Re-closing linearized plasmids
... Transformation: • Transform the entire ligation mix into 100 µL of E. coli using the calcium chloride method. Make sure to pre-grow the cells in SOC or LB medium with no antibiotic prior to plating. See the protocol page for “Transformation of E. coli.” Screening for correct clones: • Pick 3-6 singl ...
... Transformation: • Transform the entire ligation mix into 100 µL of E. coli using the calcium chloride method. Make sure to pre-grow the cells in SOC or LB medium with no antibiotic prior to plating. See the protocol page for “Transformation of E. coli.” Screening for correct clones: • Pick 3-6 singl ...
DNA Quiz #1 - Houston ISD
... 12. ____________ is complementary to the original DNA strand? 13. The mRNA carries information from the nucleus to a _________. 14. What is the correct base pairing of RNA? ___=___ ___=___ 15. Translation takes place in the ________________. 16. Replication, transcription, and translation are the st ...
... 12. ____________ is complementary to the original DNA strand? 13. The mRNA carries information from the nucleus to a _________. 14. What is the correct base pairing of RNA? ___=___ ___=___ 15. Translation takes place in the ________________. 16. Replication, transcription, and translation are the st ...
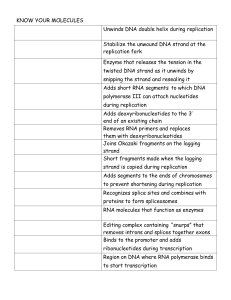
Know your molecules organizer
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
DNA polymerase
... How can techniques developed by molecular biologists be used to answer ecological questions? Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are present in all calls – Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes. Molecular techniques use nucleic acids to identify species and determine relationships without having to grow or cult ...
... How can techniques developed by molecular biologists be used to answer ecological questions? Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are present in all calls – Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes. Molecular techniques use nucleic acids to identify species and determine relationships without having to grow or cult ...
DNA structure and replication Three key features needed for any
... 1) Must allow for faithful replication - each strand of DNA serves as a template for replication 2) Must have information content - the sequence of bases predict the sequence of amino acids in proteins 3) Must be able to change in order to explain mutations changes in DNA sequences result in changes ...
... 1) Must allow for faithful replication - each strand of DNA serves as a template for replication 2) Must have information content - the sequence of bases predict the sequence of amino acids in proteins 3) Must be able to change in order to explain mutations changes in DNA sequences result in changes ...
DNA ppt
... 1. Enzyme (helicase) unzips the DNA. 2. DNA polymerase (enzyme) matches the correct nucleotide to each side of the unzipped DNA. 3. DNA polymerase – proofreads their replication to make sure they did not make any mistakes. ...
... 1. Enzyme (helicase) unzips the DNA. 2. DNA polymerase (enzyme) matches the correct nucleotide to each side of the unzipped DNA. 3. DNA polymerase – proofreads their replication to make sure they did not make any mistakes. ...
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
... • Procedure where cells can take up plasmids (DNA) from the surrounding environment • The cell receiving the new DNA must be ...
... • Procedure where cells can take up plasmids (DNA) from the surrounding environment • The cell receiving the new DNA must be ...
Unit 4 exam - Geneti..
... D. produce enzymes different from the parent 15. To produce large tomatoes that are resistant to cracking and splitting, some seed companies use the pollen from one variety of tomato plant to fertilize a different variety of tomato plant. This process is an example of A. direct harvesting B. DNA seq ...
... D. produce enzymes different from the parent 15. To produce large tomatoes that are resistant to cracking and splitting, some seed companies use the pollen from one variety of tomato plant to fertilize a different variety of tomato plant. This process is an example of A. direct harvesting B. DNA seq ...
Final Exam Review - Blue Valley Schools
... What is the difference between a biotic factor and an abiotic factor? Know the 3 major types of symbiotic relationships. (commensalism, parasitism, mutualism) List the 5 levels of ecological study. What are three methods for estimating the size of a population? How do you calculate population densit ...
... What is the difference between a biotic factor and an abiotic factor? Know the 3 major types of symbiotic relationships. (commensalism, parasitism, mutualism) List the 5 levels of ecological study. What are three methods for estimating the size of a population? How do you calculate population densit ...
Recombinant DNA Registration Form
... If you answered yes to any of these questions please submit your Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects or Animal Care and Use approval letter. ...
... If you answered yes to any of these questions please submit your Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects or Animal Care and Use approval letter. ...
Chapter 17 Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology
... • genetic engineering requires lots of DNA – cloning produces lots of exact copies – DNA clones are replicated by host cells – DNA is cloned in a DNA vector – a DNA vector has an origin of replication (ori) that the host cell recognizes ...
... • genetic engineering requires lots of DNA – cloning produces lots of exact copies – DNA clones are replicated by host cells – DNA is cloned in a DNA vector – a DNA vector has an origin of replication (ori) that the host cell recognizes ...
Biology: Unit 13 Directed Reading Guide
... ______ Why must a genetically engineered plasmid contain a genetic marker? e. to prevent the construction of an artificial chromosome f. to separate cells that contain recombinant DNA from those that do not g. to produce multiple copies of the recombined plasmid after heat treatment h. to break apar ...
... ______ Why must a genetically engineered plasmid contain a genetic marker? e. to prevent the construction of an artificial chromosome f. to separate cells that contain recombinant DNA from those that do not g. to produce multiple copies of the recombined plasmid after heat treatment h. to break apar ...
Biotechnoloy :Guides for Exam 2
... A. absence of clotting factor VIII B. absence of clotting factor IX C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial for human gene therapy must be approved by A. the RAC c ...
... A. absence of clotting factor VIII B. absence of clotting factor IX C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial for human gene therapy must be approved by A. the RAC c ...
Contemporary Biology Per
... Study Guide - Test #7, Section 8.4 & Chapter 9 1. Cells regulate gene transcription because they do not always need a gene’s product. A gene is said to be __________ or “turned on” when it is ____________ to mRNA. 2. E. coli contains about 2000 genes, three of which are called ____ genes, each codin ...
... Study Guide - Test #7, Section 8.4 & Chapter 9 1. Cells regulate gene transcription because they do not always need a gene’s product. A gene is said to be __________ or “turned on” when it is ____________ to mRNA. 2. E. coli contains about 2000 genes, three of which are called ____ genes, each codin ...
BIOLOGY CONTENT STANDARDS REVIEW
... information from DNA into mRNA. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 18. Describe DNA replication. 19. Describe transcription and translation (include the terms nucleus, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, and amino acids). Th ...
... information from DNA into mRNA. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 18. Describe DNA replication. 19. Describe transcription and translation (include the terms nucleus, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, and amino acids). Th ...
What do Genes Look Like - Effingham County Schools
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
Ch. 12 Review- pg. 315 1-23 Answers The process by which one
... Name two major types of mutations. Why do they have in common? Who are they different? Give an example for each. Gene and chromosomal; both change the DNA sequence that affects genetic information. Gene mutations involve a change in one or several nucleotides in a single gene, whereas chromosomal mu ...
... Name two major types of mutations. Why do they have in common? Who are they different? Give an example for each. Gene and chromosomal; both change the DNA sequence that affects genetic information. Gene mutations involve a change in one or several nucleotides in a single gene, whereas chromosomal mu ...
Minilab 11-1
... bonds to each codon from column B. ffiil ldentify the process responsible by writing its name on the arrow in column C. ffi complete column E by writing the name of the correct amino acid that is coded by each base sequence. Use Table 11.2 on page 298 to translate the mRNA base sequences to amino ac ...
... bonds to each codon from column B. ffiil ldentify the process responsible by writing its name on the arrow in column C. ffi complete column E by writing the name of the correct amino acid that is coded by each base sequence. Use Table 11.2 on page 298 to translate the mRNA base sequences to amino ac ...
Human Cloning
... Reproductive cloning is a technology used to generate an animal that has the same nuclear DNA as another currently or previously existing animal In a process called "somatic cell nuclear transfer" (SCNT), scientists transfer genetic material from the nucleus of a donor adult cell to an egg whose nuc ...
... Reproductive cloning is a technology used to generate an animal that has the same nuclear DNA as another currently or previously existing animal In a process called "somatic cell nuclear transfer" (SCNT), scientists transfer genetic material from the nucleus of a donor adult cell to an egg whose nuc ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.