
P-Element Transformation with period Locus DNA Restores
... were recorded and analyzed had previously been tested for circadian rhythmic@. Three of them were rhythmic in both locomotor and singing behavior, two were arrhythmic for both characters, and one exhibited no circadian rhythm but subsequently sang in a rhythmic manner. As in the case of circadian rh ...
... were recorded and analyzed had previously been tested for circadian rhythmic@. Three of them were rhythmic in both locomotor and singing behavior, two were arrhythmic for both characters, and one exhibited no circadian rhythm but subsequently sang in a rhythmic manner. As in the case of circadian rh ...
How dormant origins promote complete genome replication
... With these considerations in mind, we recently modelled the behaviour of origin activation within a single 250 kb origin cluster [41]. Origins were assigned a certain initiation probability per unit time and were then activated stochastically during S phase (Figure 4a). Model parameters (mean origin ...
... With these considerations in mind, we recently modelled the behaviour of origin activation within a single 250 kb origin cluster [41]. Origins were assigned a certain initiation probability per unit time and were then activated stochastically during S phase (Figure 4a). Model parameters (mean origin ...
DNA and RNA Extraction Controls Performance Summary
... A common practice in real-time PCR is to add a known amount of “spiked” control DNA after nucleic acid extraction. This monitors PCR inhibition but has no value as an extraction control. The ideal situation is to have the test sample and internal control undergo the same processing prior to real-tim ...
... A common practice in real-time PCR is to add a known amount of “spiked” control DNA after nucleic acid extraction. This monitors PCR inhibition but has no value as an extraction control. The ideal situation is to have the test sample and internal control undergo the same processing prior to real-tim ...
Supplemental Digital Content
... extension. As positive control and reference an in-house cyclophilin (gCYC) qPCR was included. The specificities of the in house KRAS mutation assays varied between 0.1% and better than 0.01%. The final primer mixtures are shown in Table 1. All qPCR reactions were performed in a volume of 25 µl in ...
... extension. As positive control and reference an in-house cyclophilin (gCYC) qPCR was included. The specificities of the in house KRAS mutation assays varied between 0.1% and better than 0.01%. The final primer mixtures are shown in Table 1. All qPCR reactions were performed in a volume of 25 µl in ...
http://www.life.umd.edu/grad/mlfsc/ DNA Bracelets
... 1) General Directions: You will need to form a group of 5 students. Remove the staple from this packet and assign one page to each student. All students will need to refer to this beginning page for the amino acid/bead conversion chart. Each student will use their assigned DNA sequence, make any req ...
... 1) General Directions: You will need to form a group of 5 students. Remove the staple from this packet and assign one page to each student. All students will need to refer to this beginning page for the amino acid/bead conversion chart. Each student will use their assigned DNA sequence, make any req ...
5 DNA Replication
... proceeds at a rate ranging from 500 to 5,000 nucleotides per minute at each replication fork (considerably slower than bacterial replication). Even at 5,000 nucleotides per minute at each fork, DNA synthesis starting from a single origin would require 7 days to replicate a typical human chromosome c ...
... proceeds at a rate ranging from 500 to 5,000 nucleotides per minute at each replication fork (considerably slower than bacterial replication). Even at 5,000 nucleotides per minute at each fork, DNA synthesis starting from a single origin would require 7 days to replicate a typical human chromosome c ...
PDF
... manipulation of paramagnetic beads using a gradient of magnetic field [14]. The two techniques have been developing head to head to achieve nowadays a remarkable level of sophistication. They have their own unique advantages but, largely, offer similar capabilities and require the same workflow. The ...
... manipulation of paramagnetic beads using a gradient of magnetic field [14]. The two techniques have been developing head to head to achieve nowadays a remarkable level of sophistication. They have their own unique advantages but, largely, offer similar capabilities and require the same workflow. The ...
Expression and purification of four different rhizobial acyl carrier
... (1) Cloning of the first half of the acpP gene. Two degenerate oligonucleotides were used in a PCR to amplify and subsequently clone that part of the gene encoding the aminoterminal half of the AcpP of S. meliloti. These oligonucleotides were deduced from the amino acid sequence of different ACPs, a ...
... (1) Cloning of the first half of the acpP gene. Two degenerate oligonucleotides were used in a PCR to amplify and subsequently clone that part of the gene encoding the aminoterminal half of the AcpP of S. meliloti. These oligonucleotides were deduced from the amino acid sequence of different ACPs, a ...
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) Purification Kit
... activity with the bacteria they genetically transformed using the plasmid, pGLO. Transformed bacteria which produce the genetically engineered Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) are removed from their agar plates and allowed to multiply in liquid nutrient media. The bacterial cells are then broken open ...
... activity with the bacteria they genetically transformed using the plasmid, pGLO. Transformed bacteria which produce the genetically engineered Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) are removed from their agar plates and allowed to multiply in liquid nutrient media. The bacterial cells are then broken open ...
Molecular characterization of dioxygenases from polycyclic aromatic
... Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading genes nidA and nidB that encode the K and L subunits of the aromatic ringhydroxylating dioxygenase have been cloned and sequenced from Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 [Khan et al., Appl. Environ Microbiol. 67 (2001) 3577^3585]. In this study, the prese ...
... Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading genes nidA and nidB that encode the K and L subunits of the aromatic ringhydroxylating dioxygenase have been cloned and sequenced from Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 [Khan et al., Appl. Environ Microbiol. 67 (2001) 3577^3585]. In this study, the prese ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... at 40 kb intervals and fire as small clusters whose synchrony increases during S phase and that replication fork velocity (mean 0.7 kb/min, maximum 2.0 kb/min) remains constant and narrowly distributed through S phase. However, multi-scale analysis of a genome-wide replication timing profile shows a b ...
... at 40 kb intervals and fire as small clusters whose synchrony increases during S phase and that replication fork velocity (mean 0.7 kb/min, maximum 2.0 kb/min) remains constant and narrowly distributed through S phase. However, multi-scale analysis of a genome-wide replication timing profile shows a b ...
Differential effect of auxotrophies on the release of macromolecules
... animals (Levine et al., 1996). Whether attenuation differentially influences delivery properties has not been studied systematically so far. The delivery of antigens or DNA vaccines requires liberation of the particular macromolecule from the bacteria after invasion of the host. Various secretion sy ...
... animals (Levine et al., 1996). Whether attenuation differentially influences delivery properties has not been studied systematically so far. The delivery of antigens or DNA vaccines requires liberation of the particular macromolecule from the bacteria after invasion of the host. Various secretion sy ...
CSE 181 Project guidelines
... • Some forms of RNA can form secondary structures by “pairing up” with itself. This can have change its properties • Several types exist, classified by function • mRNA – this is what is usually being referred to when a Bioinformatician says “RNA”. This is used to carry a gene’s message out of the nu ...
... • Some forms of RNA can form secondary structures by “pairing up” with itself. This can have change its properties • Several types exist, classified by function • mRNA – this is what is usually being referred to when a Bioinformatician says “RNA”. This is used to carry a gene’s message out of the nu ...
UNIT – I: NUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND
... base, uracil , which can also base pair with adenine In addition, RNA molecules normally exist as a single polynucletide strand and do not form a double helix. However, it is possible for base pairing to occur between complementary parts of the same RNA strand resulting in short double stranded regi ...
... base, uracil , which can also base pair with adenine In addition, RNA molecules normally exist as a single polynucletide strand and do not form a double helix. However, it is possible for base pairing to occur between complementary parts of the same RNA strand resulting in short double stranded regi ...
Document
... An E. coli strain has acquired a lethal mutation in the promoter -10 box of an essential gene. Researchers subjected the strain to a mutagen, and selected a secondary mutation (i.e not in the same gene), which restored growth. Which of the following genes is most likely to carry the secondary mutat ...
... An E. coli strain has acquired a lethal mutation in the promoter -10 box of an essential gene. Researchers subjected the strain to a mutagen, and selected a secondary mutation (i.e not in the same gene), which restored growth. Which of the following genes is most likely to carry the secondary mutat ...
Appendix – Biology for Bioinformatics Fig A1.1 A typical
... Fig A1.36 (A) Schematic drawing of the transmembrane topology of the G-proteincoupled receptor, which is characterized by seven transmembrane segments. (B) None of the structures of G-protein-coupled receptors has been determined yet, but their transmembrane structures are expected to be similar to ...
... Fig A1.36 (A) Schematic drawing of the transmembrane topology of the G-proteincoupled receptor, which is characterized by seven transmembrane segments. (B) None of the structures of G-protein-coupled receptors has been determined yet, but their transmembrane structures are expected to be similar to ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... that point in time, Crick was a "skeptic, an agnostic with a strong inclination towards atheism". His quest for reason was a strong motivating force in his scientific career. After early schooling from the local "Grammar" school, Crick completed his schooling from the Mill Hill Public School in Nort ...
... that point in time, Crick was a "skeptic, an agnostic with a strong inclination towards atheism". His quest for reason was a strong motivating force in his scientific career. After early schooling from the local "Grammar" school, Crick completed his schooling from the Mill Hill Public School in Nort ...
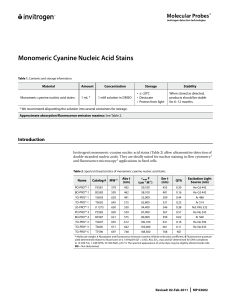
Monomeric Cyanine Nucleic Acid Stains
... Further information on Molecular Probes products, including product bibliographies, is available from your local distributor or directly from Molecular Probes. Customers in Europe, Africa and the Middle East should contact our office in Paisley, United Kingdom. All others should contact our Technica ...
... Further information on Molecular Probes products, including product bibliographies, is available from your local distributor or directly from Molecular Probes. Customers in Europe, Africa and the Middle East should contact our office in Paisley, United Kingdom. All others should contact our Technica ...
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein
... Transformation means change. In molecular biology, transformation refers to a form of genetic change in which the genetic material carried by an individual cell is altered by incorporation of foreign DNA into its genome. Genetic transformation is used in many areas of biotechnology. Genes coding ...
... Transformation means change. In molecular biology, transformation refers to a form of genetic change in which the genetic material carried by an individual cell is altered by incorporation of foreign DNA into its genome. Genetic transformation is used in many areas of biotechnology. Genes coding ...
BI0I 121 cel]
... Smallest of the RNA molecules; many different kinds. B. Single long strand that passes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. C. Part of the mRNA that is translated into a polypeptide. D. Noncoding part of the mRNA transcript that is excised before the mRNA leaves the nucleus. E. Made in the nucleus; •p ...
... Smallest of the RNA molecules; many different kinds. B. Single long strand that passes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. C. Part of the mRNA that is translated into a polypeptide. D. Noncoding part of the mRNA transcript that is excised before the mRNA leaves the nucleus. E. Made in the nucleus; •p ...
Chpt11_TxnPromoters.doc
... a. 5' end label: T4 polynucleotide kinase and [ 32P] ATP. The reaction is most efficient if the 5' phosphate is removed (by alkaline phosphatase) prior to the kinase treatment. b. 3' end label: Klenow DNA polymerase plus [ 32P] dNTP. The labeled dNTP is chosen to be complementary to the first posi ...
... a. 5' end label: T4 polynucleotide kinase and [ 32P] ATP. The reaction is most efficient if the 5' phosphate is removed (by alkaline phosphatase) prior to the kinase treatment. b. 3' end label: Klenow DNA polymerase plus [ 32P] dNTP. The labeled dNTP is chosen to be complementary to the first posi ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.





















![BI0I 121 cel]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004132586_1-822dfb440517eec80339a913dc1e4e97-300x300.png)
