
Document
... 10. Compared to the charge of a proton, the charge of an electron has a. A greater magnitude and the same sign b. A greater magnitude and the opposite sign c. The same magnitude and the same sign d. The same magnitude and the opposite sign 11. Which phrase describes an atom? a. A negatively charged ...
... 10. Compared to the charge of a proton, the charge of an electron has a. A greater magnitude and the same sign b. A greater magnitude and the opposite sign c. The same magnitude and the same sign d. The same magnitude and the opposite sign 11. Which phrase describes an atom? a. A negatively charged ...
key - Greenslime.info
... The elements in group 17, including fluorine, bromine, chlorine and iodine, are called the halogens. Describe the reactivity of the halogens, and why they have this reactivity. The halogens are very reactive, because they each have seven valence electrons, and only need to gain one valence electron ...
... The elements in group 17, including fluorine, bromine, chlorine and iodine, are called the halogens. Describe the reactivity of the halogens, and why they have this reactivity. The halogens are very reactive, because they each have seven valence electrons, and only need to gain one valence electron ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... Atomic Number and Mass • The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of the element • The mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons and is used to distinguish one isotope ...
... Atomic Number and Mass • The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of the element • The mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons and is used to distinguish one isotope ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... – (a) atoms can slide past each other without breaking their bonds ...
... – (a) atoms can slide past each other without breaking their bonds ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Outcomes
... compounds occurs State octet rule Give an electron dot diagram (Lewis dot diagram) of atoms forming ions and ionic bonding (3 equations) Use model for the structure of an ionic compound to explain its properties Define molecular (covalent bonding) and give structural formula of molecular compounds. ...
... compounds occurs State octet rule Give an electron dot diagram (Lewis dot diagram) of atoms forming ions and ionic bonding (3 equations) Use model for the structure of an ionic compound to explain its properties Define molecular (covalent bonding) and give structural formula of molecular compounds. ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... a. They are composed of anions and cations. c. They are composed of cations only. b. They are composed of anions only. d. They are formed from two or more nonmetallic elements. ____ 42) Which element, when combined with bromine, would most likely form an ionic compound? a. lithium b. carbon c. phosp ...
... a. They are composed of anions and cations. c. They are composed of cations only. b. They are composed of anions only. d. They are formed from two or more nonmetallic elements. ____ 42) Which element, when combined with bromine, would most likely form an ionic compound? a. lithium b. carbon c. phosp ...
atoms-chemical
... outermost shell, the valence shell. Atoms with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical behavior. An atom with a completed valence shell is unreactive. All other atoms are chemically reactive because they have incomplete valence shells. ...
... outermost shell, the valence shell. Atoms with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical behavior. An atom with a completed valence shell is unreactive. All other atoms are chemically reactive because they have incomplete valence shells. ...
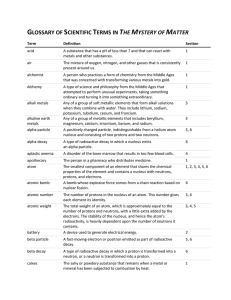
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... A form of energy resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. Electromagnetism is the force that causes the interaction between electrically charged particles; the areas in which this ...
... A form of energy resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. Electromagnetism is the force that causes the interaction between electrically charged particles; the areas in which this ...
Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 7 Explain what the strong force is and the purpose of it. The strong force is the force that keeps the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It holds them together even though all of the protons are positively charged and should be repel. 8 What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element that have di ...
... 7 Explain what the strong force is and the purpose of it. The strong force is the force that keeps the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It holds them together even though all of the protons are positively charged and should be repel. 8 What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element that have di ...
Final Exam Chemistry B2A Mr. Kimball`s Class 2003
... 22. Which of the following is FALSE regarding an electron? a) has a relative charge of -1 b) is abbreviated ec) has a mass of approximately 1 amu d) exists outside the nucleus e) exists in energy levels 23. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the nucleus of an atom? a) a small, low density reg ...
... 22. Which of the following is FALSE regarding an electron? a) has a relative charge of -1 b) is abbreviated ec) has a mass of approximately 1 amu d) exists outside the nucleus e) exists in energy levels 23. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the nucleus of an atom? a) a small, low density reg ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... line (emission) spectra and Niels Bohr; the wave properties of the electron; quantum mechanical view of the atom; atomic orbital shapes; electron spin (para/dia magnetism); the Pauli exclusion principle; atomic subshell energies and electron assignments; atomic electron configurations; electron conf ...
... line (emission) spectra and Niels Bohr; the wave properties of the electron; quantum mechanical view of the atom; atomic orbital shapes; electron spin (para/dia magnetism); the Pauli exclusion principle; atomic subshell energies and electron assignments; atomic electron configurations; electron conf ...
3 molecules
... 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e.g. N + 3e N3- (Ne outer shell) ...
... 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e.g. N + 3e N3- (Ne outer shell) ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... 2) All atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different and have different properties. 3) Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. 4) Compounds are form ...
... 2) All atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different and have different properties. 3) Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. 4) Compounds are form ...
File
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
Practice Exam 3 - University of Missouri
... C2H2(g) is a. 2 C(s) + H2(g) → C2H2(g) b. 2 C(g) + 2H(g) → C2H2(g) c. 2 C2(g) + 2H(g) → C2H2(g) d. C2H6(g) → C2H2(g) + H2 e. none of the above 8. Which of the following has a standard molar enthalpy of formation of zero at 25° and 1 atm pressure? a. CO2(g) b. H2O(l) c. Zn(s) d. NO(g) ...
... C2H2(g) is a. 2 C(s) + H2(g) → C2H2(g) b. 2 C(g) + 2H(g) → C2H2(g) c. 2 C2(g) + 2H(g) → C2H2(g) d. C2H6(g) → C2H2(g) + H2 e. none of the above 8. Which of the following has a standard molar enthalpy of formation of zero at 25° and 1 atm pressure? a. CO2(g) b. H2O(l) c. Zn(s) d. NO(g) ...
Intro to Soln Stoich
... ◦ O-H bonds are covalent, e- not shared equally ◦ Oxygen has a slight negative, hydrogen slight positive Polar molecule Oxygen has a strong attraction to cations, hydrogen to anions ...
... ◦ O-H bonds are covalent, e- not shared equally ◦ Oxygen has a slight negative, hydrogen slight positive Polar molecule Oxygen has a strong attraction to cations, hydrogen to anions ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... • Ionic bonds form between atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons • Ionic compounds form crystals instead of individual molecules • Example: Na+Cl-(sodium chloride) ...
... • Ionic bonds form between atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons • Ionic compounds form crystals instead of individual molecules • Example: Na+Cl-(sodium chloride) ...
Terminology 1
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... • Ionic bonds form between atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons • Ionic compounds form crystals instead of individual molecules • Example: Na+Cl-(sodium chloride) ...
... • Ionic bonds form between atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons • Ionic compounds form crystals instead of individual molecules • Example: Na+Cl-(sodium chloride) ...
bonding, structure, properties and energy changes
... • Group 17: the halogens – the most reactive nonmetals • Group 18: the noble gases – these elements are very unreactive. Elements in the same group (column) have the same number of valence electrons (similar electron arrangements). The number of valence electrons increases across a row (period). T ...
... • Group 17: the halogens – the most reactive nonmetals • Group 18: the noble gases – these elements are very unreactive. Elements in the same group (column) have the same number of valence electrons (similar electron arrangements). The number of valence electrons increases across a row (period). T ...
ap chemistry chapter 8 bonding
... takes place when separated gaseous ions are packed together to form an ionic solid. Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) If exothermic, the sign will be negative and the ionic solid will be the stable form. We can use a variety of steps to determine the heat of formation of an ionic solid from its elements. Th ...
... takes place when separated gaseous ions are packed together to form an ionic solid. Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) If exothermic, the sign will be negative and the ionic solid will be the stable form. We can use a variety of steps to determine the heat of formation of an ionic solid from its elements. Th ...






![Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000860497_1-e3bea510ba504d09bc42d6f5e4936390-300x300.png)















