IUSTI Australia MAMEF poster
... In the present study, detection of CT DNA is mediated by a two-step process. First, CT cells are rapidly lysed and the DNA fragmented using lysing chambers composed of gold or aluminum triangles deposited on glass slides and heated using conventional microwave irradiation (Figure 2). After a centrif ...
... In the present study, detection of CT DNA is mediated by a two-step process. First, CT cells are rapidly lysed and the DNA fragmented using lysing chambers composed of gold or aluminum triangles deposited on glass slides and heated using conventional microwave irradiation (Figure 2). After a centrif ...
are we fully shaped and determined by our genes?
... homeoboxes. The homeoboxes are small genes, determining an aminoacid sequence of a small polypeptide, which has no causal power to act, but when it appears in the cytoplasm, it evokes a coordinated reaction, just like the traffic lights coordinate the movement of cars on the street. A traffic light ...
... homeoboxes. The homeoboxes are small genes, determining an aminoacid sequence of a small polypeptide, which has no causal power to act, but when it appears in the cytoplasm, it evokes a coordinated reaction, just like the traffic lights coordinate the movement of cars on the street. A traffic light ...
DNA - Madison Public Schools
... DNA outside of a living cell DNA polymerases are used to make copies of DNA material This is useful to forensic scientists because small samples could be multiplied. ...
... DNA outside of a living cell DNA polymerases are used to make copies of DNA material This is useful to forensic scientists because small samples could be multiplied. ...
Glossary of Bacterial Genetics
... DNA molecules in which sequences, not normally contiguous, have been placed next to each other by in vitro methods ...
... DNA molecules in which sequences, not normally contiguous, have been placed next to each other by in vitro methods ...
f^*Co*e -z`
... of the gradient and other in the light density position would be seen and in the subsequent generations the amount of DNA in the light density position would increase with eaci generation. But the fact that intermediate density DNA was found ruled out the conservative model. ...
... of the gradient and other in the light density position would be seen and in the subsequent generations the amount of DNA in the light density position would increase with eaci generation. But the fact that intermediate density DNA was found ruled out the conservative model. ...
DNA Detectives What is Your DNA Alias? The central dogma of
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
Creating a Fingerprint from DNA Evidence
... specific sequence of nucleotide bases exist on the DNA strand. Once locating the site where the sequence exists, the enzyme cuts through the DNA. Some restriction enzymes cut straight through and create blunt end fragments while others cut through leaving exposed bases. This type of cut is referred ...
... specific sequence of nucleotide bases exist on the DNA strand. Once locating the site where the sequence exists, the enzyme cuts through the DNA. Some restriction enzymes cut straight through and create blunt end fragments while others cut through leaving exposed bases. This type of cut is referred ...
HotStart DNA Polymerase
... In some applications, more than 1.5 mM MgCl2, as provided in the 1X HotStart Buffer, is needed for optimal results. For this reason, 25 mM MgCl2 is included in the kit. Table 2 provides the volume of 25 mM MgCl2 to add to the master mix if a higher MgCl2 concentration is required. Table 1. Reaction ...
... In some applications, more than 1.5 mM MgCl2, as provided in the 1X HotStart Buffer, is needed for optimal results. For this reason, 25 mM MgCl2 is included in the kit. Table 2 provides the volume of 25 mM MgCl2 to add to the master mix if a higher MgCl2 concentration is required. Table 1. Reaction ...
Ways to detect unique sequences within mammalian DNA
... Used for detection of genetic diseases, forensics, paternity, evolutionary links Based on the characteristics of mammalian DNA Eukaryotic genome 1000x larger than bacterial genome DNA divided into 3 classes Nonrepetitive DNA Moderately repetitive DNA Highly repetitive DNA- called SATELLITE DNA ...
... Used for detection of genetic diseases, forensics, paternity, evolutionary links Based on the characteristics of mammalian DNA Eukaryotic genome 1000x larger than bacterial genome DNA divided into 3 classes Nonrepetitive DNA Moderately repetitive DNA Highly repetitive DNA- called SATELLITE DNA ...
DNA Double Helix KEY
... Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the cellular DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become ap ...
... Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the cellular DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become ap ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the cellular DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become ap ...
... Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the cellular DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become ap ...
DNA replication
... Functional genomics • The various genome projects have yielded the complete DNA sequences of many organisms. E.g. human, mouse, yeast, fruitfly, etc. Human: 3 billion base-pairs, 30-40 thousand genes. ...
... Functional genomics • The various genome projects have yielded the complete DNA sequences of many organisms. E.g. human, mouse, yeast, fruitfly, etc. Human: 3 billion base-pairs, 30-40 thousand genes. ...
Mutations are any changes in the genetic material
... 1. DNA is cut into smaller pieces using restriction enzymes 2. An electrical current is applied 3. DNA is separated by size. Shorter fragments move farther down the gel than longer fragments ...
... 1. DNA is cut into smaller pieces using restriction enzymes 2. An electrical current is applied 3. DNA is separated by size. Shorter fragments move farther down the gel than longer fragments ...
Name
... Directions: Open the PowerPoint titled “Translation Tutorial” and press the F5 button to start. Place your keyboard aside (if possible) and only use the mouse. Translation 1. What happens at the ribosome? _________________________________________________________________ 2. Define TRANSLATION. ______ ...
... Directions: Open the PowerPoint titled “Translation Tutorial” and press the F5 button to start. Place your keyboard aside (if possible) and only use the mouse. Translation 1. What happens at the ribosome? _________________________________________________________________ 2. Define TRANSLATION. ______ ...
Molecular Biology-restrection enzyme
... enzymes. Each enzyme cuts DNA at a specific short base sequence. For instance, EcoR1 cuts the DNA at the sequence GAATTC, and BamH1 cuts at GGATCC. There are hundreds of restriction enzymes known. • Using properly chosen enzymes, the gene you want can be cut out of the chromosome intact, with very l ...
... enzymes. Each enzyme cuts DNA at a specific short base sequence. For instance, EcoR1 cuts the DNA at the sequence GAATTC, and BamH1 cuts at GGATCC. There are hundreds of restriction enzymes known. • Using properly chosen enzymes, the gene you want can be cut out of the chromosome intact, with very l ...
Mutations (1 of 2)
... 3. There are effects at the cellular level. When red blood cells carrying mutant hemoglobin are deprived of oxygen, they become “sickle-shaped” instead of the usual round shape (see picture). This shape can sometimes interrupt blood flow. 4. There are negative effects at the whole organism level. Un ...
... 3. There are effects at the cellular level. When red blood cells carrying mutant hemoglobin are deprived of oxygen, they become “sickle-shaped” instead of the usual round shape (see picture). This shape can sometimes interrupt blood flow. 4. There are negative effects at the whole organism level. Un ...
Biology
... 1. How are DNA fragments separated during gel electrophoresis? What is another name for gel electrophoresis if a person’s entire DNA is used? 2. What are the 3 types of stem cells? Which ones are pluripotent? What does pluripotent mean? 3. Describe the process of genetic engineering or producing rec ...
... 1. How are DNA fragments separated during gel electrophoresis? What is another name for gel electrophoresis if a person’s entire DNA is used? 2. What are the 3 types of stem cells? Which ones are pluripotent? What does pluripotent mean? 3. Describe the process of genetic engineering or producing rec ...
Genetics Practice Test (H)
... D) The parent duplex is left intact and an entirely new double-stranded molecule is formed. ...
... D) The parent duplex is left intact and an entirely new double-stranded molecule is formed. ...
Chapter 10: Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... 4. Nucleotides are joined to new chain by covalent bonds b/t phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar and are joined to original DNA strand by H-bonds Ex: Original DNA sequence: ATTCCG DNA polymerase builds new strand that is complementary or TAAGGC ...
... 4. Nucleotides are joined to new chain by covalent bonds b/t phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar and are joined to original DNA strand by H-bonds Ex: Original DNA sequence: ATTCCG DNA polymerase builds new strand that is complementary or TAAGGC ...
Introduction to some basic features of genetic information
... base pairing with its sister DNA strand, forming the double helix. The complementarities of the nucleotide bases also facilitate replication, or copying of the genetic material. How does an organism pass this DNA to daughter cells and offspring? Inheritance, the passing of genetic information (genes ...
... base pairing with its sister DNA strand, forming the double helix. The complementarities of the nucleotide bases also facilitate replication, or copying of the genetic material. How does an organism pass this DNA to daughter cells and offspring? Inheritance, the passing of genetic information (genes ...
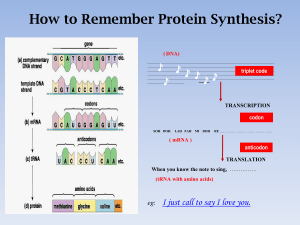
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... _________________________________________________ one amino acid transcription ribosome cytoplasm ...
... _________________________________________________ one amino acid transcription ribosome cytoplasm ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The “language” that translates the sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA (mRNA) into the amino acids of a protein. • Codon = three nucleotides on mRNA • One codon specifies one amino acid • Some codons are redundant (code for the ...
... The “language” that translates the sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA (mRNA) into the amino acids of a protein. • Codon = three nucleotides on mRNA • One codon specifies one amino acid • Some codons are redundant (code for the ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.