Introduction to Chemical Bonding
... The bond of Sodium and Fluorine is an example of Ionic bonding: electrons have been transferred in order for the atoms to have a full outer level. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes what is called an ion. An ion is no longer neutrally charged because it has different numbers of proton ...
... The bond of Sodium and Fluorine is an example of Ionic bonding: electrons have been transferred in order for the atoms to have a full outer level. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes what is called an ion. An ion is no longer neutrally charged because it has different numbers of proton ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their COMMON name. All compounds containing hydrogen are MOLECULAR compounds. How do we indicate the physical state of a compound? (something is writte ...
... We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their COMMON name. All compounds containing hydrogen are MOLECULAR compounds. How do we indicate the physical state of a compound? (something is writte ...
Electron Arrangement
... have high melting and boiling points because all the atoms are interlinked by strong covalent bonds which take a lot of energy to break. Ionic Bonding Between a metal and a non-metal atom. The metal loses its outer electrons to form a positive ion. The non-metal takes these electrons to form a negat ...
... have high melting and boiling points because all the atoms are interlinked by strong covalent bonds which take a lot of energy to break. Ionic Bonding Between a metal and a non-metal atom. The metal loses its outer electrons to form a positive ion. The non-metal takes these electrons to form a negat ...
1A - The changing atom History of the atom • The model of the atom
... As the atom has the same number of protons and electrons it will have the same chemical properties. They are all hydrogen atoms because they all have the same number of protons Hydrogen can be used as an example:- ...
... As the atom has the same number of protons and electrons it will have the same chemical properties. They are all hydrogen atoms because they all have the same number of protons Hydrogen can be used as an example:- ...
Figure 2: Alternative Periodic Table
... b) If a new element, X, with atomic weight 25.84 is discovered, what would its properties be? Where would it fit in the periodic table you constructed? Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) ...
... b) If a new element, X, with atomic weight 25.84 is discovered, what would its properties be? Where would it fit in the periodic table you constructed? Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) ...
Fall Exam 1
... demonstrated the existence of more than one charge. neutrons. B. proved that Thomson’s “plum D. determined the charge on a single pudding” model of the atom’s electron. structure was correct. 19. Nobel prize winner Ernest Rutherford conducted an experiment with gold foil and alpha particles, leading ...
... demonstrated the existence of more than one charge. neutrons. B. proved that Thomson’s “plum D. determined the charge on a single pudding” model of the atom’s electron. structure was correct. 19. Nobel prize winner Ernest Rutherford conducted an experiment with gold foil and alpha particles, leading ...
How Atoms Bond: Ionic Bonds
... And atoms themselves? Heads up – this next part contains information that might prove useful in a later quiz: Because atoms have equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons , the electric charges cancel each other out. Net charge: zero. OK, now back to electrons. While the positive prot ...
... And atoms themselves? Heads up – this next part contains information that might prove useful in a later quiz: Because atoms have equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons , the electric charges cancel each other out. Net charge: zero. OK, now back to electrons. While the positive prot ...
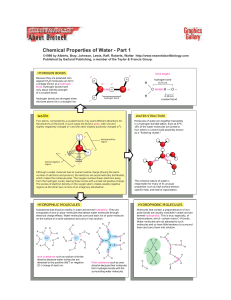
Water Chemistry - Biology12-Lum
... electrical charge effects. Water molecules surround each ion or polar molecule on the surface of a solid substance and carry it into solution. ...
... electrical charge effects. Water molecules surround each ion or polar molecule on the surface of a solid substance and carry it into solution. ...
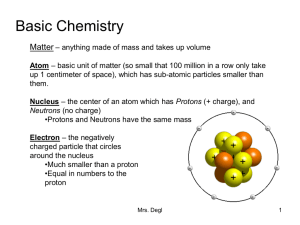
Basic Atomic Theory
... themselves with variation of No of electrons (Atomic Number) • Elements can be arranged periodically to ...
... themselves with variation of No of electrons (Atomic Number) • Elements can be arranged periodically to ...
presentation - WordPress.com
... an extra electron is added to an atom. For the bond formation electron gain enthalpy of an element should be high. ...
... an extra electron is added to an atom. For the bond formation electron gain enthalpy of an element should be high. ...
Chemistry MSL Practical Style Review 1. What is the nuclear
... The pressure increases, which in turn increases the production of products. The concentration of reactants increases with an increase in temperature. The average kinetic energy increases, so the likelihood of more effective collisions between ions increases. Systems are more stable at high temperatu ...
... The pressure increases, which in turn increases the production of products. The concentration of reactants increases with an increase in temperature. The average kinetic energy increases, so the likelihood of more effective collisions between ions increases. Systems are more stable at high temperatu ...
Lewis Structures Notes • Draw the dot diagram for
... • Ionic Dot Diagrams- the electrons are gained and lost, not shared. Put each atom in a bracket with its balance electrons around it. The charge of the atom goes outside of the bracket. o Ex: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) ...
... • Ionic Dot Diagrams- the electrons are gained and lost, not shared. Put each atom in a bracket with its balance electrons around it. The charge of the atom goes outside of the bracket. o Ex: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) ...
Inorganic Chemistry Basics
... Plot of charge/radius ratio against the ionization energy (M to M2+) for some divalent metal ions ...
... Plot of charge/radius ratio against the ionization energy (M to M2+) for some divalent metal ions ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... - More feasible with larger molecules such as PAHs and fullerenes. - Observed with naphthalene and C60. ...
... - More feasible with larger molecules such as PAHs and fullerenes. - Observed with naphthalene and C60. ...
Hinge Point Questions
... Please feel free to adapt them for your own use. I have written them for the areas I feel my pupils struggle with most. Some are straightforward one right answer, others have more than one correct answer, while others are aimed to promote ideas and discussion. ...
... Please feel free to adapt them for your own use. I have written them for the areas I feel my pupils struggle with most. Some are straightforward one right answer, others have more than one correct answer, while others are aimed to promote ideas and discussion. ...
Basic Chemistry
... neutrons. Some Carbon atoms have 6 neutrons and some have 7/ 8. •Some isotopes can be radioactive (unstable nuclei that breaks down at a constant rate over time). Compound – when two or more elements are chemically combined •Bonds attach one element to another to from a compound •The compound has to ...
... neutrons. Some Carbon atoms have 6 neutrons and some have 7/ 8. •Some isotopes can be radioactive (unstable nuclei that breaks down at a constant rate over time). Compound – when two or more elements are chemically combined •Bonds attach one element to another to from a compound •The compound has to ...
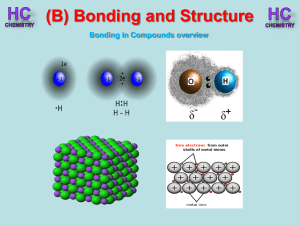
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... - non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions - electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals ...
... - non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions - electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals ...
Bez tytułu slajdu
... One of the main problems in mass spectrometry is how to ionize a molecule, without destroying it. Only ionized (i.e. those which lost or gained an electron) atoms and/or molecules and/or radicals can be trapped and transported by (relatively) weak electric and magnetic fields. But ionization by coll ...
... One of the main problems in mass spectrometry is how to ionize a molecule, without destroying it. Only ionized (i.e. those which lost or gained an electron) atoms and/or molecules and/or radicals can be trapped and transported by (relatively) weak electric and magnetic fields. But ionization by coll ...
Chapter 2 Reading Guide
... Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) ...
... Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... charge). For example, both Li and Na react with water to form aqueous solutions of their ionic hydroxides and hydrogen gas: 2 Li(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 LiOH(aq) + H2(g) 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g) The reaction with lithium is very gentle, but with sodium it usually results in an explosion of ...
... charge). For example, both Li and Na react with water to form aqueous solutions of their ionic hydroxides and hydrogen gas: 2 Li(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 LiOH(aq) + H2(g) 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g) The reaction with lithium is very gentle, but with sodium it usually results in an explosion of ...
study guide first semester chemistry
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. ...
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. ...
Unit 1
... Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge diff ...
... Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge diff ...
Unit 1
... Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge diff ...
... Bond between molecules NOT between atoms Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge diff ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 1 Outline – 2012-2013
... a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use the Bohr Model on the ...
... a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use the Bohr Model on the ...
lesson 5
... Not all atoms form compounds. Only atoms that have outer shells that are not full form compounds. The elements of Group 18 have complete outer shells. These atoms usually do not form compounds. All other atoms have outer shells that are not full. All other atoms form compounds. Atoms form compounds ...
... Not all atoms form compounds. Only atoms that have outer shells that are not full form compounds. The elements of Group 18 have complete outer shells. These atoms usually do not form compounds. All other atoms have outer shells that are not full. All other atoms form compounds. Atoms form compounds ...