Discrete devices: FETs - UBC Engineering Physics Project Lab
... Vout is 1/√2 of Vin at -3dB Log of frequency is used to ensure linear plots from 1/f or 1/fn functions ...
... Vout is 1/√2 of Vin at -3dB Log of frequency is used to ensure linear plots from 1/f or 1/fn functions ...
An Intelligent Technique for Generating Equivalent TT Circuits Using
... CCII circuits. Also, it generates 16 circuits using TA. Some of thegenerated TTcircuits and the conventional op-amp realized filtersare simulated using SPICEand compared to each other’s.A standard CMOS model of 0.25 µm is used.By applying the TT_GA Technique we can get all possible solutions program ...
... CCII circuits. Also, it generates 16 circuits using TA. Some of thegenerated TTcircuits and the conventional op-amp realized filtersare simulated using SPICEand compared to each other’s.A standard CMOS model of 0.25 µm is used.By applying the TT_GA Technique we can get all possible solutions program ...
Physics 160 Lecture 13
... transistors do not have a stable bias point. They are either in saturation or turned off, and the op-amp output is at one limit or the other. This can be useful as a comparator. ...
... transistors do not have a stable bias point. They are either in saturation or turned off, and the op-amp output is at one limit or the other. This can be useful as a comparator. ...
Simulating FPGA Power Integrity Using S-Parameter Models
... spreading inductance associated with the package or PCB combines with the decap's intrinsic inductance to effectively model the loop inductance. This loop inductance plus the package inductance resonates with the die capacitance to form a parallel anti-resonant circuit with a unique impedance profil ...
... spreading inductance associated with the package or PCB combines with the decap's intrinsic inductance to effectively model the loop inductance. This loop inductance plus the package inductance resonates with the die capacitance to form a parallel anti-resonant circuit with a unique impedance profil ...
Q3 2009 Issue Analog Applications Journal
... highly dependent upon the input frequency. For every doubling of the input frequency (e.g., fIN = 20 MHz versus fIN = 10 MHz), the spur amplitude increases by 6 dB! Hence, as system designers consider sampling in higher Nyquist zones, this relationship becomes very important to them. ...
... highly dependent upon the input frequency. For every doubling of the input frequency (e.g., fIN = 20 MHz versus fIN = 10 MHz), the spur amplitude increases by 6 dB! Hence, as system designers consider sampling in higher Nyquist zones, this relationship becomes very important to them. ...
Formal approach to dataflow analysis
... – initialize worklist with all equations – initialize solution vector S to all ^ – while worklist not empty do • get equation from worklist • evaluate rhs of equation with current solution vector values and update entry corresponding to lhs variable in solution vector • put all equations that use th ...
... – initialize worklist with all equations – initialize solution vector S to all ^ – while worklist not empty do • get equation from worklist • evaluate rhs of equation with current solution vector values and update entry corresponding to lhs variable in solution vector • put all equations that use th ...
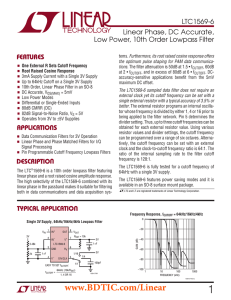
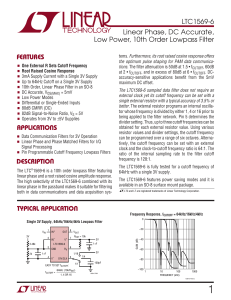
LTC1569-6 - Linear Phase, DC Accurate, Low Power, 10th Order Lowpass Filter
... the optimum pulse shaping for PAM data communications. The filter attenuation is 50dB at 1.5 • fCUTOFF, 60dB at 2 • fCUTOFF, and in excess of 80dB at 6 • fCUTOFF. DCaccuracy-sensitive applications benefit from the 5mV maximum DC offset. ...
... the optimum pulse shaping for PAM data communications. The filter attenuation is 50dB at 1.5 • fCUTOFF, 60dB at 2 • fCUTOFF, and in excess of 80dB at 6 • fCUTOFF. DCaccuracy-sensitive applications benefit from the 5mV maximum DC offset. ...
MAX7490/MAX7491 Dual Universal Switched-Capacitor Filters General Description Features
... amps, and behave like a virtual ground. There is no sampling energy present on these inputs. ...
... amps, and behave like a virtual ground. There is no sampling energy present on these inputs. ...
Homework #1 SOLUTIONS
... The aim here is to choose values for the Rs that will give the largest change in Vab for a small change in Rx . Another way to say this is that if we plot the value of Vab as a function of Rx (the output characteristic), we’d like that function to have a slope as steep as possible. If we only consid ...
... The aim here is to choose values for the Rs that will give the largest change in Vab for a small change in Rx . Another way to say this is that if we plot the value of Vab as a function of Rx (the output characteristic), we’d like that function to have a slope as steep as possible. If we only consid ...
Folded Dipole Antenna
... • Major difference is in terms of input impedance. • Input impedance of folded dipole is much higher than half wave dipole. • Other 2 parameters relatively different from half wave are directivity and Bandwidth. • main reasons for using the folded dipole aerial is the increase in feed impedance that ...
... • Major difference is in terms of input impedance. • Input impedance of folded dipole is much higher than half wave dipole. • Other 2 parameters relatively different from half wave are directivity and Bandwidth. • main reasons for using the folded dipole aerial is the increase in feed impedance that ...
supplementary
... resistance. The double layer is modelled as either a capacitor or a CPE. The advantage of the R-C fits is that the capacitive values resultant from the fits to different solutions or even different materials can be directly compared. The advantage of fitting to R-CPE circuits is that the least squar ...
... resistance. The double layer is modelled as either a capacitor or a CPE. The advantage of the R-C fits is that the capacitive values resultant from the fits to different solutions or even different materials can be directly compared. The advantage of fitting to R-CPE circuits is that the least squar ...
PWA_Mod08_Prob04_v05
... You suggested that to find the Thevenin impedance at the two terminals, a and b, we should replace all the components with their equivalent impedances, and combine using series and parallel impedance rules. Unfortunately, this is not a straightforward process for this circuit. There is a dependent s ...
... You suggested that to find the Thevenin impedance at the two terminals, a and b, we should replace all the components with their equivalent impedances, and combine using series and parallel impedance rules. Unfortunately, this is not a straightforward process for this circuit. There is a dependent s ...
Designing of a variable frequency standalone impedance analyzer
... impedance of biological samples is basically high in the range of 10 kΩ to 1MΩ. So the mentioned currents sources do not provide a constant current in the specified range. Voltage controlled constant current source (VCCS) is a simple method for maintaining a constant current up to a range of 3MΩ. Du ...
... impedance of biological samples is basically high in the range of 10 kΩ to 1MΩ. So the mentioned currents sources do not provide a constant current in the specified range. Voltage controlled constant current source (VCCS) is a simple method for maintaining a constant current up to a range of 3MΩ. Du ...
Resonant Frequency Splitting Analysis and Optimation of
... 4.2. The Impact of Load Changes on Resonance Frequency ...
... 4.2. The Impact of Load Changes on Resonance Frequency ...
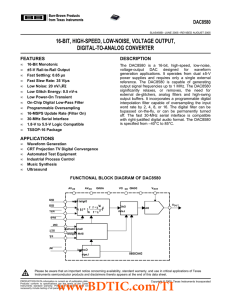
DAC8580 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The DAC8580 is a 16-bit, high-speed, low-noise, voltage-output DAC designed for waveform generation applications. It operates from dual ±5-V power supplies and requires only a single external reference. The DAC8580 is capable of generating output signal frequencies up to 1 MHz. The DAC8580 significa ...
... The DAC8580 is a 16-bit, high-speed, low-noise, voltage-output DAC designed for waveform generation applications. It operates from dual ±5-V power supplies and requires only a single external reference. The DAC8580 is capable of generating output signal frequencies up to 1 MHz. The DAC8580 significa ...
OSFS, OSFD Active Filters
... The harmful effects of harmonics from single loads, load groups or a complete electrical system can be mitigated down to an acceptable degree, if not removed totally from the network. OSFS and OSFD Active Filters combine numerous advantages. They are top-of-the-range instruments hallmarked by extrem ...
... The harmful effects of harmonics from single loads, load groups or a complete electrical system can be mitigated down to an acceptable degree, if not removed totally from the network. OSFS and OSFD Active Filters combine numerous advantages. They are top-of-the-range instruments hallmarked by extrem ...
resonance
... sharpness of resonance, is indicated by the factor Q. The higher the ratio of the reactance at resonance to the series resistance, the higher the Q and the sharper the resonance effect. The Q of the resonant circuit can be considered a magnification factor that determines how much the voltage ac ...
... sharpness of resonance, is indicated by the factor Q. The higher the ratio of the reactance at resonance to the series resistance, the higher the Q and the sharper the resonance effect. The Q of the resonant circuit can be considered a magnification factor that determines how much the voltage ac ...
LTC1569-6 - Linear Phase, DC Accurate, Low Power, 10th Order
... the optimum pulse shaping for PAM data communications. The filter attenuation is 50dB at 1.5 • fCUTOFF, 60dB at 2 • fCUTOFF, and in excess of 80dB at 6 • fCUTOFF. DCaccuracy-sensitive applications benefit from the 5mV maximum DC offset. ...
... the optimum pulse shaping for PAM data communications. The filter attenuation is 50dB at 1.5 • fCUTOFF, 60dB at 2 • fCUTOFF, and in excess of 80dB at 6 • fCUTOFF. DCaccuracy-sensitive applications benefit from the 5mV maximum DC offset. ...
Compensation of Frequency Dependent Parasitic Resistance in a
... Non-Foster circuits such as negative inductors and negative capacitors offer the potential for increased bandwidth in a variety of applications such as wideband antennas, artificial magnetic conductors, and metamaterials with negative permeability [1]. For antennas, negative inductors can be used to ...
... Non-Foster circuits such as negative inductors and negative capacitors offer the potential for increased bandwidth in a variety of applications such as wideband antennas, artificial magnetic conductors, and metamaterials with negative permeability [1]. For antennas, negative inductors can be used to ...
L. Huang, W. Rieutort-Louis, A. Gualdino, L. Teagno, Y. Hu, J. Mouro, J. Sanz-Robinson, J.C. Sturm, S. Wagner, V. Chu, J. Conde, and N. Verma, "An ASIC for Readout of Post-processed Thin-film MEMS Resonators by Employing Capacitive Interfacing and Active Parasitic Cancellation", VLSI Symp. on Circuits (VLSI) (JUN2014).
... the integrator, while, with VCP out of phase, the corresponding DC component is nulled. In fact, this approach not only isolates the RMLMCM admittance, but further enhances its resonant peak. In particular, off resonance, the admittance reduces in magnitude, but also rapidly deviates ...
... the integrator, while, with VCP out of phase, the corresponding DC component is nulled. In fact, this approach not only isolates the RMLMCM admittance, but further enhances its resonant peak. In particular, off resonance, the admittance reduces in magnitude, but also rapidly deviates ...
The Comparison of the Input Impedance
... the voltage source series with input impedance while the resonance method may be found the input impedance as the current source paralleled with the input impedance. The experimental results are in the same trend in some frequency range of input impedance values, both common mode and differential mo ...
... the voltage source series with input impedance while the resonance method may be found the input impedance as the current source paralleled with the input impedance. The experimental results are in the same trend in some frequency range of input impedance values, both common mode and differential mo ...
Impedance Simulator for Testing of Instruments for Bioimpedance
... typically consists of a signal component related to the physiological phenomenon of interest, dc offset because of the base impedance, and artifacts caused by impedance variations due to motion or other physiological phenomena. Sensed signals may also be contaminated by noise due to internal bioelec ...
... typically consists of a signal component related to the physiological phenomenon of interest, dc offset because of the base impedance, and artifacts caused by impedance variations due to motion or other physiological phenomena. Sensed signals may also be contaminated by noise due to internal bioelec ...
Local Oscillator for FM broadcast band 88-108 MHz
... calculated above, the emitter voltage of the first stage is 6V-0.7V=5.3V, which is high enough to drive this buffer stage. So we connect the emitter of the oscillator transistor to the base of the buffer amplifier without adding any other biasing circuit. ...
... calculated above, the emitter voltage of the first stage is 6V-0.7V=5.3V, which is high enough to drive this buffer stage. So we connect the emitter of the oscillator transistor to the base of the buffer amplifier without adding any other biasing circuit. ...
Understanding Adjustable Speed Drive Common
... Common Mode Filter Characteristics There are many misconceptions about what a filter with common mode characteristics look like. Common mode signals are identical on all three phases. A very effective means to understand the common mode filtering characteristics of a three phase filter topology is t ...
... Common Mode Filter Characteristics There are many misconceptions about what a filter with common mode characteristics look like. Common mode signals are identical on all three phases. A very effective means to understand the common mode filtering characteristics of a three phase filter topology is t ...
Distributed element filter
A distributed element filter is an electronic filter in which capacitance, inductance and resistance (the elements of the circuit) are not localised in discrete capacitors, inductors and resistors as they are in conventional filters. Its purpose is to allow a range of signal frequencies to pass, but to block others. Conventional filters are constructed from inductors and capacitors, and the circuits so built are described by the lumped element model, which considers each element to be ""lumped together"" at one place. That model is conceptually simple, but it becomes increasingly unreliable as the frequency of the signal increases, or equivalently as the wavelength decreases. The distributed element model applies at all frequencies, and is used in transmission line theory; many distributed element components are made of short lengths of transmission line. In the distributed view of circuits, the elements are distributed along the length of conductors and are inextricably mixed together. The filter design is usually concerned only with inductance and capacitance, but because of this mixing of elements they cannot be treated as separate ""lumped"" capacitors and inductors. There is no precise frequency above which distributed element filters must be used but they are especially associated with the microwave band (wavelength less than one metre).Distributed element filters are used in many of the same applications as lumped element filters, such as selectivity of radio channel, bandlimiting of noise and multiplexing of many signals into one channel. Distributed element filters may be constructed to have any of the bandforms possible with lumped elements (low-pass, band-pass, etc.) with the exception of high-pass, which is usually only approximated. All filter classes used in lumped element designs (Butterworth, Chebyshev, etc.) can be implemented using a distributed element approach.There are many component forms used to construct distributed element filters, but all have the common property of causing a discontinuity on the transmission line. These discontinuities present a reactive impedance to a wavefront travelling down the line, and these reactances can be chosen by design to serve as approximations for lumped inductors, capacitors or resonators, as required by the filter.The development of distributed element filters was spurred on by the military need for radar and electronic counter measures during World War II. Lumped element analogue filters had long before been developed but these new military systems operated at microwave frequencies and new filter designs were required. When the war ended, the technology found applications in the microwave links used by telephone companies and other organisations with large fixed-communication networks, such as television broadcasters. Nowadays the technology can be found in several mass-produced consumer items, such as the converters (figure 1 shows an example) used with satellite television dishes.