* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 (Part 4) - Basic Filter
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Waveguide filter wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Analogue filter wikipedia , lookup
Kolmogorov–Zurbenko filter wikipedia , lookup
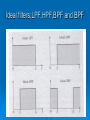
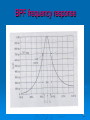
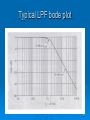
Chapter 1 Part 4 Introduction to Basic Filter 1 What is filter? Filter is a circuit that passes a specific range of frequencies while rejecting other frequencies. 2 Introduction to Filters What is passive filter /active filter ? A passive filter consists of passive circuit elements such as capacitors, inductors and resistors . An active filter uses active devices such as op-amps combined with passive elements. 3 Introduction to Filters The passive elements provide frequency selectivity. The active devices provide voltage gain, high input impedance and low output impedance. 4 Types of filters Four basic types of filters: 1. LOW PASS FILTER 3. BAND PASS FILTER 2. HIGH PASS FILTER FILTER 4. BAND STOP 5 Types of filters Low Pass Filter (LPF) High Pass Filter (LPF) Pass all frequencies below cutoff frequency and reject all frequencies above cutoff frequency Pass all frequencies above the cutoff frequency and reject all frequencies below the cutoff frequency 6 Types of filters Band Pass Filter (BPF) Passes all frequencies within a band of frequencies and reject all other frequencies outside the band. Band Stop Filter ( Notch) Reject all frequencies within a band of frequencies and passes all other frequencies outside the band. 7 Ideal filters;LPF,HPF,BPF and BPF 8 Simple RC LPF Circuit 9 Simple RC LPF response curve or Bode Plot. 10 Characteristics of Filters The most common way to describe the frequency response characteristics of a filter is to plot the filter voltage gain (Vout/Vin) in dB as a function of frequency (f). What is cutoff Frequency? The frequency at which the output power gain drops to 50% of the maximun value is called cutoff frequency. 11 Characteristics of Filters (cont..) When the output power gain drops to 50%, the voltage gain drops 3 dB (0.707 of the maximun value. The filter network voltage gain in dB is calculated from the actual voltage gain (A) using the equation A(dB) = 20 log A Where A=Vout/Vin 12 Characteristics of Filters (cont..) What is Roll-Off Rates (ROR)? ROR is given in dB per decade (dB/dec) or dB per octave (dB/oct). # dB/dec = (20/6) x # dB/oct. 13 Characteristics of Filters (cont..) What is Q or Shape Factor (SF)? 14 BPF frequency response 15 Typical LPF bode plot 16 Examples 3.1 What determines the Q of a filter? 3.2 What is the bandwidth of a filter with a Q of 75 and a center frequency of 375 MHz? 3.3 If the -6B bandwidth of a filter is 3.1 KHz, determine the -60dB bandwidth if the filter shape factor is 1.45? 17 END OF CHAPTER 1 18