Chapter 23 (Part 1)
... • Usually present in multiple copies per cell • Plasmids can be cleaved by restriction enzymes, leaving sticky ends • Artificial plasmids can be constructed by linking new DNA fragments to the sticky ends of plasmid ...
... • Usually present in multiple copies per cell • Plasmids can be cleaved by restriction enzymes, leaving sticky ends • Artificial plasmids can be constructed by linking new DNA fragments to the sticky ends of plasmid ...
gewone vergadering - Bataafsch Genootschap
... We are discovering how proteins work together in complex and dynamic assemblies that accomplish the work of living cells. We determine how proteins assemble into functional nanomachinery when and where they are needed. Understanding the details of normal molecular function, how this is disturbed in ...
... We are discovering how proteins work together in complex and dynamic assemblies that accomplish the work of living cells. We determine how proteins assemble into functional nanomachinery when and where they are needed. Understanding the details of normal molecular function, how this is disturbed in ...
Your name
... 21. What kind of ends are possible with the use of restriction enzymes? Sticky ends and blunt ends 22. What is the end result of the central dogma? proteins 23. What are the most basic units of genetic information? ...
... 21. What kind of ends are possible with the use of restriction enzymes? Sticky ends and blunt ends 22. What is the end result of the central dogma? proteins 23. What are the most basic units of genetic information? ...
Slide 1
... • Asexual reproduction is reproduction by mitotic cell divisions. • An amoeba is an organism that reproduces asexually. • An amoeba simply grows and then divides in to two organisms! ...
... • Asexual reproduction is reproduction by mitotic cell divisions. • An amoeba is an organism that reproduces asexually. • An amoeba simply grows and then divides in to two organisms! ...
Practice questions for exam 3
... DNA in your chromosomes is composed of _______. a. amino acids b. nucleotides c. nucleic acid d. glycogen e. both b and c are correct ...
... DNA in your chromosomes is composed of _______. a. amino acids b. nucleotides c. nucleic acid d. glycogen e. both b and c are correct ...
FlyCutTM XmaI - AP
... Blue/White screening (Terminal integrity): A DNA vector is digested at a unique site within lacZα gene with a 10-fold excess of enzyme, and then ligated, transformed and plated on X-gal/IPTG plate. Successful expression of the β-galactosidase indicates that lacZα gene remains integrity after cloning ...
... Blue/White screening (Terminal integrity): A DNA vector is digested at a unique site within lacZα gene with a 10-fold excess of enzyme, and then ligated, transformed and plated on X-gal/IPTG plate. Successful expression of the β-galactosidase indicates that lacZα gene remains integrity after cloning ...
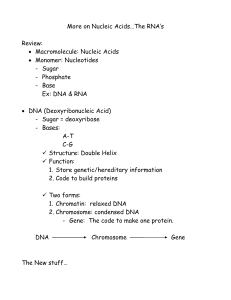
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides - func ...
... o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides - func ...
DNA Technology
... • Almost all DNA between humans is identical (99.9%), except in non-protein coding sites called microsatellite regions • Where we look when comparing DNA to solve crimes or for paternity ...
... • Almost all DNA between humans is identical (99.9%), except in non-protein coding sites called microsatellite regions • Where we look when comparing DNA to solve crimes or for paternity ...
Genetic Engineering - University of Rhode Island
... enzymes that form a new chemical bond to join two molecules, and restriction enzymes, which can cut double-stranded DNA, can be very useful in the gene splicing process as well. The ability to modify DNA has great potential benefits. It could give humans the ability to cure disease, increase immunit ...
... enzymes that form a new chemical bond to join two molecules, and restriction enzymes, which can cut double-stranded DNA, can be very useful in the gene splicing process as well. The ability to modify DNA has great potential benefits. It could give humans the ability to cure disease, increase immunit ...
DNA RNA Protein Hwk KEY
... GTP (like ATP) Provides energy to charge tRNA's, catalyze peptide bonding, and move ribosomes… mRNA Its sequence of codons determines order of a.a.'s in protein ribosome Holds mRNA; takes in tRNA-a.a.'s; rbs enzymes make peptide bonds between a.a.'s tRNA Adapter molecules that carry a.a.'s to the rb ...
... GTP (like ATP) Provides energy to charge tRNA's, catalyze peptide bonding, and move ribosomes… mRNA Its sequence of codons determines order of a.a.'s in protein ribosome Holds mRNA; takes in tRNA-a.a.'s; rbs enzymes make peptide bonds between a.a.'s tRNA Adapter molecules that carry a.a.'s to the rb ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... Do not allow histone wrapped around DNA. Most of the DNA of a human cell is contained in the nucleus. Distinguish between unique and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. ...
... Do not allow histone wrapped around DNA. Most of the DNA of a human cell is contained in the nucleus. Distinguish between unique and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. ...
analysis
... 1. This method was devised by Sanger and used dideoxynucleotides to terminate chain elongation during DNA synthesis B. Purpose 1. Use sequence to deduce amino acid sequence of proteins 2. Find restriction sites 3. Find introns a) Compare genomic DNA to cDNA 4. Find DNA structures a) Inverted repeats ...
... 1. This method was devised by Sanger and used dideoxynucleotides to terminate chain elongation during DNA synthesis B. Purpose 1. Use sequence to deduce amino acid sequence of proteins 2. Find restriction sites 3. Find introns a) Compare genomic DNA to cDNA 4. Find DNA structures a) Inverted repeats ...
DNA Restriction and mechanism
... • The mammalian enzymes methylate the cytosine in mainly CG sequences to 5-methylcytosine (5-meC), but they do it efficiently only if the cytosine in the opposite strand already bears a methyl residue. The result is that CG sequences that are methylated perpetuate their methylated state following DN ...
... • The mammalian enzymes methylate the cytosine in mainly CG sequences to 5-methylcytosine (5-meC), but they do it efficiently only if the cytosine in the opposite strand already bears a methyl residue. The result is that CG sequences that are methylated perpetuate their methylated state following DN ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... DNA found in a bacterial cell where the large ring is the bacterium’s chromosome 3rd –transfer into the host organism The plasmid or foreign DNA are cut with the same restriction enzyme then the ends will match and they will join together reconnecting the plasmid ring ...
... DNA found in a bacterial cell where the large ring is the bacterium’s chromosome 3rd –transfer into the host organism The plasmid or foreign DNA are cut with the same restriction enzyme then the ends will match and they will join together reconnecting the plasmid ring ...
Lecture 14
... ii. Second degree: wrapped around protein assembly, called histones iii. Nucleosome, not base pair specific iv. Then packed into coils continuous contracting of molecule v. Most of the time, contracted DNA is still accessible to proteins that engage in third degree surface specific recognition vi. ...
... ii. Second degree: wrapped around protein assembly, called histones iii. Nucleosome, not base pair specific iv. Then packed into coils continuous contracting of molecule v. Most of the time, contracted DNA is still accessible to proteins that engage in third degree surface specific recognition vi. ...
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.McDermid Lecture #1: DNA is the Genetic Material
... Figure 8-3 Bacteriophage (bacterial virus) T2 Radioisotope 32P to follow DNA; P not found in protein 35S labels protein; S not found in DNA Results 35S protein -> 32P DNA -> Conclusion: If DNA is the hereditary material then: 1) How do cells replicate their DNA? 2) How is genetic information stored? ...
... Figure 8-3 Bacteriophage (bacterial virus) T2 Radioisotope 32P to follow DNA; P not found in protein 35S labels protein; S not found in DNA Results 35S protein -> 32P DNA -> Conclusion: If DNA is the hereditary material then: 1) How do cells replicate their DNA? 2) How is genetic information stored? ...
Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
... fundamental process occurring in all living organisms to copy their DNA. The basis for biological inheritance is basically when DNA makes ...
... fundamental process occurring in all living organisms to copy their DNA. The basis for biological inheritance is basically when DNA makes ...
suggested essay-type questions for next exam
... “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the definition of the linking difference. In this definition, Lo refers to the linking number for relaxed B-DNA. This number reflects the number of base pairs that stack in one helical turn. Does this number change when ethidium bromide is interca ...
... “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the definition of the linking difference. In this definition, Lo refers to the linking number for relaxed B-DNA. This number reflects the number of base pairs that stack in one helical turn. Does this number change when ethidium bromide is interca ...
7529 DNA Sequencing - ACM
... Krusty Krab out of business. So, SpongeBob and his co-workers decided to switch to a brand new job. Their new startup is Krusty-Royan, a biological research institute whose main focus is on DNA sequencing. Their first customer is Sandy, the squirrel scientist, who has found the corpse of an alien fr ...
... Krusty Krab out of business. So, SpongeBob and his co-workers decided to switch to a brand new job. Their new startup is Krusty-Royan, a biological research institute whose main focus is on DNA sequencing. Their first customer is Sandy, the squirrel scientist, who has found the corpse of an alien fr ...
What holds chromosomes together: Researchers
... same chromosome with each other. Learning from bacteria Simple organisms like bacteria also use this method of DNA packaging. The scientists, in Credit: Max Planck Society collaboration with colleagues from South Korea, have now elucidated the structure of a precursor of human SMC-kleisin complexes ...
... same chromosome with each other. Learning from bacteria Simple organisms like bacteria also use this method of DNA packaging. The scientists, in Credit: Max Planck Society collaboration with colleagues from South Korea, have now elucidated the structure of a precursor of human SMC-kleisin complexes ...
DNA Technology
... electrophoresis (separates DNA according to size and charge) ▫ 3. placed in wells made on gel and run electric ...
... electrophoresis (separates DNA according to size and charge) ▫ 3. placed in wells made on gel and run electric ...
DNA Fingerprinting Notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Base your answer to the question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram shows the results of a technique used to analyze DNA. This laboratory t ...
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Base your answer to the question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram shows the results of a technique used to analyze DNA. This laboratory t ...
Genetic Engineering
... molecules gene (X) of interest (the target DNA) is inserted into a plasmid vector . The target DNA may be a single fragment isolated from an agarose gel , or a mixture of many fragments from, for example, genomic DNA . If the target has been prepared by digestion with EcoRI, then the fragment can be ...
... molecules gene (X) of interest (the target DNA) is inserted into a plasmid vector . The target DNA may be a single fragment isolated from an agarose gel , or a mixture of many fragments from, for example, genomic DNA . If the target has been prepared by digestion with EcoRI, then the fragment can be ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.