Chapter 4 Lecture Notes in PowerPoint
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
Section 18.2 Power Point Presentation
... reduction based on a table of standard reduction potentials • Calculate the net cell voltage, Eo, of a combination of half cells from standard electrode potential data • Determine whether a given redox reaction will be spontaneous or non-spontaneous ...
... reduction based on a table of standard reduction potentials • Calculate the net cell voltage, Eo, of a combination of half cells from standard electrode potential data • Determine whether a given redox reaction will be spontaneous or non-spontaneous ...
BioN01 Introduction, pH and buffer Summer 2014
... Each bond is very stable. strength of bonds: triple > double > Single) They link C atoms together in chains and rings. These serve as a backbones. ...
... Each bond is very stable. strength of bonds: triple > double > Single) They link C atoms together in chains and rings. These serve as a backbones. ...
Review Unit: Chemistry Review
... simplest way possible. Scientists refine the descriptions of the natural world so that these descriptions are as precise and complete as possible. In science, reliable and accurate descriptions of phenomena become scientific laws. In scientific problem solving, descriptions, predictions, and explana ...
... simplest way possible. Scientists refine the descriptions of the natural world so that these descriptions are as precise and complete as possible. In science, reliable and accurate descriptions of phenomena become scientific laws. In scientific problem solving, descriptions, predictions, and explana ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... you’ll find that you have carbon (C) in one of its various forms (e.g., graphite, charcoal, diamond). Or, collect a bunch of atoms with seven electrons and you’ll have nitrogen (N); choose eight, and you’ll get oxygen (O). These materials – carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and anything else you find on che ...
... you’ll find that you have carbon (C) in one of its various forms (e.g., graphite, charcoal, diamond). Or, collect a bunch of atoms with seven electrons and you’ll have nitrogen (N); choose eight, and you’ll get oxygen (O). These materials – carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and anything else you find on che ...
Molecular geometry
... standard atomic orbitals; chemical bonds result from an overlap of these orbitals. Molecular orbital theory (MO): An advanced model of chemical bonding in which electrons reside in molecular orbitals delocalized over the entire molecule. In the simplest version, the molecular orbitals are simply l ...
... standard atomic orbitals; chemical bonds result from an overlap of these orbitals. Molecular orbital theory (MO): An advanced model of chemical bonding in which electrons reside in molecular orbitals delocalized over the entire molecule. In the simplest version, the molecular orbitals are simply l ...
Conductometric and Potentiometric Determination of the Solubility
... such as precipitation reactions, where the degree of feasibility of titration depends on the degree of completeness of the precipitation reaction. The solubility product (KSP) of the formed ion-associates were determined conductometrically [11] as described under the experimental part, the equilibri ...
... such as precipitation reactions, where the degree of feasibility of titration depends on the degree of completeness of the precipitation reaction. The solubility product (KSP) of the formed ion-associates were determined conductometrically [11] as described under the experimental part, the equilibri ...
13. transition metal chemistry
... The formal definition of a transition metal is ‘an element that forms at least one stable ion with a partially full d-shell.’ Zinc forms only one stable ion, Zn2+ which has an electronic configuration of [Ar] 4so 3d10 i.e. has a full d shell. (1 mark for definition, 1 mark for full explanation of wh ...
... The formal definition of a transition metal is ‘an element that forms at least one stable ion with a partially full d-shell.’ Zinc forms only one stable ion, Zn2+ which has an electronic configuration of [Ar] 4so 3d10 i.e. has a full d shell. (1 mark for definition, 1 mark for full explanation of wh ...
Question Bank Topic 5
... Which of the following statements concerning zinc-carbon cells are correct? (1) Used zinc-carbon cells can be disposed of in fire. (2) Zinc-carbon cells leak even though they are not in use. (3) The voltage of zinc-carbon cells drops rapidly over discharge. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2 ...
... Which of the following statements concerning zinc-carbon cells are correct? (1) Used zinc-carbon cells can be disposed of in fire. (2) Zinc-carbon cells leak even though they are not in use. (3) The voltage of zinc-carbon cells drops rapidly over discharge. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2 ...
Chemistry Curriculum
... - Identify the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons an element has - Identify the special group and element is a member of, the element’s state of matter at room temperature, and the element’s identity as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid using the periodic table Students will be able to - Deter ...
... - Identify the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons an element has - Identify the special group and element is a member of, the element’s state of matter at room temperature, and the element’s identity as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid using the periodic table Students will be able to - Deter ...
Q - PIMS
... The substance whose analysis is required for the separation of isotopes is converted into vapours. The pressure of vapours is reduced to 106—107 torr. These vapours at low pressure are allowed to enter the ionization chamber. (ii) Ionization chamber: In this chamber fast moving electrons are bomba ...
... The substance whose analysis is required for the separation of isotopes is converted into vapours. The pressure of vapours is reduced to 106—107 torr. These vapours at low pressure are allowed to enter the ionization chamber. (ii) Ionization chamber: In this chamber fast moving electrons are bomba ...
No Slide Title - McMaster Chemistry
... Zn goes from O.N. = 0 in the metal to O.N. = +2 in the chloride salt H goes from O.N. = +1 in HCl (aq) to O.N. = 0 in the elemental gas 1A03/1E03 Types of Reactions (2) ...
... Zn goes from O.N. = 0 in the metal to O.N. = +2 in the chloride salt H goes from O.N. = +1 in HCl (aq) to O.N. = 0 in the elemental gas 1A03/1E03 Types of Reactions (2) ...
Lecture Resource ()
... • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
... • Most drugs, vitamins, and many other natural products are heterocycles • A natural product is a compound synthesized by a plant or an animal ...
June Exam Review Material World
... 9. Which of the following is true about the periodic table? a) The period indicates the number of neutrons that an atom has b) The Group number indicates the number of electrons that an atom has c) The period indicates the number of protons that an atom has d) The Group number indicates the number o ...
... 9. Which of the following is true about the periodic table? a) The period indicates the number of neutrons that an atom has b) The Group number indicates the number of electrons that an atom has c) The period indicates the number of protons that an atom has d) The Group number indicates the number o ...
Coordination properties of the diethyl (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)phosphonate ligand (3-pmpe)
... usually large and lie in the range 4–8 cm–1 [33, 34], the decrease of χMT at lower temperatures observed for the nickel(II) compound (Fig. 2) can be explained by weak antiferromagnetic interactions and/or zero-field splitting effects [34]. The Co(II) compound behaves as a Curie–Weiss paramagnet, at ...
... usually large and lie in the range 4–8 cm–1 [33, 34], the decrease of χMT at lower temperatures observed for the nickel(II) compound (Fig. 2) can be explained by weak antiferromagnetic interactions and/or zero-field splitting effects [34]. The Co(II) compound behaves as a Curie–Weiss paramagnet, at ...
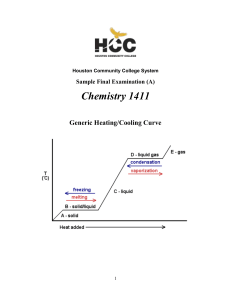
1411FINALSAMPLEs and Key
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter2
... are very close to twice as massive as nitrogen atoms. Put another way, it means that two nitrogen atoms have a total mass very close to the mass of a single silicon atom. ...
... are very close to twice as massive as nitrogen atoms. Put another way, it means that two nitrogen atoms have a total mass very close to the mass of a single silicon atom. ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements
... configurations ns2np3 (n is the period number) Oxidation states that range from -3 to +5 The metallic character of the group increases down the group ...
... configurations ns2np3 (n is the period number) Oxidation states that range from -3 to +5 The metallic character of the group increases down the group ...
The Mechanism of Electrode Erosion in Electrical Discharges
... this order must now be considered. A certain (microscopic)volume of metal lying under this area will be suddenly heated, and part of this heat must be dissipated by thermal conduction through the bulk of the metal; the rate at which this can occur has been given previously (8). Heat will also be los ...
... this order must now be considered. A certain (microscopic)volume of metal lying under this area will be suddenly heated, and part of this heat must be dissipated by thermal conduction through the bulk of the metal; the rate at which this can occur has been given previously (8). Heat will also be los ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements The Representative
... Electron configuration is ns1(n = period number). Lose their valence e- easily (great reducing agents). Most violently reactive of all the metals. React strongly with H2O(l); the vigor of the reaction increases down the group. The alkali metals are all too easily oxidized to be found in thei ...
... Electron configuration is ns1(n = period number). Lose their valence e- easily (great reducing agents). Most violently reactive of all the metals. React strongly with H2O(l); the vigor of the reaction increases down the group. The alkali metals are all too easily oxidized to be found in thei ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... A and B as well as an introduction to the a few concepts in the first three chapters of the AP Chemistry Textbook that we haven’t covered yet. Having the following skills will be essential to your success in AP Chemistry and I will expect that you already have a firm grasp on these topics as we star ...
... A and B as well as an introduction to the a few concepts in the first three chapters of the AP Chemistry Textbook that we haven’t covered yet. Having the following skills will be essential to your success in AP Chemistry and I will expect that you already have a firm grasp on these topics as we star ...
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin
... gained electrons are called ions. Atoms that have lost electrons (as a result , now contain more p+ than e-) are called cat ions which carry positive charges , while atoms that have gained excessive electrons (as a result, now contain more e- than p+ ) are called anions which carry negative charges ...
... gained electrons are called ions. Atoms that have lost electrons (as a result , now contain more p+ than e-) are called cat ions which carry positive charges , while atoms that have gained excessive electrons (as a result, now contain more e- than p+ ) are called anions which carry negative charges ...
Ksp Problem Sets 1 and 2
... x 10 . (Note: Be careful! Write the balanced equation first, then express the unknown ...
... x 10 . (Note: Be careful! Write the balanced equation first, then express the unknown ...
ap chemistry syllabus
... structure and arrangement of atoms, ions, molecules and the forces between them. Enduring Understanding 2.A-Matter can be described by its physical properties. The physical properties of a substance generally depend on the spacing between the particles (atoms, molecules, ions) that make up the subst ...
... structure and arrangement of atoms, ions, molecules and the forces between them. Enduring Understanding 2.A-Matter can be described by its physical properties. The physical properties of a substance generally depend on the spacing between the particles (atoms, molecules, ions) that make up the subst ...
Structure and Properties of Matter
... out are elements. Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743-94), a French chemist was first to explain an element. He defined an element as basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances even by chemical means. Elements serve as the building blocks for various types of other substance ...
... out are elements. Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743-94), a French chemist was first to explain an element. He defined an element as basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances even by chemical means. Elements serve as the building blocks for various types of other substance ...