Unit 1B1 - Uddingston Grammar School
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
Honors Chemistry
... If the charges add up to zero, then just put the symbols together to form the formula. If the charges do not add up to zero, switch the charges and reduce. Example: Make a compound from acetate and calcium. Calcium goes first because calcium is positive. ...
... If the charges add up to zero, then just put the symbols together to form the formula. If the charges do not add up to zero, switch the charges and reduce. Example: Make a compound from acetate and calcium. Calcium goes first because calcium is positive. ...
Chemical Bonds Study Guide Answer Key
... 1. Chemical formula - the way of expressing information about the proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound, using element symbols and numbers. 2. Molecule- electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds 3. Valence electrons- electrons locat ...
... 1. Chemical formula - the way of expressing information about the proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound, using element symbols and numbers. 2. Molecule- electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds 3. Valence electrons- electrons locat ...
Chemical bond - Physical Science
... energy levels) • Thus, they must gain or lose the same number of electrons to achieve a full outer energy level in a bond • Oxidation number: the charge of an ion • For ionic compounds, the oxidation number is the same as the charge of the ion ▫ Ex: the sodium ion (Na+) has a charge of 1+ and an oxi ...
... energy levels) • Thus, they must gain or lose the same number of electrons to achieve a full outer energy level in a bond • Oxidation number: the charge of an ion • For ionic compounds, the oxidation number is the same as the charge of the ion ▫ Ex: the sodium ion (Na+) has a charge of 1+ and an oxi ...
Exam #2
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... o When an atom or molecule gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged. For example when Cl gains an electron it becomes Cl-. o Negatively charged ions are called anions. o An atom or molecule can lose more than one electron. o When molecules loose electrons, polyatomic ions are formed. ...
... o When an atom or molecule gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged. For example when Cl gains an electron it becomes Cl-. o Negatively charged ions are called anions. o An atom or molecule can lose more than one electron. o When molecules loose electrons, polyatomic ions are formed. ...
Final Exam
... 11. In order to increase the rate at which a solute dissolves in a solvent, one could A. increase the particle size of the solute. B. decrease the volume of the solvent. C. increase the temperature of the solvent. D. decrease the pressure of the solution. ...
... 11. In order to increase the rate at which a solute dissolves in a solvent, one could A. increase the particle size of the solute. B. decrease the volume of the solvent. C. increase the temperature of the solvent. D. decrease the pressure of the solution. ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
... • A neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. • Molecular Compound – A chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. • Chemical Formula – It indicates the number of atoms by using atomic symbols and subscripts. • Molecular Formula – Shows the types and numbers of atoms ...
... • A neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. • Molecular Compound – A chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. • Chemical Formula – It indicates the number of atoms by using atomic symbols and subscripts. • Molecular Formula – Shows the types and numbers of atoms ...
Lesson 2: Electrolytes
... • When NaCl dissolves in water, sodium and chlorine ions are produced. • A dissociation equation must be balanced (a subscript on the reactant side becomes a coefficient on the product side.) • The charges on the ions must be present. (This is determined by the periodic table) • Subscripts must be w ...
... • When NaCl dissolves in water, sodium and chlorine ions are produced. • A dissociation equation must be balanced (a subscript on the reactant side becomes a coefficient on the product side.) • The charges on the ions must be present. (This is determined by the periodic table) • Subscripts must be w ...
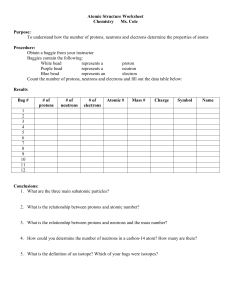
Atomic Structure Mini Lab
... To understand how the number of protons, neutrons and electrons determine the properties of atoms Procedure: Obtain a baggie from your instructor Baggies contain the following: White bead represents a proton Purple bead represents a neutron Blue bead represents an electron Count the number of proton ...
... To understand how the number of protons, neutrons and electrons determine the properties of atoms Procedure: Obtain a baggie from your instructor Baggies contain the following: White bead represents a proton Purple bead represents a neutron Blue bead represents an electron Count the number of proton ...
Pretest 4.3 2008
... Plastic is an insulator, meaning that it is a poor conductor of heat and electricity.___ Copper and silver are better conductors than aluminum and tungsten_______ To avoid extra resistance, it is better to use a longer wire than necessary______ To improve conductance, one should use as thin a wire a ...
... Plastic is an insulator, meaning that it is a poor conductor of heat and electricity.___ Copper and silver are better conductors than aluminum and tungsten_______ To avoid extra resistance, it is better to use a longer wire than necessary______ To improve conductance, one should use as thin a wire a ...
hapter 2
... Rutherford’s gold foil experiment Atoms have a nucleus Atoms are made up mostly of space Protons exist in the nucleus with a + charge Electrons mass is 9.11 x 10-31 kg, the charge is Protons mass is 1.66 x 10-27 kg, the charge is + Neutrons mass is 1.67 x 10-27 kg, there is no charge AMU means ...
... Rutherford’s gold foil experiment Atoms have a nucleus Atoms are made up mostly of space Protons exist in the nucleus with a + charge Electrons mass is 9.11 x 10-31 kg, the charge is Protons mass is 1.66 x 10-27 kg, the charge is + Neutrons mass is 1.67 x 10-27 kg, there is no charge AMU means ...
Lecture 2
... • How do we know if a replacement reaction will take place or not occur? • Refer to the activity series • Fig 10.12, p 264 ...
... • How do we know if a replacement reaction will take place or not occur? • Refer to the activity series • Fig 10.12, p 264 ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – The Basics of
... 2. Atoms are the smallest unit of matter. Each different type of atom represents an element (ex: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon). Scientists have created a chart called the periodic table of elements to organize elements by their atomic properties. 3. Four elements—carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), an ...
... 2. Atoms are the smallest unit of matter. Each different type of atom represents an element (ex: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon). Scientists have created a chart called the periodic table of elements to organize elements by their atomic properties. 3. Four elements—carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), an ...
Chapter 2 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry This chapter deals with
... Dalton's atomic theory had several postulates: 1. all matter is composed of small, invisible particles called atoms 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses an ...
... Dalton's atomic theory had several postulates: 1. all matter is composed of small, invisible particles called atoms 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses an ...
4. - period2chem
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
Plum pudding
... Problem 1a.- The plum pudding analogy hides the fact that Thomson thought the electrons were moving inside the atom. Nevertheless let’s consider a plum pudding model of a lithium ion (Li+): A spherical volume of radius R with homogeneously distributed positive charge = +3e and two electrons, with ch ...
... Problem 1a.- The plum pudding analogy hides the fact that Thomson thought the electrons were moving inside the atom. Nevertheless let’s consider a plum pudding model of a lithium ion (Li+): A spherical volume of radius R with homogeneously distributed positive charge = +3e and two electrons, with ch ...
Ei otsikkoa
... Some form the +3 or +4 ion, the latter being rare due to small size & high charge (which easily leads to covalent bonding). Examples: CrCl3, Fe2O3, MnO2 ...
... Some form the +3 or +4 ion, the latter being rare due to small size & high charge (which easily leads to covalent bonding). Examples: CrCl3, Fe2O3, MnO2 ...
Topic 3: Periodicity
... increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove a third electron). In the higher oxidation states the elements usually not exist as a free metal ions, but covalently bonded or as a oxyanions (MnO4-). ...
... increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove a third electron). In the higher oxidation states the elements usually not exist as a free metal ions, but covalently bonded or as a oxyanions (MnO4-). ...
Atomic Structure (history of atom)
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are joined, separated or rearranged Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another ...
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are joined, separated or rearranged Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... (c) Each calcium ion (Ca2+) bears two positive charges, and each phosphate ion ( ) bears three negative charges. To make the sum of the charges equal zero, we must adjust the numbers of cations and anions: ...
... (c) Each calcium ion (Ca2+) bears two positive charges, and each phosphate ion ( ) bears three negative charges. To make the sum of the charges equal zero, we must adjust the numbers of cations and anions: ...
Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... molecules have many features in common. Individual atoms often possess unpaired electrons. These atoms are usually chemically unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exot ...
... molecules have many features in common. Individual atoms often possess unpaired electrons. These atoms are usually chemically unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exot ...
Unit 6 Study Guide – Chemical Bonding 1. A _ chemical
... between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. 2. Are atoms more or less stable when they bond? _more stable____________________ 3. Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between large numbers of cations and anions is called __ionic__ ...
... between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. 2. Are atoms more or less stable when they bond? _more stable____________________ 3. Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between large numbers of cations and anions is called __ionic__ ...