Solutions - Dynamic Science
... 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) => C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) b) Production of ethanol in fermentation C6H12O6(aq) => 2C2H6O(aq) + 2CO2(g) c) Complete combustion of liquid ethanol C2H6O(l) + 3O2(g) => 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) d) How many CO2 molecules are consumed per glucose molecule? 6 e) How many CO2 molecules are produced ...
... 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) => C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) b) Production of ethanol in fermentation C6H12O6(aq) => 2C2H6O(aq) + 2CO2(g) c) Complete combustion of liquid ethanol C2H6O(l) + 3O2(g) => 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) d) How many CO2 molecules are consumed per glucose molecule? 6 e) How many CO2 molecules are produced ...
workbook Chem (WP)
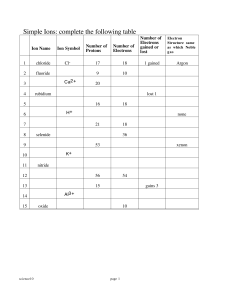
... 1. identify the theories and their authors represented by the following: a. atom looks like this b. atom looks like a planetary system c. the electrons move around the nucleus in an unknown path. d. key was the “Gold foil experiment”. Ions 1. Why do ions form? 2. Draw the Bohr diagram for the atom a ...
... 1. identify the theories and their authors represented by the following: a. atom looks like this b. atom looks like a planetary system c. the electrons move around the nucleus in an unknown path. d. key was the “Gold foil experiment”. Ions 1. Why do ions form? 2. Draw the Bohr diagram for the atom a ...
2 - mrstorie
... 9. Identify which molecules in question 9 are polar. 10. What is the general trend observed for ionization energy? Explain this trend for ionization energies; include reasoning for the trend in a group and the trend in a period. 11. What are the trends observed for electronegativity, electron affini ...
... 9. Identify which molecules in question 9 are polar. 10. What is the general trend observed for ionization energy? Explain this trend for ionization energies; include reasoning for the trend in a group and the trend in a period. 11. What are the trends observed for electronegativity, electron affini ...
Accelerator Experiments and Theoretical Models for the Electron Screening Effect in
... are splitted off and the remaining oxygen radical forms a chemical bond to the metal atoms. Essentially the same happens by direct impact excitation of the water molecule by the ions. The hydrogen implantation into the metal causes aside from the usual surface deterioration a in depth destruction of ...
... are splitted off and the remaining oxygen radical forms a chemical bond to the metal atoms. Essentially the same happens by direct impact excitation of the water molecule by the ions. The hydrogen implantation into the metal causes aside from the usual surface deterioration a in depth destruction of ...
Chemistry - CBSE Academic
... Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of mass action, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium - Le Chatelier's principle, ionic equilibrium- ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, ionization of poly ...
... Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of mass action, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium - Le Chatelier's principle, ionic equilibrium- ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, ionization of poly ...
www.rsc.org/njc
... 1:2 Complex of Mg with isonicotinic acid (Mg3) Mg3 has the formula [Mg(C6H5NO2)2(H2O)4](NO3)2 and was obtained from a solution of Mg(NO3)2.6H2O and isonicotinic acid, in a 1:1 ratio, in isopropanol, at 50 °C. It is a constitutional isomer of Mg1 and Mg2. Similarly to Mg2, the Mg centre, which in thi ...
... 1:2 Complex of Mg with isonicotinic acid (Mg3) Mg3 has the formula [Mg(C6H5NO2)2(H2O)4](NO3)2 and was obtained from a solution of Mg(NO3)2.6H2O and isonicotinic acid, in a 1:1 ratio, in isopropanol, at 50 °C. It is a constitutional isomer of Mg1 and Mg2. Similarly to Mg2, the Mg centre, which in thi ...
Ions in Crystals - American Chemical Society
... As in previous works,11,46,47 the crystal wave function has been obtained by means of ab initio Perturbed Ion (aiPI)60-62 calculations at the experimental geometry.14 The aiPI method is a localized Hartree-Fock (HF) scheme60,63,64 that has been extensively used to describe accurately the electronic ...
... As in previous works,11,46,47 the crystal wave function has been obtained by means of ab initio Perturbed Ion (aiPI)60-62 calculations at the experimental geometry.14 The aiPI method is a localized Hartree-Fock (HF) scheme60,63,64 that has been extensively used to describe accurately the electronic ...
Electron attachment to amino acid clusters in helium nanodroplets
... Gutowski et al.36 on the possible structures of glycine monomer and its anion and the dipole moments of these species have been calculated. The most stable species is a neutral 共i.e., nonzwitterionic兲 structure which is calculated to have a low dipole moment 共1.2 D兲. This is too small to allow forma ...
... Gutowski et al.36 on the possible structures of glycine monomer and its anion and the dipole moments of these species have been calculated. The most stable species is a neutral 共i.e., nonzwitterionic兲 structure which is calculated to have a low dipole moment 共1.2 D兲. This is too small to allow forma ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... (i) the quest for an understanding of matter and material change, (ii) the utilization of material change for human ends. Ideally, the first activity provides the necessary know-how for the pursuit of the second, but in practice, the help it can give is only partial, and the second activity has to f ...
... (i) the quest for an understanding of matter and material change, (ii) the utilization of material change for human ends. Ideally, the first activity provides the necessary know-how for the pursuit of the second, but in practice, the help it can give is only partial, and the second activity has to f ...
Characterization of Nano Materials using Electron Microscopy
... dispersing 1 -100 nm oxide particles for aero-space applications [1]. In the field of medicine, possibilities are immense. Carbon nano tubes are special nano-materials discovered by Iijima in 1991 [1]. They have better electrical conductivity than copper, exceptional mechanical strength and high fle ...
... dispersing 1 -100 nm oxide particles for aero-space applications [1]. In the field of medicine, possibilities are immense. Carbon nano tubes are special nano-materials discovered by Iijima in 1991 [1]. They have better electrical conductivity than copper, exceptional mechanical strength and high fle ...
Moles and Equations
... Up to this point state symbols have not been used in any of the equations: (s) ...
... Up to this point state symbols have not been used in any of the equations: (s) ...
Audit Schedule
... 3. When you learn the definition of molarity, be sure to learn moles of solute per liter of solution, not just moles per liter. Remember that when preparing a solution, liters of solvent added is not always the same as the final volume of the solution. If you learn the complete definition for molar ...
... 3. When you learn the definition of molarity, be sure to learn moles of solute per liter of solution, not just moles per liter. Remember that when preparing a solution, liters of solvent added is not always the same as the final volume of the solution. If you learn the complete definition for molar ...
formula writing and nomenclature of inorganic - Parkway C-2
... share electrons in forming a chemical bond. The number of electrons that an atom loses, gains, or shares when it bonds with another atom is known as the oxidation number of the atom. Elements which lose electrons in a chemical reaction, or which have electrons which are shared with another element d ...
... share electrons in forming a chemical bond. The number of electrons that an atom loses, gains, or shares when it bonds with another atom is known as the oxidation number of the atom. Elements which lose electrons in a chemical reaction, or which have electrons which are shared with another element d ...
Document
... (b) When an electric field is applied to a covalent solid, the valence electrons in the covalent bonds are shifted very easily with respect to the positive ionic cores. The whole solid becomes polarized due to the collective shift in the negative charge distribution of the valence electrons. (Supple ...
... (b) When an electric field is applied to a covalent solid, the valence electrons in the covalent bonds are shifted very easily with respect to the positive ionic cores. The whole solid becomes polarized due to the collective shift in the negative charge distribution of the valence electrons. (Supple ...
I- Introduction
... weight of sodium hydroxide) giving a normality of 0.1 meq/ml. Back titration: In back-titration, a known number of millimoles of reactant are taken in excess of the analyte. The unreacted portion is titrated for example, in the titration of antacid tablets with a strong acid such as HCl. ...
... weight of sodium hydroxide) giving a normality of 0.1 meq/ml. Back titration: In back-titration, a known number of millimoles of reactant are taken in excess of the analyte. The unreacted portion is titrated for example, in the titration of antacid tablets with a strong acid such as HCl. ...
factors affecting strength of acids
... ARRHENIUS BASES - Bases are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to produce hydroxide ions (OH-) NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 - Arrhenius bases are ionic compounds in the pure state ...
... ARRHENIUS BASES - Bases are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to produce hydroxide ions (OH-) NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 - Arrhenius bases are ionic compounds in the pure state ...
Click here for printer-friendly version
... The magnetic and geographic north pole of the earth is not located in the same place. Opposite poles attract. For example, hold two bar magnets near each other, the “N” pole of one magnet is attracted by the “S” pole of another. If the bar magnet is balanced by a thread, however, then the “N” pole o ...
... The magnetic and geographic north pole of the earth is not located in the same place. Opposite poles attract. For example, hold two bar magnets near each other, the “N” pole of one magnet is attracted by the “S” pole of another. If the bar magnet is balanced by a thread, however, then the “N” pole o ...
Chapter 20
... molecular compounds. However, oxygen is reduced in the formation of water for example. In water the two shared e- in the H – O bond are shifted toward the O and away from the H. ...
... molecular compounds. However, oxygen is reduced in the formation of water for example. In water the two shared e- in the H – O bond are shifted toward the O and away from the H. ...
Molecular Orbital
... antibonding molecular orbital. The same thing happens when the 2py orbitals interact, only in this case we get a y and a y* antibonding molecular orbital. Because there is no difference between the energies of the 2px and 2py atomic orbitals, there is no difference between the energies of the x and ...
... antibonding molecular orbital. The same thing happens when the 2py orbitals interact, only in this case we get a y and a y* antibonding molecular orbital. Because there is no difference between the energies of the 2px and 2py atomic orbitals, there is no difference between the energies of the x and ...
Class 11 Class 12 The p- Block Element • Group13 (B to Tl
... elements of group 2. From left to right in the period, the magnitude of nuclear charge increases but the electrons are added to, the same shell. These electrons do not screen each other, therefore, the electrons experience greater nuclear charge. • In other words, effective nuclear ...
... elements of group 2. From left to right in the period, the magnitude of nuclear charge increases but the electrons are added to, the same shell. These electrons do not screen each other, therefore, the electrons experience greater nuclear charge. • In other words, effective nuclear ...
Charge transport in a polypeptide chain
... amino acids where one of these amino acids contains a natural chromophore, i.e. trypotophan. Charge is introduced into the system via photoexcitation. In their experiment, they found that charge transport through these model polypeptides could be extremely efficient for some choices of amino acids, ...
... amino acids where one of these amino acids contains a natural chromophore, i.e. trypotophan. Charge is introduced into the system via photoexcitation. In their experiment, they found that charge transport through these model polypeptides could be extremely efficient for some choices of amino acids, ...
Chemistry Revision Checklist F4 2017 (inc F3)
... Construct word equations and simple balanced chemical equations Describe lithium, sodium and potassium in Group I as a collection of relatively soft metals showing a trend in melting point, density and reaction with water Identify trends in Groups, given information about the elements concerned Pred ...
... Construct word equations and simple balanced chemical equations Describe lithium, sodium and potassium in Group I as a collection of relatively soft metals showing a trend in melting point, density and reaction with water Identify trends in Groups, given information about the elements concerned Pred ...
Table of Contents Pages Unit 1- Matter and Change 1
... called filtering. Some simple methods also exist for separating homogeneous mixtures. A solid dissolved in a liquid solution can be separated by letting it dry out in the process of ___________________. Mixtures are separated into pure _____________________. A pure substance always has the same comp ...
... called filtering. Some simple methods also exist for separating homogeneous mixtures. A solid dissolved in a liquid solution can be separated by letting it dry out in the process of ___________________. Mixtures are separated into pure _____________________. A pure substance always has the same comp ...
Physical Earth Daily Learning Guide DRAFT - Burlington
... 9-11 PS2C Periodic trends are related to atomic structure. 9-11 PS2D The formation of ions and ionic compounds. 9-11 PS2E Covalent bonding and molecular substances. 9-11 PS2F* All forms of life are composed of large molecules that contain carbon. 9-11 PS2G Chemical reactions change the arrangement o ...
... 9-11 PS2C Periodic trends are related to atomic structure. 9-11 PS2D The formation of ions and ionic compounds. 9-11 PS2E Covalent bonding and molecular substances. 9-11 PS2F* All forms of life are composed of large molecules that contain carbon. 9-11 PS2G Chemical reactions change the arrangement o ...