Effect of vitamin E and beta-carotene on DNA strand
... major carcinogens in cigarette smoke. Chronic inflammation may promote the carcinogenic effect of these nitrosamines through the generation of oxygen radicals. To evaluate the effect of oxygen radicals on TSNA-induced genetic damage, cultured human lung cells treated with NNN or NNK were exposed to ...
... major carcinogens in cigarette smoke. Chronic inflammation may promote the carcinogenic effect of these nitrosamines through the generation of oxygen radicals. To evaluate the effect of oxygen radicals on TSNA-induced genetic damage, cultured human lung cells treated with NNN or NNK were exposed to ...
Thao_Molecular cell
... The one pair of allele that masks the effect of the other when present in the same cell. • Recessive The one pair of allele that is masked by the other when present in the same cell and capable of producing its characteristics phenotype in the organism only when two alleles is present and identi ...
... The one pair of allele that masks the effect of the other when present in the same cell. • Recessive The one pair of allele that is masked by the other when present in the same cell and capable of producing its characteristics phenotype in the organism only when two alleles is present and identi ...
DNA Recombination
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
Sentence Synthesis Instructions RNA polymerase Instructions, cont
... Sentence Synthesis Modeling Transcription and Translation ...
... Sentence Synthesis Modeling Transcription and Translation ...
HL-SAN for DNA removal in protein purification - A4
... of DNA-binding proteins as they interfere with purification, downstream analysis or applications. Nucleases activity is usually difficult to remove while HL-SAN is easily inactivated or separated from other proteins. This enables nuclease treatment without residual nuclease activity in downstream ap ...
... of DNA-binding proteins as they interfere with purification, downstream analysis or applications. Nucleases activity is usually difficult to remove while HL-SAN is easily inactivated or separated from other proteins. This enables nuclease treatment without residual nuclease activity in downstream ap ...
doc Practice Midterm 2006
... 1. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pairs is more stable? Why? How does this property affect the melting temperature of DNA? 2. You obtain the sequence of a gene containing 10 exons, 9 introns, and a 3’ untranslated region containing a polyadenylation consensus sequence. The fifth intron also c ...
... 1. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pairs is more stable? Why? How does this property affect the melting temperature of DNA? 2. You obtain the sequence of a gene containing 10 exons, 9 introns, and a 3’ untranslated region containing a polyadenylation consensus sequence. The fifth intron also c ...
AP Biology Ch. 20 - apbiologyclass / FrontPage
... • Gene therapy is the alteration of an afflicted individual’s genes • Gene therapy holds great potential for treating disorders traceable to a single defective gene • Vectors are used for delivery of genes into specific types of cells, for example bone marrow • Gene therapy raises ethical questions, ...
... • Gene therapy is the alteration of an afflicted individual’s genes • Gene therapy holds great potential for treating disorders traceable to a single defective gene • Vectors are used for delivery of genes into specific types of cells, for example bone marrow • Gene therapy raises ethical questions, ...
A1979HZ32700001
... Dr. Geschwind and I had mostly, but not exclusively favorable comments on it. A late, well-known biochemist from New York expressed his disdain for this and similar quantitative methods when they are used in conjunction with a microscope, rather than a test tube. However, subsequent applications of ...
... Dr. Geschwind and I had mostly, but not exclusively favorable comments on it. A late, well-known biochemist from New York expressed his disdain for this and similar quantitative methods when they are used in conjunction with a microscope, rather than a test tube. However, subsequent applications of ...
ROYAL SCOTLAND, ROYAL STEWART scotlandsdna.com
... About 20% of all men who carry the famous surname share Sir John’s lineage while 30% are descended from Sir John’s brother, James, the 5th High Steward of Scotland. His son, Walter, married Marjorie Bruce, the daughter of Robert I, having helped him win the great victory at Bannockburn, and their so ...
... About 20% of all men who carry the famous surname share Sir John’s lineage while 30% are descended from Sir John’s brother, James, the 5th High Steward of Scotland. His son, Walter, married Marjorie Bruce, the daughter of Robert I, having helped him win the great victory at Bannockburn, and their so ...
DNA Timeline - WordPress.com
... • Help discover that there is a link between inherited characteristics and also a specific chromosome • Made their discovery in the United States • The Ellen Richards Research Prize was given to Stevens ...
... • Help discover that there is a link between inherited characteristics and also a specific chromosome • Made their discovery in the United States • The Ellen Richards Research Prize was given to Stevens ...
1-3 - PLOS
... is then linearized by double restriction at the Selection site. The linearized double stranded device is then subjected to heat renaturation, randomly annealing single strands from different devices in the library and exposing the mismatched bases between their input modules. As discussed earlier, o ...
... is then linearized by double restriction at the Selection site. The linearized double stranded device is then subjected to heat renaturation, randomly annealing single strands from different devices in the library and exposing the mismatched bases between their input modules. As discussed earlier, o ...
Seventh Grade 2nd Quarter CRT Review
... The cell grows and copies its DNA. 3. Why are chromosomes even numbers? So that they may divide in half because one comes from mom and one from dad. 4. A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to become drier. As a result, the grasses that cover the island change from dark green to ...
... The cell grows and copies its DNA. 3. Why are chromosomes even numbers? So that they may divide in half because one comes from mom and one from dad. 4. A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to become drier. As a result, the grasses that cover the island change from dark green to ...
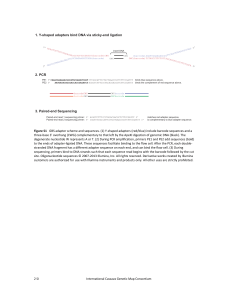
Figure S1 - G3: Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
Document
... 2. Of the offspring, select individuals that have the largest side buds and breed them. 3. Of the offspring, select individuals that have the largest side buds and breed them. ...
... 2. Of the offspring, select individuals that have the largest side buds and breed them. 3. Of the offspring, select individuals that have the largest side buds and breed them. ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Translation Review
... 3. What type of bond holds the sugar and phosphate together? Is this bond strong or weak? What is the significance of this? They are joined by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages. These are strong bonds that are not meant to break. This helps to keep a strand of DNA or RNA intact. 4. What ...
... 3. What type of bond holds the sugar and phosphate together? Is this bond strong or weak? What is the significance of this? They are joined by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages. These are strong bonds that are not meant to break. This helps to keep a strand of DNA or RNA intact. 4. What ...
Microbiology Chapter 9
... DNA replication – the process of making an exact copy of DNA molecule DNA replication has to occur before cell division in order for each cell to have a copy of the genetic information 1. One strand of DNA acts as template for the formation of the corresponding strand 2. 2. Replication is carried ou ...
... DNA replication – the process of making an exact copy of DNA molecule DNA replication has to occur before cell division in order for each cell to have a copy of the genetic information 1. One strand of DNA acts as template for the formation of the corresponding strand 2. 2. Replication is carried ou ...
CHAPTER 1
... proteins as the fly or worm because of mRNA transcript "alternative splicing" and chemical modifications to the proteins. This process can yield different protein products from the same gene. • Humans share most of the same protein families with worms, flies, and plants, but the number of gene famil ...
... proteins as the fly or worm because of mRNA transcript "alternative splicing" and chemical modifications to the proteins. This process can yield different protein products from the same gene. • Humans share most of the same protein families with worms, flies, and plants, but the number of gene famil ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.