BIOL 317 LECTURE NOTES – WEEK 10 SUMMARY SPECIATION
... phylogenetic tree, the nodes, or branching points, indicate speciation events. What are species? Species are usually considered to be the basic unit of biodiversity, but what does this mean? Ever since Darwin, biologists have been debating the nature of species, even debating the reality of species. ...
... phylogenetic tree, the nodes, or branching points, indicate speciation events. What are species? Species are usually considered to be the basic unit of biodiversity, but what does this mean? Ever since Darwin, biologists have been debating the nature of species, even debating the reality of species. ...
Module 3
... should be observed under specific conditions if the explanation is true. a. Hypothesis are predictions based upon both research and observation b. Hypotheses used to determine what data to collect and as a guide for interpreting the data. Key Idea 3: the observations made while testing proposed expl ...
... should be observed under specific conditions if the explanation is true. a. Hypothesis are predictions based upon both research and observation b. Hypotheses used to determine what data to collect and as a guide for interpreting the data. Key Idea 3: the observations made while testing proposed expl ...
Wilkins PPT
... • Just because there are the same number of total organisms and species in two areas does not mean that they have the same biodiversity. • Conclusion should be made once data is collected. The hypothesis analyzed and new hypothesis typically formed based on the data. ...
... • Just because there are the same number of total organisms and species in two areas does not mean that they have the same biodiversity. • Conclusion should be made once data is collected. The hypothesis analyzed and new hypothesis typically formed based on the data. ...
Protein sequence database
... Most SNPs are benign, with absolutely no effect on gene structure or ...
... Most SNPs are benign, with absolutely no effect on gene structure or ...
File
... DNA Fingerprinting Activity Introduction: DNA fingerprinting relies on the fact that the DNA code is universal for all living things and that there are differences between individuals within that code. Because human DNA is very similar to every other human’s DNA, DNA fingerprinting primarily focuses ...
... DNA Fingerprinting Activity Introduction: DNA fingerprinting relies on the fact that the DNA code is universal for all living things and that there are differences between individuals within that code. Because human DNA is very similar to every other human’s DNA, DNA fingerprinting primarily focuses ...
Clike here - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... reaction can make a large number of copies of a specific sequence. The PCR reaction includes: •Template DNA •DNA Primers •DNA Polymerase •DNA monomers The PCR is often used to answer the same question that is answered by a radioactive probe - is a ...
... reaction can make a large number of copies of a specific sequence. The PCR reaction includes: •Template DNA •DNA Primers •DNA Polymerase •DNA monomers The PCR is often used to answer the same question that is answered by a radioactive probe - is a ...
DO NOT WRITE ON
... 15. Define homeostasis. 16. Identify which cell organelle is most identifiable in newly discovered species. 17. State the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (i.e. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus). 18. Know that genetically similar organisms that can produce fertile offspring are called ...
... 15. Define homeostasis. 16. Identify which cell organelle is most identifiable in newly discovered species. 17. State the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. (i.e. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus). 18. Know that genetically similar organisms that can produce fertile offspring are called ...
Document
... worthless for the restriction site-based reconstructions of intrafamilial phylogeny for which cpDNA is so well suited. • The occasional losses of mitochondrial genes and introns may also serve as useful markers of phylogeny. • The low rate of mtDNA substitutions suggests that comparative sequencing ...
... worthless for the restriction site-based reconstructions of intrafamilial phylogeny for which cpDNA is so well suited. • The occasional losses of mitochondrial genes and introns may also serve as useful markers of phylogeny. • The low rate of mtDNA substitutions suggests that comparative sequencing ...
Answer keyDNA Practice problems
... If you were to replicate the above strand of DNA in this direction ----, from left to right, which of the parent stands is used to build the leading strand of DNA? The lagging strand??? Here is a model for the above DNA strands: 3’-------------------------------5’----this is the parent strand which ...
... If you were to replicate the above strand of DNA in this direction ----, from left to right, which of the parent stands is used to build the leading strand of DNA? The lagging strand??? Here is a model for the above DNA strands: 3’-------------------------------5’----this is the parent strand which ...
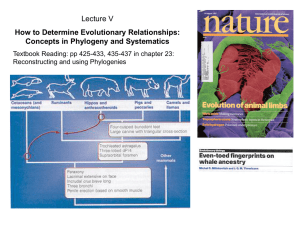
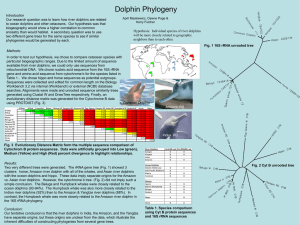
Phylogeny and Systematics
... derived characteristics the organisms share. Primitive traits (plesiomorphic traits) are characteristics which have the same structure and function and which evolved early on in the organism’s development. Derived traits (apomorphic traits) are characteristics which have the same structure and funct ...
... derived characteristics the organisms share. Primitive traits (plesiomorphic traits) are characteristics which have the same structure and function and which evolved early on in the organism’s development. Derived traits (apomorphic traits) are characteristics which have the same structure and funct ...
NoLimits 1000bp DNA Fragment
... The NoLimits™ DNA Fragment is a chromatographypurified, exceptionally pure individual DNA fragment. It is produced using specifically designed plasmid DNA purified by a proprietary patent-pending technology. ...
... The NoLimits™ DNA Fragment is a chromatographypurified, exceptionally pure individual DNA fragment. It is produced using specifically designed plasmid DNA purified by a proprietary patent-pending technology. ...
two genes from two species when the
... cornmeal/yeast/agar medium at 21 0e. These stocks have been used extensively in laboratory behavioral investigations (e.g., Noor, 1996). Two isofemale lines of D. miranda (Mather and Mount St. Helena) were also cultured, both only 2 generations removed from the wild. Individual males from these line ...
... cornmeal/yeast/agar medium at 21 0e. These stocks have been used extensively in laboratory behavioral investigations (e.g., Noor, 1996). Two isofemale lines of D. miranda (Mather and Mount St. Helena) were also cultured, both only 2 generations removed from the wild. Individual males from these line ...
Introduction continued
... 5. How the Genome is Studied Maps and sequences Locus: location of a gene in a chromosome. Two genes are assorted (or segregated, i.e. are on the same chromosome) if an offspring has about 50% chance of inheriting both characteristics (deduced from the genes) from the same parent. Recombination: due ...
... 5. How the Genome is Studied Maps and sequences Locus: location of a gene in a chromosome. Two genes are assorted (or segregated, i.e. are on the same chromosome) if an offspring has about 50% chance of inheriting both characteristics (deduced from the genes) from the same parent. Recombination: due ...
Manipulating DNA Notes
... • In order to study genes, biologists need to make many copies • Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): technique that allows molecular biologists to make many copies of a particular ...
... • In order to study genes, biologists need to make many copies • Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): technique that allows molecular biologists to make many copies of a particular ...
BONUS BAMBI Summary Report 2016
... discussions on genetic monitoring programs for Swedish waters. ...
... discussions on genetic monitoring programs for Swedish waters. ...
On the origin of species, Really
... times, but sperm only fertilize females of same species – Molecular genetic studies have identified several of the proteins (on sperm and egg) mediating this species-specific interaction ...
... times, but sperm only fertilize females of same species – Molecular genetic studies have identified several of the proteins (on sperm and egg) mediating this species-specific interaction ...
No Slide Title - Faculty Virginia
... Systematists classify organisms and determine evolutionary relationships based on analysis of homologous characters (traits) •Systematic investigation is based on analysis of homologous characters (traits); characters may be morphological, molecular, behavioral, physiological.. •Homologous charac ...
... Systematists classify organisms and determine evolutionary relationships based on analysis of homologous characters (traits) •Systematic investigation is based on analysis of homologous characters (traits); characters may be morphological, molecular, behavioral, physiological.. •Homologous charac ...
Genealogy: To DNA or not to DNA?
... 3. Autosomal DNA testing is the kind that works across all lines of a family, both male and female. People that share the same autosomal DNA will have common ancestors. However, further analysis would be required to determine to which family line they are connected. The autosomal DNA test is the lat ...
... 3. Autosomal DNA testing is the kind that works across all lines of a family, both male and female. People that share the same autosomal DNA will have common ancestors. However, further analysis would be required to determine to which family line they are connected. The autosomal DNA test is the lat ...