Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
... promoters and suppressors–call them gene whisperers- expands the list of possible targets for intervention considerably. In some diseases, in cystic fibrosis for example, we have discovered the genetic mutation that causes it, but we have been unable to repair it. Now we only know that one of the bi ...
... promoters and suppressors–call them gene whisperers- expands the list of possible targets for intervention considerably. In some diseases, in cystic fibrosis for example, we have discovered the genetic mutation that causes it, but we have been unable to repair it. Now we only know that one of the bi ...
Unit Study Guide
... 17. Discuss what happens during P.M.A.T. of Mitosis. 18. Contrast the processes of Mitosis and Meiosis. Include: a. The types of cells that go through these processes. b. How many chromosomes are in the resulting cells? c. The purpose for each process. 19. What is the first stage of sexual reproduct ...
... 17. Discuss what happens during P.M.A.T. of Mitosis. 18. Contrast the processes of Mitosis and Meiosis. Include: a. The types of cells that go through these processes. b. How many chromosomes are in the resulting cells? c. The purpose for each process. 19. What is the first stage of sexual reproduct ...
Project Title: Characterization of new genes mediating exchange of
... new assay for sensitivity to in vivo expression of the DNA endonuclease HO. This nuclease creates a break in yeast chromosome III at a single site that cannot be repaired if cells are defective in intrachromosomal DNA recombination. She identified 10 previously unrecognized genes that cause cells to ...
... new assay for sensitivity to in vivo expression of the DNA endonuclease HO. This nuclease creates a break in yeast chromosome III at a single site that cannot be repaired if cells are defective in intrachromosomal DNA recombination. She identified 10 previously unrecognized genes that cause cells to ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... several copies of the virus are formed that destroy the host cell (lytic cycle). In other cases, the genetic material is integrated into the genome of the bacterium and duplicates with it ...
... several copies of the virus are formed that destroy the host cell (lytic cycle). In other cases, the genetic material is integrated into the genome of the bacterium and duplicates with it ...
Vectors for Even Larger Genomic DNA Inserts
... cloned with lambda than with many other plasmids. In addition, the recombinant DNA can be packaged in vitro for efficient transfer to a host cell. Plasmid vectors containing the lambda cos sites are called cosmids, and they can carry a large fragment of foreign DNA. ...
... cloned with lambda than with many other plasmids. In addition, the recombinant DNA can be packaged in vitro for efficient transfer to a host cell. Plasmid vectors containing the lambda cos sites are called cosmids, and they can carry a large fragment of foreign DNA. ...
Biology Final Exam
... 4. During DNA replication, complementary strands of DNA are made from the original DNA strands. Using this template (original strand of DNA) and the base-pairing rules, give the complementary strand: TACCCCGAGAGG 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the ...
... 4. During DNA replication, complementary strands of DNA are made from the original DNA strands. Using this template (original strand of DNA) and the base-pairing rules, give the complementary strand: TACCCCGAGAGG 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the ...
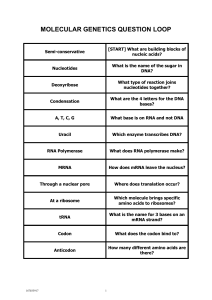
Genetics
... What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic ...
... What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic ...
What is a protein?
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
Chapter 16 - drtracey.net
... vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
... vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
Document
... terminal sequence of the protein encoding this gene was known, however, and a synthetic oligonucleotide that corresponded to amino acids 1 through 10 of this protein was produced and labeled; it hybridized only to the 9 kb, 13 kb and 15 kb fragments. 6. True or false. The 3’ end of the mRNA made fro ...
... terminal sequence of the protein encoding this gene was known, however, and a synthetic oligonucleotide that corresponded to amino acids 1 through 10 of this protein was produced and labeled; it hybridized only to the 9 kb, 13 kb and 15 kb fragments. 6. True or false. The 3’ end of the mRNA made fro ...
Biochemistry Review Worksheet - CHS Science Department Mrs
... considered semi-conservative. _____________ “unzips” the double stranded DNA. _________________ attaches complementary bases to each strand in the 5’ – 3’ direction. Okazaki fragments are a result of replication on the lagging strand of DNA. Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms contain ma ...
... considered semi-conservative. _____________ “unzips” the double stranded DNA. _________________ attaches complementary bases to each strand in the 5’ – 3’ direction. Okazaki fragments are a result of replication on the lagging strand of DNA. Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms contain ma ...
Multiple choice questions
... is more accurate than the clone contig method is normally used with large genomes takes more time than other genome sequencing approaches Restriction endonucleases are located in the nucleus of cells degrade DNA completely bind to DNA are enzymes are proteins were discovered in the 1980s ...
... is more accurate than the clone contig method is normally used with large genomes takes more time than other genome sequencing approaches Restriction endonucleases are located in the nucleus of cells degrade DNA completely bind to DNA are enzymes are proteins were discovered in the 1980s ...
pbs weekly syllabus - Madison Local Schools
... PBS WEEKLY SYLLABUS WEEK OF 2/10 – 2/14 CONCEPTS WE’LL BE LEARNING THIS WEEK: ...
... PBS WEEKLY SYLLABUS WEEK OF 2/10 – 2/14 CONCEPTS WE’LL BE LEARNING THIS WEEK: ...
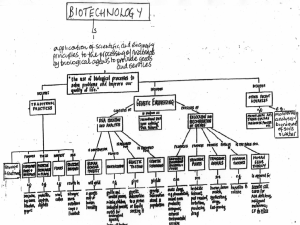
Biotech applic
... Example: RoundupTM -tolerant corn, soybeans, and sugar beets, have been created by moving gene for herbicide resistance from a different plant. RoundupTM, a powerful herbicide, can then be used to kill all weeds, without affecting the crop. ...
... Example: RoundupTM -tolerant corn, soybeans, and sugar beets, have been created by moving gene for herbicide resistance from a different plant. RoundupTM, a powerful herbicide, can then be used to kill all weeds, without affecting the crop. ...
DNA Replication - The Biology Corner
... 5. The other side is the lagging strand - its moving away from the helicase (in the 5' to 3' direction). Problem: it reaches the replication fork, but the helicase is moving in the opposite direction. It stops, and another polymerase binds farther down the chain. This process creates several fragmen ...
... 5. The other side is the lagging strand - its moving away from the helicase (in the 5' to 3' direction). Problem: it reaches the replication fork, but the helicase is moving in the opposite direction. It stops, and another polymerase binds farther down the chain. This process creates several fragmen ...
Complementary base pairing Hydrogen bonding between purines
... genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation components are brought together messenger RNA (mRNA) A ribonucleic acid mole ...
... genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation components are brought together messenger RNA (mRNA) A ribonucleic acid mole ...
doc14873 - Mrothery.co.uk
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
consumer perceptions of food biotechnology
... Molecular biology Study of genes and gene replication, mutation and expression Genome is the collection of all base pairs within the cell Human Genome project started in 1980s ...
... Molecular biology Study of genes and gene replication, mutation and expression Genome is the collection of all base pairs within the cell Human Genome project started in 1980s ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 26. If a protein has 10 codons, how many amino acids are there in the protein?_____________ 27. How many amino acids are used by the human body to make proteins?________ 28. Why is the shape of a protein important? _______________________________________ _____________________________________________ ...
... 26. If a protein has 10 codons, how many amino acids are there in the protein?_____________ 27. How many amino acids are used by the human body to make proteins?________ 28. Why is the shape of a protein important? _______________________________________ _____________________________________________ ...
7. Recombinant DNA Vectors
... 2. Conventional cloning vectors and applications a. Different cloning vectors used for different applications: plasmids--analyzing small DNA regions, expressing genes in cell viruses--cloning larger regions (lambda virus), gene therapy (adenovirus) artificial chromosome vectors (BACs, PACs, YACs)--c ...
... 2. Conventional cloning vectors and applications a. Different cloning vectors used for different applications: plasmids--analyzing small DNA regions, expressing genes in cell viruses--cloning larger regions (lambda virus), gene therapy (adenovirus) artificial chromosome vectors (BACs, PACs, YACs)--c ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.