9701/04 - StudyGuide.PK
... (ii) Explain how the variation in conductivity is related to the structure and bonding in the elements. ...
... (ii) Explain how the variation in conductivity is related to the structure and bonding in the elements. ...
Contents and Concepts Learning Objectives
... Next, we construct the ICE chart with the initial [Cl-] = 0.020 M. We then solve for x, the molar solubility. ...
... Next, we construct the ICE chart with the initial [Cl-] = 0.020 M. We then solve for x, the molar solubility. ...
AP Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 8.37 Which group in the periodic table has elements with high IE1 and very negative first electron affinities (EA1)? What is the charge on the ions that these atoms form? 8.59 Write the charge and full ground-state electron configuration of the monatomic ion most likely to be formed by each of the f ...
... 8.37 Which group in the periodic table has elements with high IE1 and very negative first electron affinities (EA1)? What is the charge on the ions that these atoms form? 8.59 Write the charge and full ground-state electron configuration of the monatomic ion most likely to be formed by each of the f ...
The Bio-Organometallic Chemistry of Technetium and Rhenium
... of an atom in a compound is determined by the following rules: a. The oxidation number of an atom in the elemental form is zero b. The oxidation number of an atom in a simple ionic compound is typically equal to the charge on that atom (with the appropriate sign) c. The oxidation number of an atom i ...
... of an atom in a compound is determined by the following rules: a. The oxidation number of an atom in the elemental form is zero b. The oxidation number of an atom in a simple ionic compound is typically equal to the charge on that atom (with the appropriate sign) c. The oxidation number of an atom i ...
Chemistry booklet
... The mole concept gives us a means of managing fixed numbers of atoms / ions / molecules in ...
... The mole concept gives us a means of managing fixed numbers of atoms / ions / molecules in ...
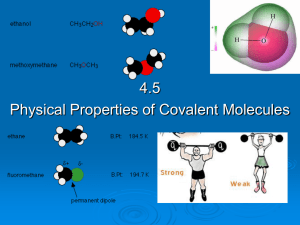
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Simple covalent molecules tend to be gases, liquids or low melting point solids. A covalent molecule has an increasing tendency to become a solid as its molecular mass increases. This is because the strength of the van der waals forces increases, decreasing the distance between the molecules. E. ...
... Simple covalent molecules tend to be gases, liquids or low melting point solids. A covalent molecule has an increasing tendency to become a solid as its molecular mass increases. This is because the strength of the van der waals forces increases, decreasing the distance between the molecules. E. ...
Acids, bases and combustion
... (a) So that they may stick to the gas Jar to prevent them from falling into water when the gas jar is inverted (b) Iron filings turned to reddish brown because they reacted with oxygen in presence of moisture to form rust. - The level of water inside the gas jar rise so as to occupy the volume initi ...
... (a) So that they may stick to the gas Jar to prevent them from falling into water when the gas jar is inverted (b) Iron filings turned to reddish brown because they reacted with oxygen in presence of moisture to form rust. - The level of water inside the gas jar rise so as to occupy the volume initi ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... oxidized. (Lose Electrons: Oxidation) • And the substance that gains electrons in the reaction is reduced. (Gain Electrons: Reduction) LEO goes GER • You cannot have one without the other. • We also define redox in terms of changes in oxidation number – Oxidation number increases for element being o ...
... oxidized. (Lose Electrons: Oxidation) • And the substance that gains electrons in the reaction is reduced. (Gain Electrons: Reduction) LEO goes GER • You cannot have one without the other. • We also define redox in terms of changes in oxidation number – Oxidation number increases for element being o ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... (c) There are some advantages of drinking hard water. Give one of them. (1 mark) (d) What happens if you use temporarily hard water in a kettle? (2 marks) (e) Explain how an ion-exchange column softens hard water. (2 marks) (f) Another way of softening hard water is to use sodium carbonate. Explain ...
... (c) There are some advantages of drinking hard water. Give one of them. (1 mark) (d) What happens if you use temporarily hard water in a kettle? (2 marks) (e) Explain how an ion-exchange column softens hard water. (2 marks) (f) Another way of softening hard water is to use sodium carbonate. Explain ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... which are broken during melting of SiO2, require much more energy (higher temperature) to break compared to the relatively weak London dispersion and dipole forces, which are broken during the melting of SO2. d. Liquid Cl2 is held together by London dispersion forces, which although weak increase in ...
... which are broken during melting of SiO2, require much more energy (higher temperature) to break compared to the relatively weak London dispersion and dipole forces, which are broken during the melting of SO2. d. Liquid Cl2 is held together by London dispersion forces, which although weak increase in ...
Standard Voltages Cell Voltage
... • Order species according to their ease of oxidation or reduction based on a table of standard reduction potentials • Calculate the net cell voltage, Eo, of a combination of half cells from standard electrode potential data • Determine whether a given redox reaction will be spontaneous or non-sponta ...
... • Order species according to their ease of oxidation or reduction based on a table of standard reduction potentials • Calculate the net cell voltage, Eo, of a combination of half cells from standard electrode potential data • Determine whether a given redox reaction will be spontaneous or non-sponta ...
CHAPtER 4 Electrolysis
... The anode in an electrolytic cell is positive since the DC source withdraws electrons from it. Electrons are supplied to the positive anode by the oxidation of the copper electrode itself. In an electrolytic cell, the polarity of the electrodes is determined by the external DC source. In contrast, t ...
... The anode in an electrolytic cell is positive since the DC source withdraws electrons from it. Electrons are supplied to the positive anode by the oxidation of the copper electrode itself. In an electrolytic cell, the polarity of the electrodes is determined by the external DC source. In contrast, t ...
4. Solution Guide to Supplementary Exercises
... electrode while metal Z is the positive electrode. Metal W forms ions more readily than metal Z. This gives the descending order of reactivity of the four metals: Y, X, W, Z. 19 D For a simple chemical cell, the farther apart the two metals are in the electrochemical series (or the reactivity series ...
... electrode while metal Z is the positive electrode. Metal W forms ions more readily than metal Z. This gives the descending order of reactivity of the four metals: Y, X, W, Z. 19 D For a simple chemical cell, the farther apart the two metals are in the electrochemical series (or the reactivity series ...
Lesson 11.1 properties of solutions
... In general, nonreactive gases or vapors can mix in all proportions to give a gaseous mixture. Fluids that mix with or dissolve in each other in all proportions are said to be miscible fluids. Gases are thus miscible. If two fluids do not mix but form layers, they are said to be immiscible. Liquid So ...
... In general, nonreactive gases or vapors can mix in all proportions to give a gaseous mixture. Fluids that mix with or dissolve in each other in all proportions are said to be miscible fluids. Gases are thus miscible. If two fluids do not mix but form layers, they are said to be immiscible. Liquid So ...
Electrostatics in material medium
... Electrostatics in material medium Dielectrics & polarization: are basically insulators which have only bound charges in contrast to the free charges of a conductor. Here we study electrostatics in presence of dielectrics – important also for chemistry and biology people to understand. Polarization: ...
... Electrostatics in material medium Dielectrics & polarization: are basically insulators which have only bound charges in contrast to the free charges of a conductor. Here we study electrostatics in presence of dielectrics – important also for chemistry and biology people to understand. Polarization: ...
Atoms and Molecules
... An atom is the smallest particle of the element that can exist independently and retain all its chemical properties. A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound capable of independent existence under ordinary conditions. It shows all the properties of the substance. A chemical fo ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of the element that can exist independently and retain all its chemical properties. A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound capable of independent existence under ordinary conditions. It shows all the properties of the substance. A chemical fo ...
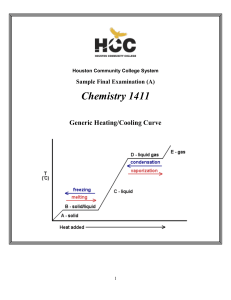
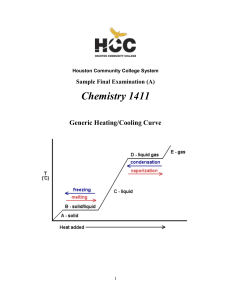
CHEM-1411 Final Practice Exam
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
California Standards Practice - Student Edition
... atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bo ...
... atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bo ...
Solid-state chemistry of lithium power sources
... band. Li1 2 xCr2O4, for example, when combined with a lithium negative electrode gives an open circuit potential of 5 V associated with the Cr4+/3+ mixed-valence state.17 As lithium is inserted into the intercalation host forming a continuous range of solid solutions, the electrons fill up the band ...
... band. Li1 2 xCr2O4, for example, when combined with a lithium negative electrode gives an open circuit potential of 5 V associated with the Cr4+/3+ mixed-valence state.17 As lithium is inserted into the intercalation host forming a continuous range of solid solutions, the electrons fill up the band ...
chemistry — released items - North Carolina Public Schools
... because potassium ions are attracted to the partial negative charge of hydrogen ...
... because potassium ions are attracted to the partial negative charge of hydrogen ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes in PowerPoint
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...