the nucleic acids - This is MySchool
... The sister strands of the DNA molecule run in opposite directions (antiparallel) They are joined by the bases Each base is paired with a specific partner: A is always paired with T G is always paired with C Purine with Pyrimidine This the sister strands are complementary but not identical Th ...
... The sister strands of the DNA molecule run in opposite directions (antiparallel) They are joined by the bases Each base is paired with a specific partner: A is always paired with T G is always paired with C Purine with Pyrimidine This the sister strands are complementary but not identical Th ...
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. ...
... form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. ...
Parallel Computing with DNA
... Researchers also investigated how the ability to repeatedly recombine DNA strands can be used to construct “computational devices” that work massively parallel and are highly energy efficient. It is not obvious how such devices can be programmed to solve computational problems for which currently co ...
... Researchers also investigated how the ability to repeatedly recombine DNA strands can be used to construct “computational devices” that work massively parallel and are highly energy efficient. It is not obvious how such devices can be programmed to solve computational problems for which currently co ...
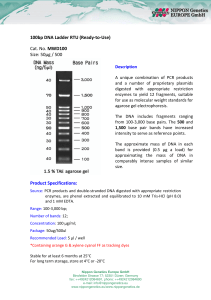
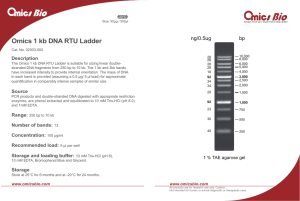
Omics 1 kb DNA RTU Ladder
... in each band is provided (assuming a 0.5 μg/ 5 μl load) for approximate quantification in comparably intense samples of similar size. ...
... in each band is provided (assuming a 0.5 μg/ 5 μl load) for approximate quantification in comparably intense samples of similar size. ...
Why is DNA called the "blueprint of life"?
... Key Learning: DNA segments contain information for the production of proteins necessary for growth and ...
... Key Learning: DNA segments contain information for the production of proteins necessary for growth and ...
DNA History Function Structure
... • Genes, a segment of DNA codes for a certain protein. • For example the Gene for making Insulin (protein) is coded for in a section of DNA. • The Gene has to be read and pass on the information to the ribosome. • DNA RNA PROTIEN ...
... • Genes, a segment of DNA codes for a certain protein. • For example the Gene for making Insulin (protein) is coded for in a section of DNA. • The Gene has to be read and pass on the information to the ribosome. • DNA RNA PROTIEN ...
DNA Fingerprinting
... II. How is it used to solve crimes? A. Everywhere you go, you shed cells B. At crime scenes, investigators can look for them 1. skin 2. hair 3. blood 4. any body fluids ...
... II. How is it used to solve crimes? A. Everywhere you go, you shed cells B. At crime scenes, investigators can look for them 1. skin 2. hair 3. blood 4. any body fluids ...
Maurice Wilkins

Maurice Hugh Frederick Wilkins CBE FRS (15 December 1916 – 5 October 2004) was a New Zealand-born English physicist and molecular biologist, and Nobel Laureate whose research contributed to the scientific understanding of phosphorescence, isotope separation, optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction, and to the development of radar. He is best known for his work at King's College, London on the structure of DNA which falls into three distinct phases. The first was in 1948–50 where his initial studies produced the first clear X-ray images of DNA which he presented at a conference in Naples in 1951 attended by James Watson. During the second phase of work (1951–52) he produced clear ""B form"" ""X"" shaped images from squid sperm which he sent to James Watson and Francis Crick causing Watson to write ""Wilkins... has obtained extremely excellent X-ray diffraction photographs""[of DNA]. Throughout this period Wilkins was consistent in his belief that DNA was helical even when Rosalind Franklin expressed strong views to the contrary.In 1953 Franklin instructed Raymond Gosling to give Wilkins, without condition, a high quality image of ""B"" form DNA which she had unexpectedly produced months earlier but had “put it aside” to concentrate on other work. Wilkins, having checked that he was free to personally use the photograph to confirm his earlier results, showed it to Watson without the consent of Rosalind Franklin. This image, along with the knowledge that Linus Pauling had published an incorrect structure of DNA, “mobilised” Watson to restart model building efforts with Crick. Important contributions and data from Wilkins, Franklin (obtained via Max Perutz) and colleagues in Cambridge enabled Watson and Crick to propose a double-helix model for DNA. The third and longest phase of Wilkins' work on DNA took place from 1953 onwards. Here Wilkins led a major project at King's College, London, to test, verify and make significant corrections to the DNA model proposed by Watson and Crick and to study the structure of RNA. Wilkins, Crick and Watson were awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, ""for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material.""