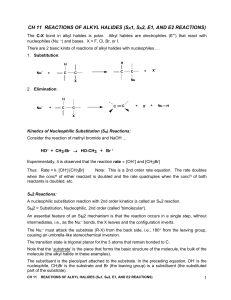
Alkyl Halides02
... 2. a rapid nucleophilic attack on the C+ (forming a protonated alcohol intermediate in this case) 3. a rapid deprotonation of the alcohol intermediate forming the product alcohol The Nu:- is not involved in the slow, rate-limiting step. In this example, H2O is the Nu:- as well as the solvent. Reacti ...
... 2. a rapid nucleophilic attack on the C+ (forming a protonated alcohol intermediate in this case) 3. a rapid deprotonation of the alcohol intermediate forming the product alcohol The Nu:- is not involved in the slow, rate-limiting step. In this example, H2O is the Nu:- as well as the solvent. Reacti ...