Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 2
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
Pierce chapter 10
... nucleotides may be complementary and pair – forming doublestranded regions • Hairpin – Region of complementary bases form base; loop formed by unpaired bases in the middle ...
... nucleotides may be complementary and pair – forming doublestranded regions • Hairpin – Region of complementary bases form base; loop formed by unpaired bases in the middle ...
8-3 Notes with Power point
... 1.The DNA is unwound and unzipped by the enzyme _______________________. The strands are held apart by single-stranded binding proteins (also known as ssbps) 2. Each original DNA strand is used as a ____________________________(or model) to make a new DNA strand with base pairing 3. The enzyme _____ ...
... 1.The DNA is unwound and unzipped by the enzyme _______________________. The strands are held apart by single-stranded binding proteins (also known as ssbps) 2. Each original DNA strand is used as a ____________________________(or model) to make a new DNA strand with base pairing 3. The enzyme _____ ...
DNA
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
GENETIC ENGINEERING CHAPTER 20
... fluorescent tag • DNA sequence is http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072556781/student_view0/ch read apter15/animation_quiz_1.html ...
... fluorescent tag • DNA sequence is http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072556781/student_view0/ch read apter15/animation_quiz_1.html ...
P5: 5` AAT GAT ACG GCG ACC ACC GA 3` P7: 5` CAA GCA GAA
... Libraries which begin with a linker, barcode, or other “non-random” sequence will not perform well unless they are basebalanced. This is particularly important on the MiSeq which has only 1 lane. If your sample has the same sequence in the first 6 positions, then we must add a balancer DNA, e.g. Phi ...
... Libraries which begin with a linker, barcode, or other “non-random” sequence will not perform well unless they are basebalanced. This is particularly important on the MiSeq which has only 1 lane. If your sample has the same sequence in the first 6 positions, then we must add a balancer DNA, e.g. Phi ...
Genetic Engineering pp 2014
... 3. Put the diploid nucleus into the empty egg. 4. Shock with electricity, the egg will start dividing. 5. Implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. 6. Clone is born. ...
... 3. Put the diploid nucleus into the empty egg. 4. Shock with electricity, the egg will start dividing. 5. Implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. 6. Clone is born. ...
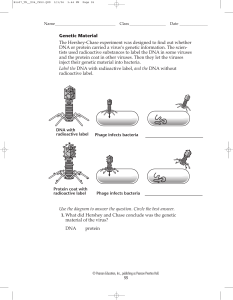
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
Slajd 1
... 2. Melting Temperature (Tm) for each primer = 50 – 65ºC. 3. Difference between Tm of primers max. 5ºC. 4. Primers should not contain 4 consecutive G/C residues. The last nucleotide at the 3’-end of the primer should be C/G. 5. Optimize concentration of forward and reverse primers to be used 6. Prime ...
... 2. Melting Temperature (Tm) for each primer = 50 – 65ºC. 3. Difference between Tm of primers max. 5ºC. 4. Primers should not contain 4 consecutive G/C residues. The last nucleotide at the 3’-end of the primer should be C/G. 5. Optimize concentration of forward and reverse primers to be used 6. Prime ...
DNA Sequencing as a Method for Larval Identification in Odonates
... Specimens were collected in Maine from June to August, 2007. These were previously identified and preserved in ethanol [(70%) various sources]. Male individuals of each species will be selected for DNA isolation and sequencing. For each individual, the legs will be removed and crushed using liquid n ...
... Specimens were collected in Maine from June to August, 2007. These were previously identified and preserved in ethanol [(70%) various sources]. Male individuals of each species will be selected for DNA isolation and sequencing. For each individual, the legs will be removed and crushed using liquid n ...
History of Genetics
... GENE -part of a DNA molecule • ________ that determines the inherited trait. • Chromosome ____________ - condensed DNA, acts as a storage unit. ...
... GENE -part of a DNA molecule • ________ that determines the inherited trait. • Chromosome ____________ - condensed DNA, acts as a storage unit. ...
Kim Phillips
... 6.) Specificity means the assay must yield a positive response only for the organism or molecule of interest. Sensitivity means the assay must be able to identify very small amounts of the target organism or molecule even with interfering substances. 7.) Chagas disease is detected by the amplificat ...
... 6.) Specificity means the assay must yield a positive response only for the organism or molecule of interest. Sensitivity means the assay must be able to identify very small amounts of the target organism or molecule even with interfering substances. 7.) Chagas disease is detected by the amplificat ...
Heterochromatin-2015
... Epigenetically imposed restrictions to plasticity are erased in the germ line ...
... Epigenetically imposed restrictions to plasticity are erased in the germ line ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... NB: The gene that is inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
... NB: The gene that is inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
Primer extension technique for the detection of single nucleotide in
... DNA alteration is known, it is quite enough to determine which nucleotide (normal or substituted) is present in certain site of the gene. I describe here simple and fast technique for detection of single nucleotide in certain position of genomic DNA which may be adopted to any genetic disease with k ...
... DNA alteration is known, it is quite enough to determine which nucleotide (normal or substituted) is present in certain site of the gene. I describe here simple and fast technique for detection of single nucleotide in certain position of genomic DNA which may be adopted to any genetic disease with k ...
36_sequencing
... Find the clones that contain coding sequences • Make a DNA copy (“cDNA”) of the mRNA using Reverse Transcriptase • Use that to probe for clones that contain coding sequences ...
... Find the clones that contain coding sequences • Make a DNA copy (“cDNA”) of the mRNA using Reverse Transcriptase • Use that to probe for clones that contain coding sequences ...
DNA-protein interaction
... Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with highthroughput sequencing A different way to read out the number of sequence bound by a protein Potentially more accurate because not cross-hybridization ...
... Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with highthroughput sequencing A different way to read out the number of sequence bound by a protein Potentially more accurate because not cross-hybridization ...
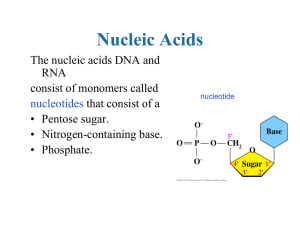
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
... consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
... consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
Chapter 12 “DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis” Reading/Study Guide
... 3. What is the Human Genome Project? (look at the DNA timeline)4. How do you describe Watson and Crick’s DNA model (see gold key on pg. 293)? ...
... 3. What is the Human Genome Project? (look at the DNA timeline)4. How do you describe Watson and Crick’s DNA model (see gold key on pg. 293)? ...
DNA Test Review What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).