High-pass.filter
... filter. See also bandpass filter. It is useful as a filter to block any unwanted low frequency components of a complex signal while passing the higher frequencies. Of course, the meanings of 'low' and 'high' frequencies are relative to the cutoff frequency chosen by the filter designer. [edit] ...
... filter. See also bandpass filter. It is useful as a filter to block any unwanted low frequency components of a complex signal while passing the higher frequencies. Of course, the meanings of 'low' and 'high' frequencies are relative to the cutoff frequency chosen by the filter designer. [edit] ...
In this project, you are going to design an active Low
... 1.1 Design Criteria’s Design an active low pass filter based on the chosen cut-off frequency (150Hz-200Hz) and available values of resistors and capacitors. Gain of the filter can be chosen arbitrarily but it should be suitable with your design specifications. ...
... 1.1 Design Criteria’s Design an active low pass filter based on the chosen cut-off frequency (150Hz-200Hz) and available values of resistors and capacitors. Gain of the filter can be chosen arbitrarily but it should be suitable with your design specifications. ...
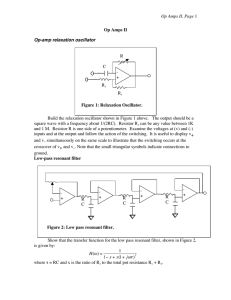
Op Amps II, Page R C -
... When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations ...
... When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations ...
highpass filter - Jejaring Blog Unnes
... polynomial, is a value that results in a zero value of the function. A pole, as a root of the denominator polynomial, is a value for which the function is infinite. ...
... polynomial, is a value that results in a zero value of the function. A pole, as a root of the denominator polynomial, is a value for which the function is infinite. ...
Data sheet
... CleanSweep Mains Filters OnFILTER CleanSweep™ EMI filters provide noise-free AC power for your sensitive equipment in end-user installations. Innovative design accomplishes maximum noise suppression of signals polluting your power lines, freeing your equipment from harmful interference. Clean power ...
... CleanSweep Mains Filters OnFILTER CleanSweep™ EMI filters provide noise-free AC power for your sensitive equipment in end-user installations. Innovative design accomplishes maximum noise suppression of signals polluting your power lines, freeing your equipment from harmful interference. Clean power ...
Lab 7 - Electronic Filters (C and G Sections Only)
... 3dB drop of signal power from highest point on gain Signal power is half of original value Cutoff Frequency (in Hz) Frequency at -3dB Point ...
... 3dB drop of signal power from highest point on gain Signal power is half of original value Cutoff Frequency (in Hz) Frequency at -3dB Point ...
Micromachined Acoustic Programmable Tunable Finite Impulse
... Simulation results are presented and compared to values estimated by the theoretical model. In general, it is observed that high substrate losses can significantly degrade the filter performance in terms of the insertion loss and filter bandwidth. Microfabrication of a filter similar to the example ...
... Simulation results are presented and compared to values estimated by the theoretical model. In general, it is observed that high substrate losses can significantly degrade the filter performance in terms of the insertion loss and filter bandwidth. Microfabrication of a filter similar to the example ...
Chapter 1 (Part 4) - Basic Filter
... is passive filter /active filter ? A passive filter consists of passive circuit elements such as capacitors, inductors and resistors . An active filter uses active devices such as op-amps combined with passive elements. ...
... is passive filter /active filter ? A passive filter consists of passive circuit elements such as capacitors, inductors and resistors . An active filter uses active devices such as op-amps combined with passive elements. ...
ee221_3
... The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the gain can be easily set to a desired value. The input and output impedance properties can be configured to eliminate loading effects. Therefore, the filter will have the same properties independent of the load. Most acti ...
... The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the gain can be easily set to a desired value. The input and output impedance properties can be configured to eliminate loading effects. Therefore, the filter will have the same properties independent of the load. Most acti ...
Wave, Filters
... • Each of the following topics must be addressed in the full report and should be placed in the proper sections – What does the 3 dB drop show about the filter? – Discuss the importance of decreasing or increasing the ‘Volts/Div’ on the oscilloscope – What can the DMM measure besides resistance? – D ...
... • Each of the following topics must be addressed in the full report and should be placed in the proper sections – What does the 3 dB drop show about the filter? – Discuss the importance of decreasing or increasing the ‘Volts/Div’ on the oscilloscope – What can the DMM measure besides resistance? – D ...
Chapter 2. Active Filter Design
... 21. What circuit Q is required to give a bandwidth of 36 MHz at a frequency of 4 GHz? 22. Find the impedance of a parallel resonant circuit with L=60 H, RW=7 ohm, and C=22 pF. 25. A low-pass filter has a cutoff frequency of 24 MHz. What is the fastest rise time that a rectangular wave that will pas ...
... 21. What circuit Q is required to give a bandwidth of 36 MHz at a frequency of 4 GHz? 22. Find the impedance of a parallel resonant circuit with L=60 H, RW=7 ohm, and C=22 pF. 25. A low-pass filter has a cutoff frequency of 24 MHz. What is the fastest rise time that a rectangular wave that will pas ...
150Vdc Servo System
... voltage by a factor of 10, substantially reducing noise in the system. Copley amplifiers typically have a 200ns-rise time (high frequency component in the Mega Hz range) so, by using the edge filter, the rise time can be increased to a 2usrise time, reducing the high frequency component by a factor ...
... voltage by a factor of 10, substantially reducing noise in the system. Copley amplifiers typically have a 200ns-rise time (high frequency component in the Mega Hz range) so, by using the edge filter, the rise time can be increased to a 2usrise time, reducing the high frequency component by a factor ...
Powerful AM transmitter Click here for the circuit diagram
... The circuit for a powerful AM transmitter using ceramic resonator/filter of 3.587 MHz is presented here. Resonators/filters of other frequencies such as 5.5 MHz, 7 MHz and 10.7 MHz may also be used. Use of different frequency filters/resonators will involve corresponding variation in the value of in ...
... The circuit for a powerful AM transmitter using ceramic resonator/filter of 3.587 MHz is presented here. Resonators/filters of other frequencies such as 5.5 MHz, 7 MHz and 10.7 MHz may also be used. Use of different frequency filters/resonators will involve corresponding variation in the value of in ...
Motor Line Feed-Through
... Spectrum Control brand has developed a family of high capacitance filters specifically designed for DC motor and other lower voltage applications. The Motor Line Feed-Through (MLFT) filter is a one-component solution that eliminates the need for multiple capacitors, inductive coils, leads and PCB as ...
... Spectrum Control brand has developed a family of high capacitance filters specifically designed for DC motor and other lower voltage applications. The Motor Line Feed-Through (MLFT) filter is a one-component solution that eliminates the need for multiple capacitors, inductive coils, leads and PCB as ...
PRELAB 12: ACTIVE FILTERS
... A low-pass filter has a constant gain (=Vout/Vin) from 0 Hz to a high cut off frequency fH. This cut off frequency is defined as the frequency where the voltage gain is reduced to 0.707, that is at fH the gain is down by 3 dB; after that (f > fH) it decreases as f increases. The frequencies between ...
... A low-pass filter has a constant gain (=Vout/Vin) from 0 Hz to a high cut off frequency fH. This cut off frequency is defined as the frequency where the voltage gain is reduced to 0.707, that is at fH the gain is down by 3 dB; after that (f > fH) it decreases as f increases. The frequencies between ...
Distributed element filter
A distributed element filter is an electronic filter in which capacitance, inductance and resistance (the elements of the circuit) are not localised in discrete capacitors, inductors and resistors as they are in conventional filters. Its purpose is to allow a range of signal frequencies to pass, but to block others. Conventional filters are constructed from inductors and capacitors, and the circuits so built are described by the lumped element model, which considers each element to be ""lumped together"" at one place. That model is conceptually simple, but it becomes increasingly unreliable as the frequency of the signal increases, or equivalently as the wavelength decreases. The distributed element model applies at all frequencies, and is used in transmission line theory; many distributed element components are made of short lengths of transmission line. In the distributed view of circuits, the elements are distributed along the length of conductors and are inextricably mixed together. The filter design is usually concerned only with inductance and capacitance, but because of this mixing of elements they cannot be treated as separate ""lumped"" capacitors and inductors. There is no precise frequency above which distributed element filters must be used but they are especially associated with the microwave band (wavelength less than one metre).Distributed element filters are used in many of the same applications as lumped element filters, such as selectivity of radio channel, bandlimiting of noise and multiplexing of many signals into one channel. Distributed element filters may be constructed to have any of the bandforms possible with lumped elements (low-pass, band-pass, etc.) with the exception of high-pass, which is usually only approximated. All filter classes used in lumped element designs (Butterworth, Chebyshev, etc.) can be implemented using a distributed element approach.There are many component forms used to construct distributed element filters, but all have the common property of causing a discontinuity on the transmission line. These discontinuities present a reactive impedance to a wavefront travelling down the line, and these reactances can be chosen by design to serve as approximations for lumped inductors, capacitors or resonators, as required by the filter.The development of distributed element filters was spurred on by the military need for radar and electronic counter measures during World War II. Lumped element analogue filters had long before been developed but these new military systems operated at microwave frequencies and new filter designs were required. When the war ended, the technology found applications in the microwave links used by telephone companies and other organisations with large fixed-communication networks, such as television broadcasters. Nowadays the technology can be found in several mass-produced consumer items, such as the converters (figure 1 shows an example) used with satellite television dishes.