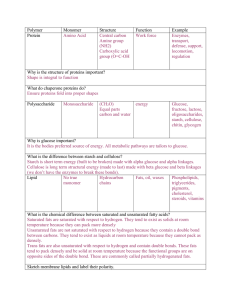
SI Worksheet 11
... 7. A sequence of pictures of polypeptides synthesis shows a ribosome holding two transfer RNAs. One tRNA has a polypeptide chain attached to it, the other tRNA has a single amino acid attaches to it. What does the next picture show? a. the polypeptide chain moves over and bonds to the single amino a ...
... 7. A sequence of pictures of polypeptides synthesis shows a ribosome holding two transfer RNAs. One tRNA has a polypeptide chain attached to it, the other tRNA has a single amino acid attaches to it. What does the next picture show? a. the polypeptide chain moves over and bonds to the single amino a ...
COMPARISON OF THREE DNA ISOLATION AND
... pyridinovorans TPIK grown in medium nutrient agar at 370C overnight. The bacteria were suspended in1 ml TE buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8).The mixture then centrifugated 1000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C . The pellet was added with 50 µL lysozyme solution and incubated at 370C for 30 min. An amount ...
... pyridinovorans TPIK grown in medium nutrient agar at 370C overnight. The bacteria were suspended in1 ml TE buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8).The mixture then centrifugated 1000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C . The pellet was added with 50 µL lysozyme solution and incubated at 370C for 30 min. An amount ...
Biol 213 Genetics (13 September 2000) Relationship between
... SQ21. What if Beadle and Tatum analyzed the original irradiated haploid spores and did not analyze spores from the heterozygous strain. What information would they have missed? III. RNA and an overview of gene expression (pp.238-240; pp.321-325) We’ve established a connection between DNA and protein ...
... SQ21. What if Beadle and Tatum analyzed the original irradiated haploid spores and did not analyze spores from the heterozygous strain. What information would they have missed? III. RNA and an overview of gene expression (pp.238-240; pp.321-325) We’ve established a connection between DNA and protein ...
DNA2016 - saddlespace.org
... The amount of G’s and C’s is approx. 45% so, the amount of A’s and T’s should be close to 55%. Thus, 55-28 = 27% AP Biology ...
... The amount of G’s and C’s is approx. 45% so, the amount of A’s and T’s should be close to 55%. Thus, 55-28 = 27% AP Biology ...
Genetics of AHC - Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Foundation
... identified in the following genes:CACNA1A, ATP1A2, SCN1A Associated with FHM, family history of migraines is usually ...
... identified in the following genes:CACNA1A, ATP1A2, SCN1A Associated with FHM, family history of migraines is usually ...
A Model for Recognition Scheme between Double Stranded DNA
... ds DNA according to the coordinates of Arnott et a1. (2) and for an antiparallel two-stranded ~ structure. Since ds DNA has two kinds of pseudo 2-fold axes perpendicular to the helix axis, one on the plane of each base pair, the other between two adjacent base pairs, we considered only the antiparal ...
... ds DNA according to the coordinates of Arnott et a1. (2) and for an antiparallel two-stranded ~ structure. Since ds DNA has two kinds of pseudo 2-fold axes perpendicular to the helix axis, one on the plane of each base pair, the other between two adjacent base pairs, we considered only the antiparal ...
File
... Helicase unwinds DNA and unzips the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases ...
... Helicase unwinds DNA and unzips the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases ...
optional activity key File
... Trans fats are also unsaturated with respect to hydrogen and contain double bonds. These fats tend to pack densely and be solid at room temperature because the functional groups are on opposite sides of the double bond. These are commonly called partially hydrogenated fats. Sketch membrane lipids an ...
... Trans fats are also unsaturated with respect to hydrogen and contain double bonds. These fats tend to pack densely and be solid at room temperature because the functional groups are on opposite sides of the double bond. These are commonly called partially hydrogenated fats. Sketch membrane lipids an ...
BIOLOGY 12 MUTATIONS FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
... We have two copies of every chromosome (one from Mom and one from Dad), and therefore we have two copies of every gene. If one gene copy is mutant, the other copy usually can provide enough gene product to the organism for normal function. Most of our DNA does not encode genes. Therefore most mutati ...
... We have two copies of every chromosome (one from Mom and one from Dad), and therefore we have two copies of every gene. If one gene copy is mutant, the other copy usually can provide enough gene product to the organism for normal function. Most of our DNA does not encode genes. Therefore most mutati ...
221_exam_3_2003
... ____ The symptoms of viral infection are primarily due to A. the body's response to the invasion B. toxins released by the virus C. insertion of the viral genome into the host cell D. all of the above _____ A repressible operon is important in regulating _____. ...
... ____ The symptoms of viral infection are primarily due to A. the body's response to the invasion B. toxins released by the virus C. insertion of the viral genome into the host cell D. all of the above _____ A repressible operon is important in regulating _____. ...
G19S Amino Acid code
... Molecules of DNA carry the genetic instructions for protein formation. Converting these DNA instructions into proteins requires a series of coordinated steps in transcription and translation. 1. Complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA bases listed in the column m ...
... Molecules of DNA carry the genetic instructions for protein formation. Converting these DNA instructions into proteins requires a series of coordinated steps in transcription and translation. 1. Complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA bases listed in the column m ...
Slide 1
... 2. DNA containing the gene of interest is isolated. 3. Plasmid DNA is treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts in one place, opening the circle. ...
... 2. DNA containing the gene of interest is isolated. 3. Plasmid DNA is treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts in one place, opening the circle. ...
Document
... • GMO positive control DNA –Verify GMO-negative result is not due to PCR reaction not working properly • Primers to universal plant gene ...
... • GMO positive control DNA –Verify GMO-negative result is not due to PCR reaction not working properly • Primers to universal plant gene ...
Molecular Structure of DNA and RNA part 1 powerpoint
... His findings suggested that there was a ‘factor’ which was transmitted from parent to offspring and inherited. This factor was not understood at that time and not until the middle of the 20th century. ...
... His findings suggested that there was a ‘factor’ which was transmitted from parent to offspring and inherited. This factor was not understood at that time and not until the middle of the 20th century. ...
Choose the BEST answer! Two points each. 1. Which of the
... DNA in your reaction flasks was a. 5'--ACCCGTTAAGGCTCCAAAGGCAGT--3' b. 3'--ACCCGTTAAGGCTCCAAAGGCAGT--5' c. 5'--TGGGCAATTCCGAGGTTTCCGTCA--3' d. 3'--TGGGCAATTCCGAGGTTTCCGTCA --5' e. need more information to determine this 29. A DNA sequence of unknown function and flanked on either end by a start codo ...
... DNA in your reaction flasks was a. 5'--ACCCGTTAAGGCTCCAAAGGCAGT--3' b. 3'--ACCCGTTAAGGCTCCAAAGGCAGT--5' c. 5'--TGGGCAATTCCGAGGTTTCCGTCA--3' d. 3'--TGGGCAATTCCGAGGTTTCCGTCA --5' e. need more information to determine this 29. A DNA sequence of unknown function and flanked on either end by a start codo ...
What are mutations and how do they affect the production
... Aim 25: What are mutations and how do they affect the production of proteins? What is a Mutation? ...
... Aim 25: What are mutations and how do they affect the production of proteins? What is a Mutation? ...
Genetic Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
... Cross-pollination--crosses two different varieties of vegetable but has traits of both parents ...
... Cross-pollination--crosses two different varieties of vegetable but has traits of both parents ...
Phase I: Computational Procedures: I. Measure original band
... A. This was just done at UC Irvine in March of 2013 with excellent results. This process was completed with the aid of Tom Fielder, scientist at UCI, and hasn’t been fully documented yet. It ...
... A. This was just done at UC Irvine in March of 2013 with excellent results. This process was completed with the aid of Tom Fielder, scientist at UCI, and hasn’t been fully documented yet. It ...
AP Bio 11 Biotechnology - STaRT
... • The remarkable ability of bacteria to express some eukaryotic proteins underscores the shared evolutionary ancestry of living species • For example, Pax-6 is a gene that directs formation of a vertebrate eye; the same gene in flies directs the formation of an insect eye (which is quite different f ...
... • The remarkable ability of bacteria to express some eukaryotic proteins underscores the shared evolutionary ancestry of living species • For example, Pax-6 is a gene that directs formation of a vertebrate eye; the same gene in flies directs the formation of an insect eye (which is quite different f ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.